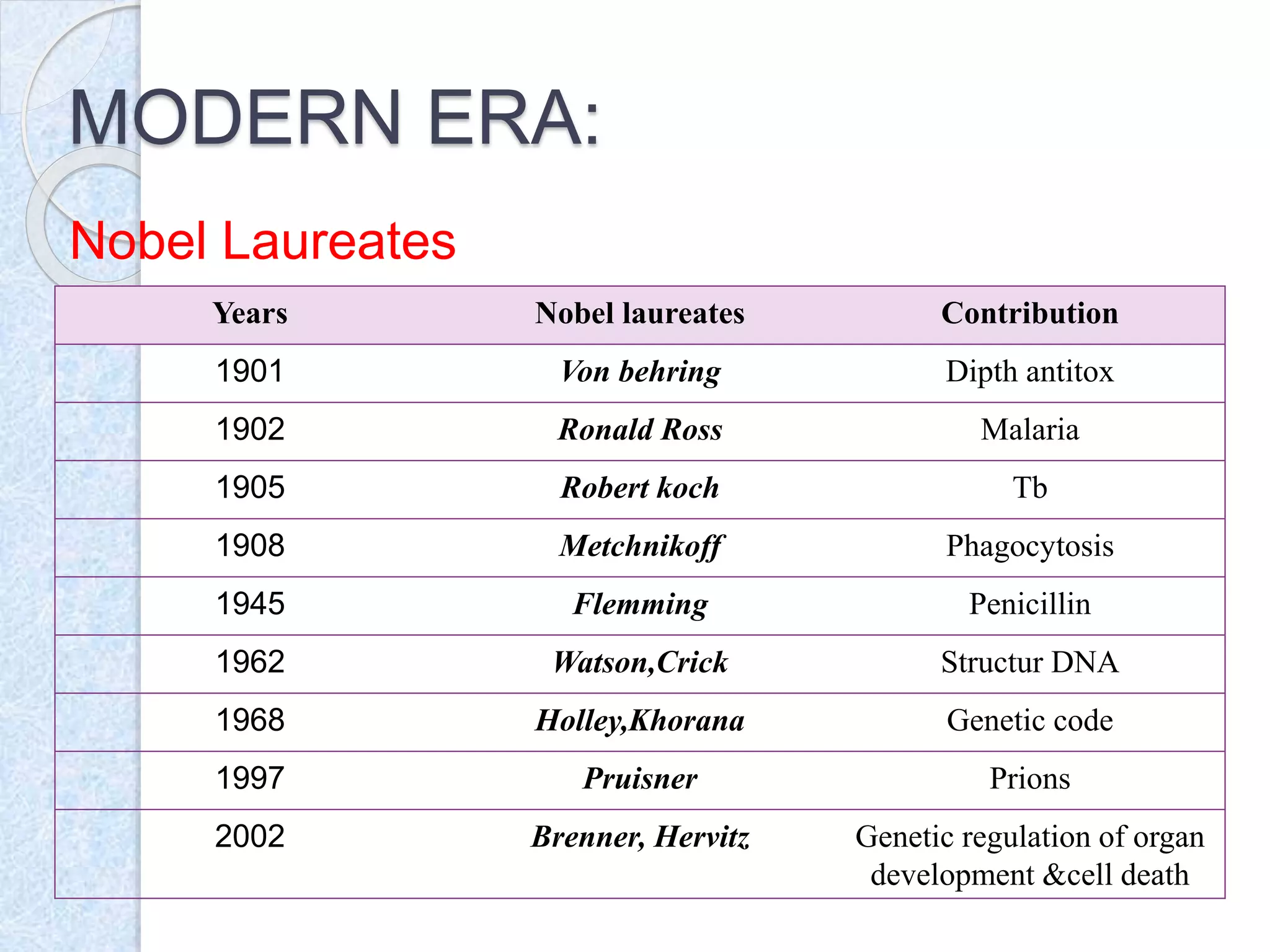
Microbiology is the study of microorganisms that are too small to be seen without a microscope. The history of microbiology began with the discovery era in the 17th century when Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek first observed microbes using microscopes. The golden era started in the 19th century when Louis Pasteur disproved spontaneous generation and demonstrated that microbes cause disease. Major advances included Robert Koch developing techniques to isolate bacteria in pure culture and prove specific bacteria cause specific diseases. The modern era saw the discovery of viruses, development of vaccines, and molecular understanding of genetics and DNA.