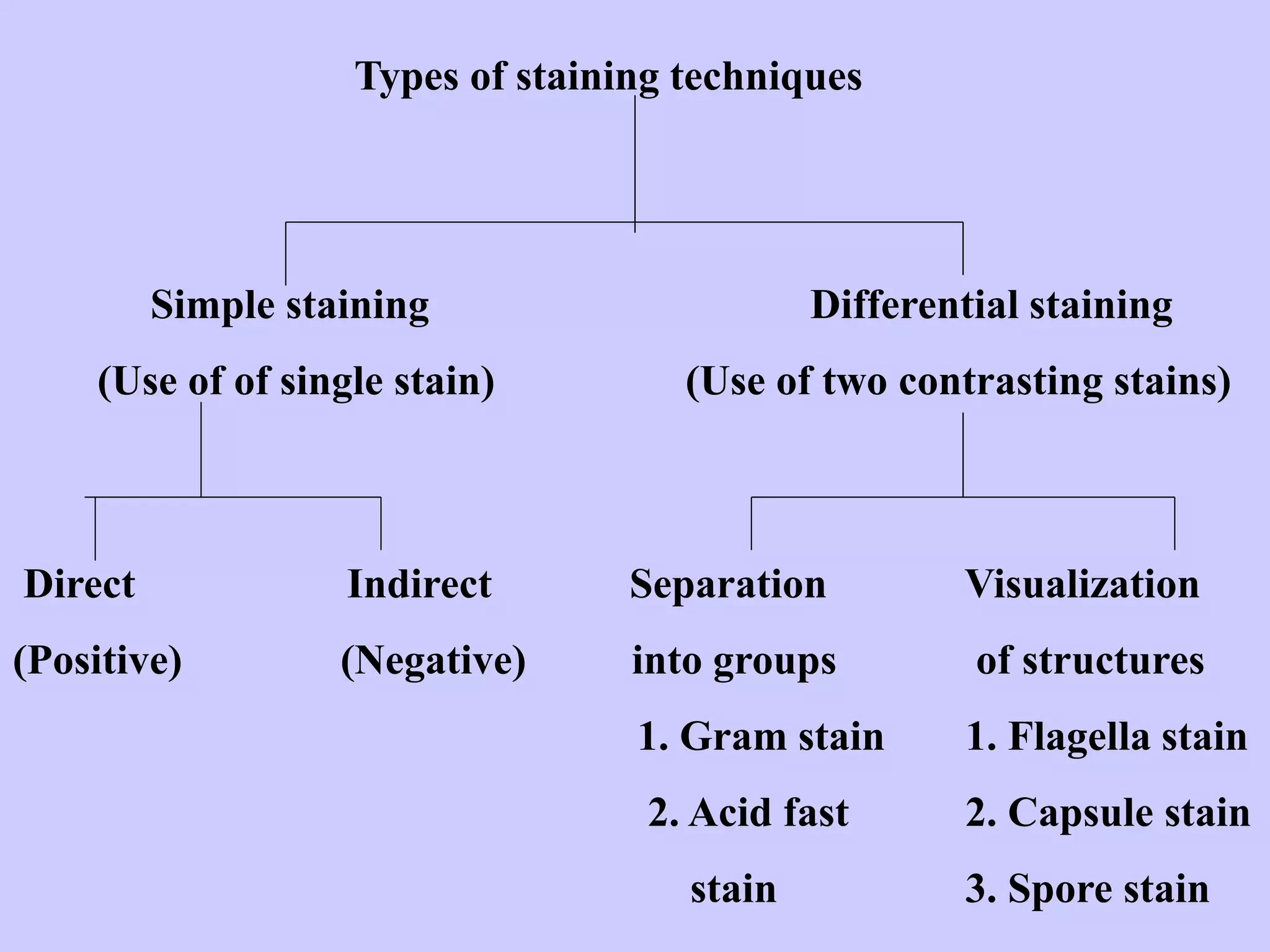
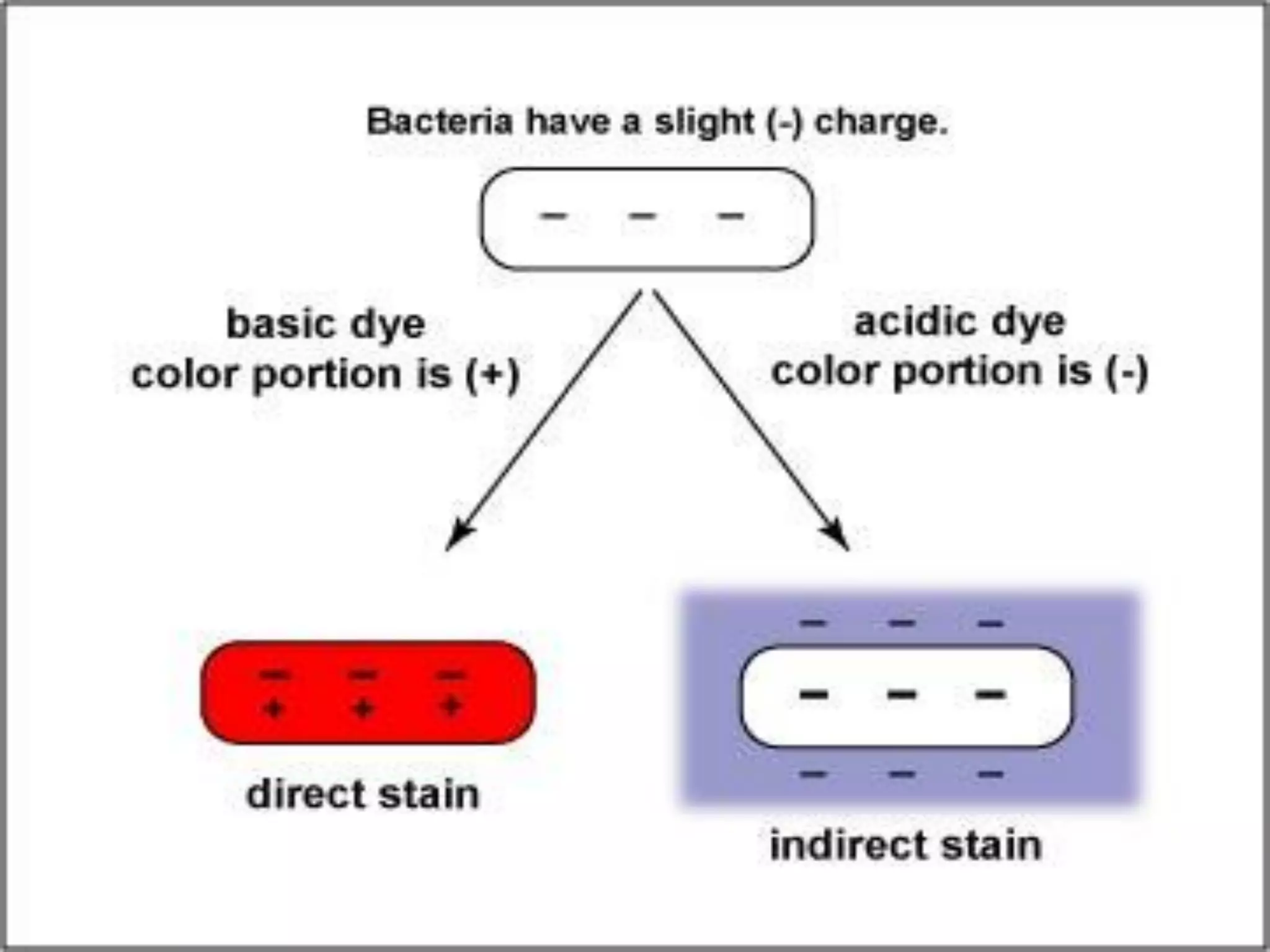
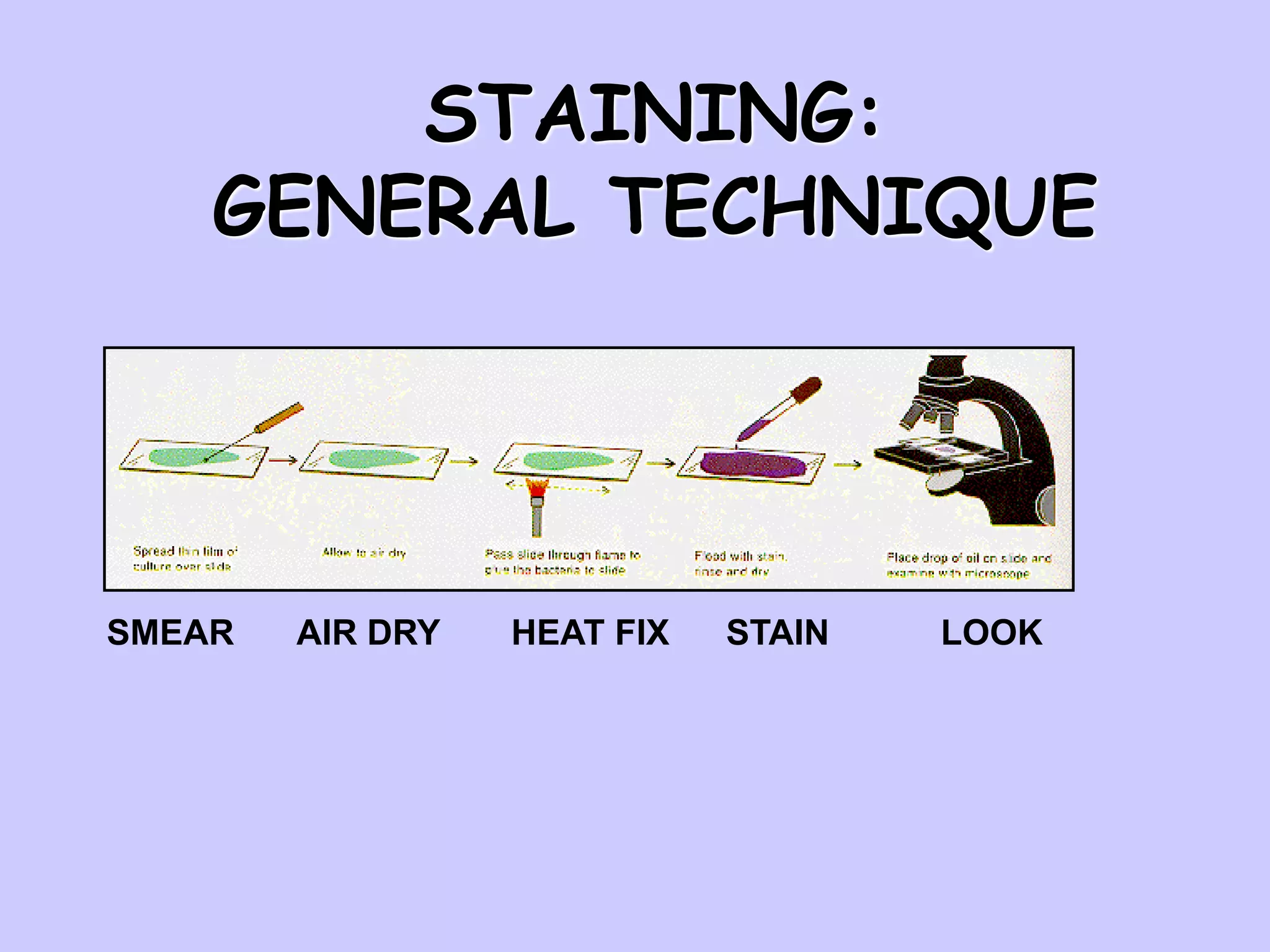
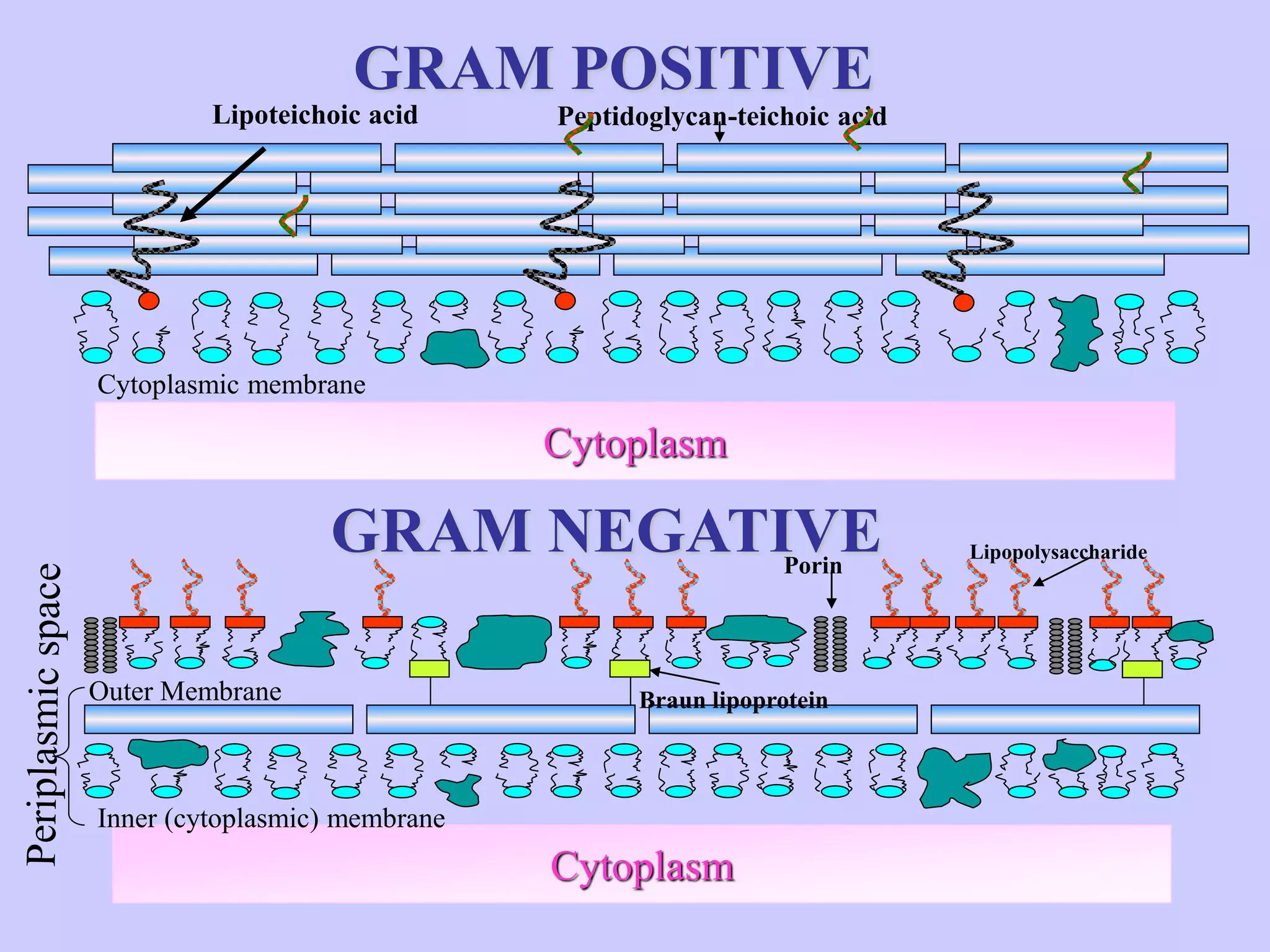
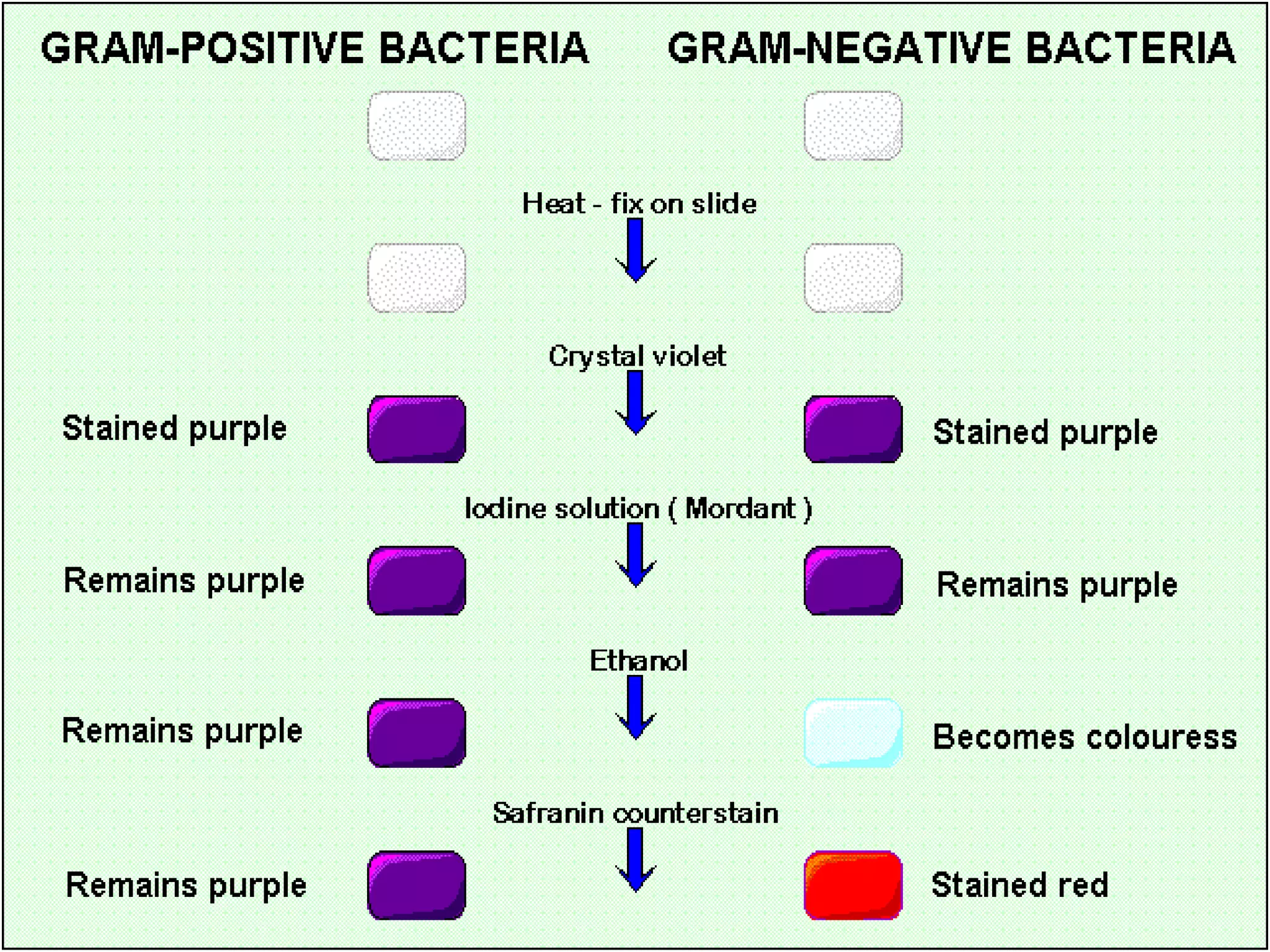
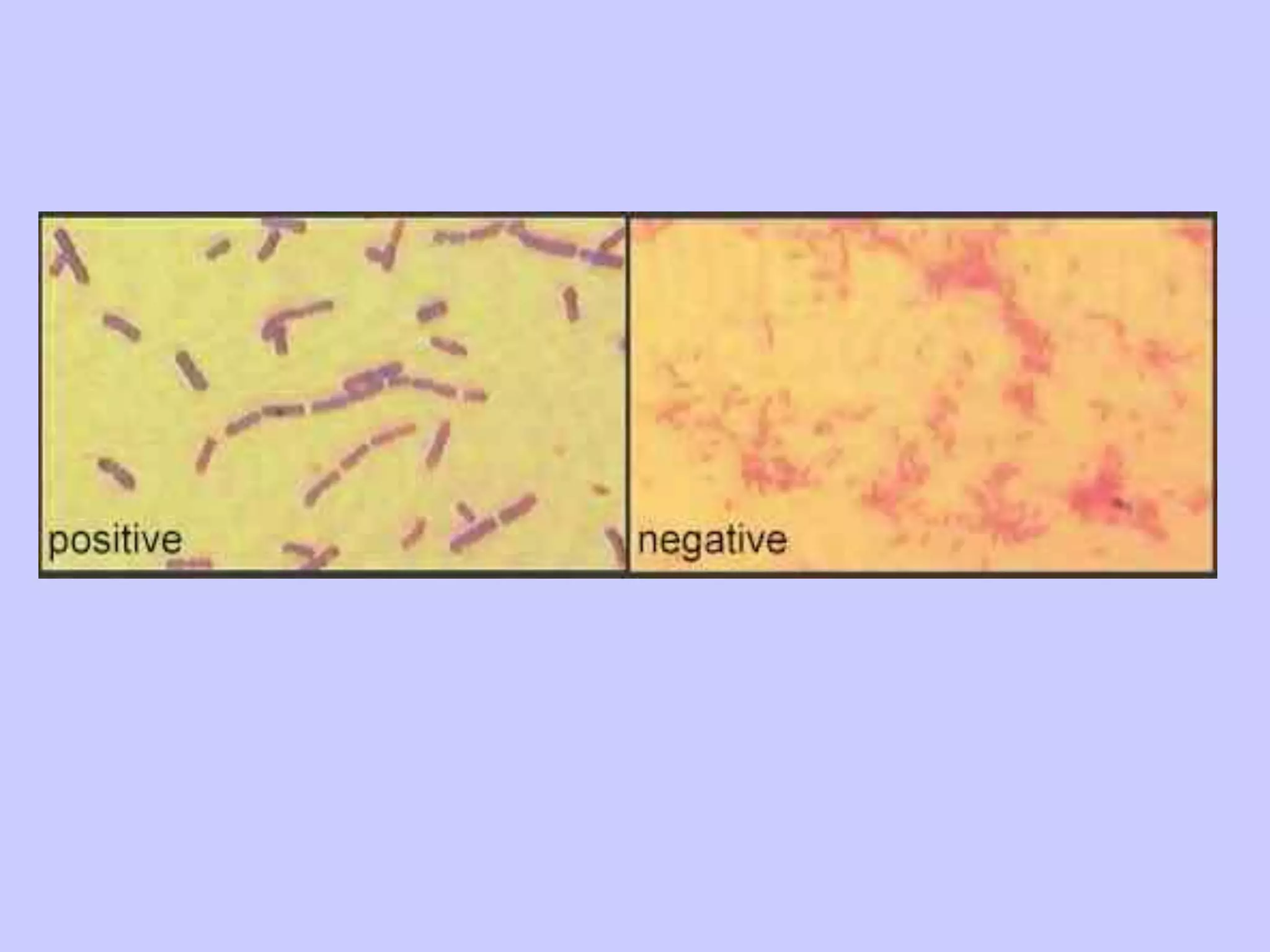
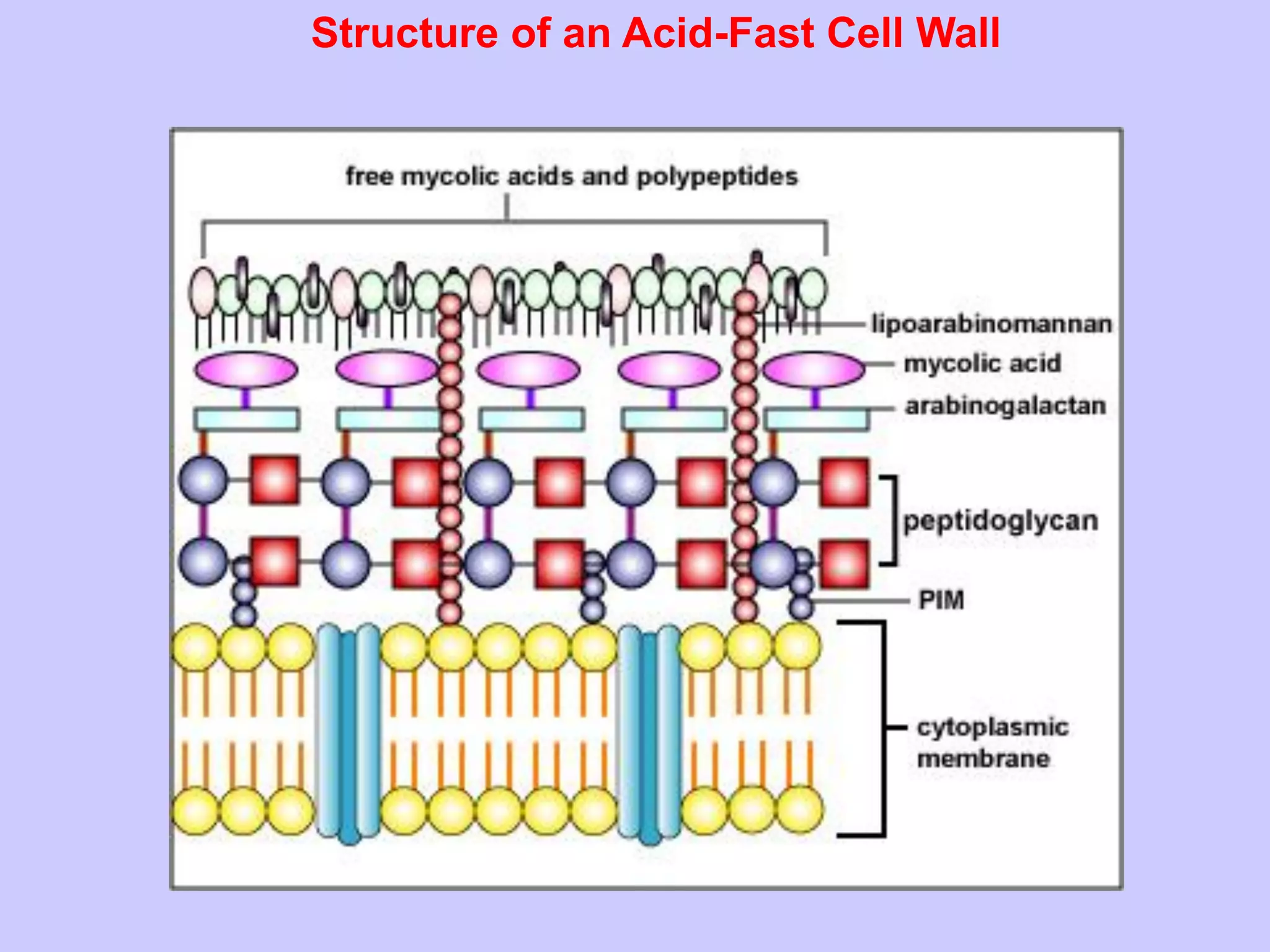
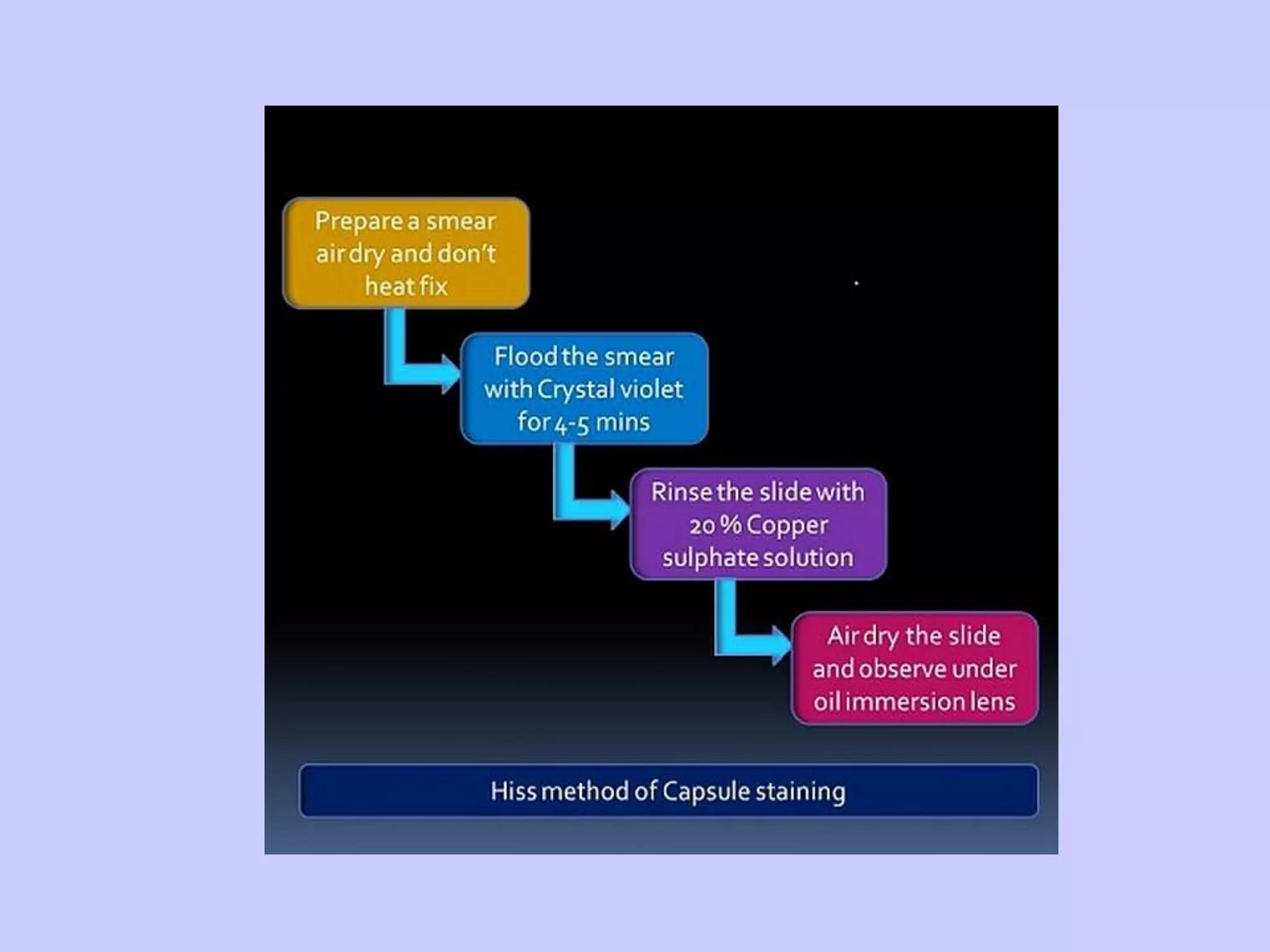
The document discusses various staining techniques used in microbiology to enhance visibility and differentiate between organisms based on their morphological characteristics. It outlines the types of stains (simple, differential, direct, and indirect) and details specific methods such as Gram staining, acid-fast staining, and endospore staining, along with their procedures and requirements. Additionally, it explains the roles of chemicals involved in the staining process, such as mordants, decarboxylators, and accentuators.