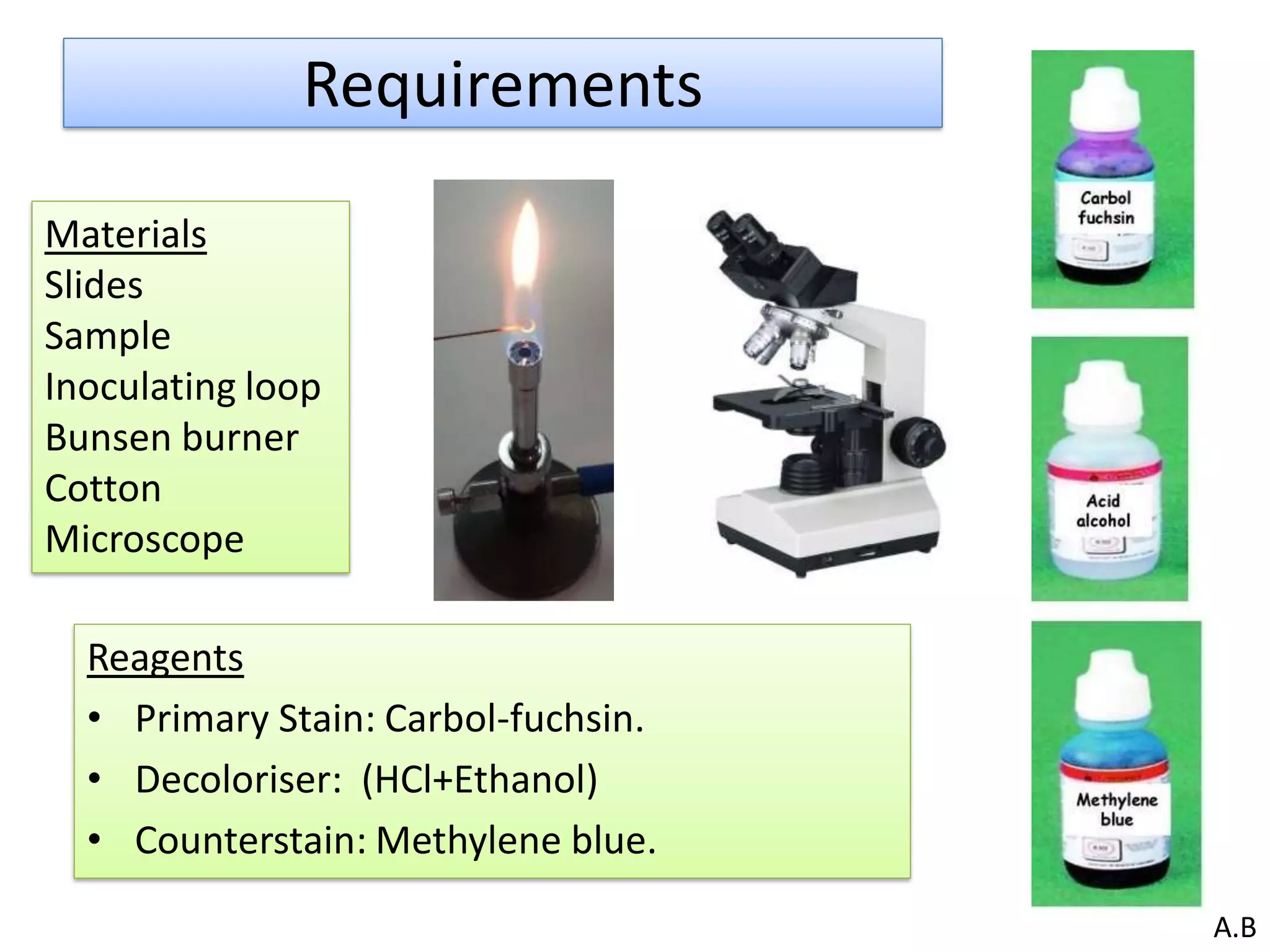
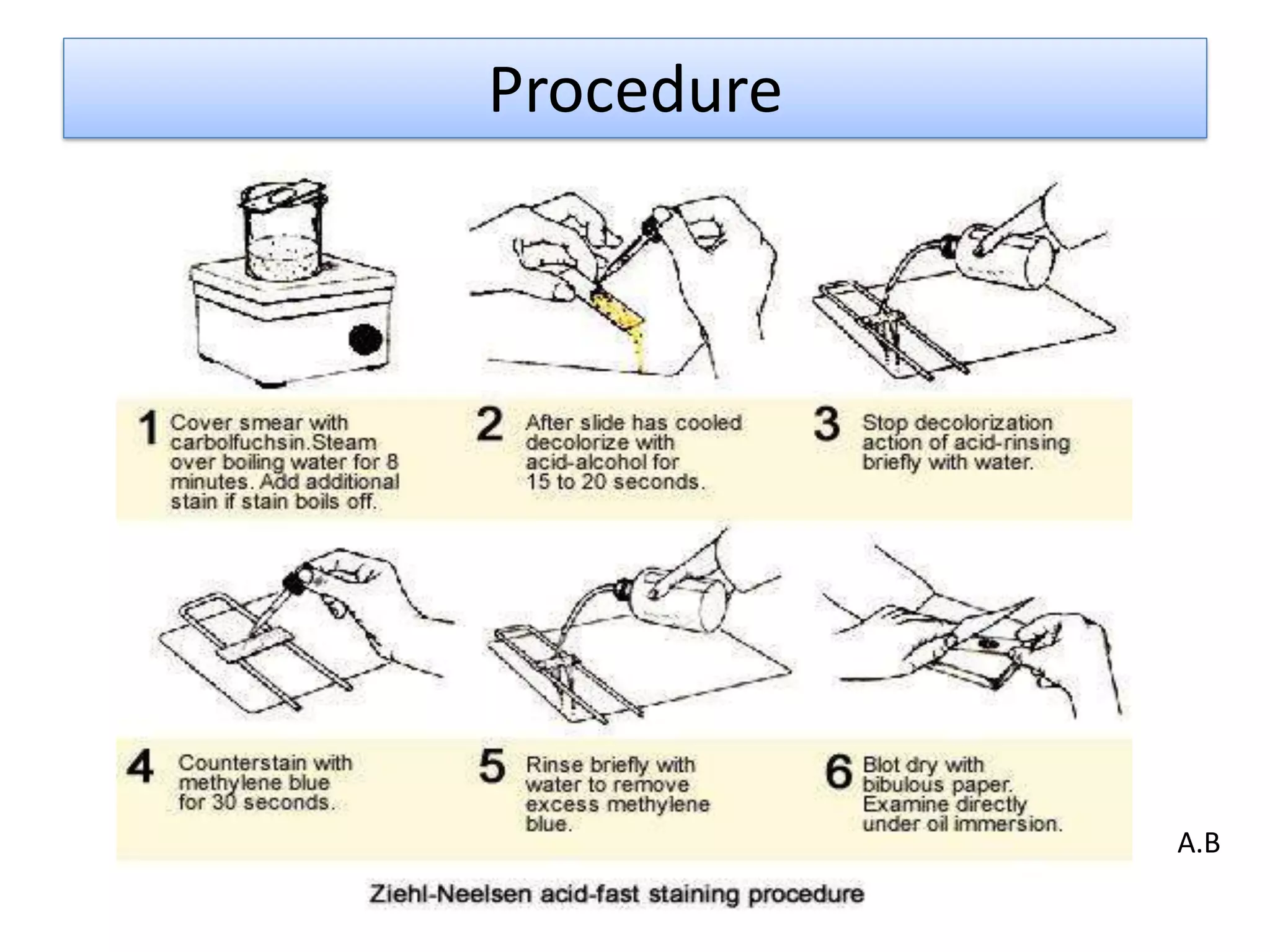
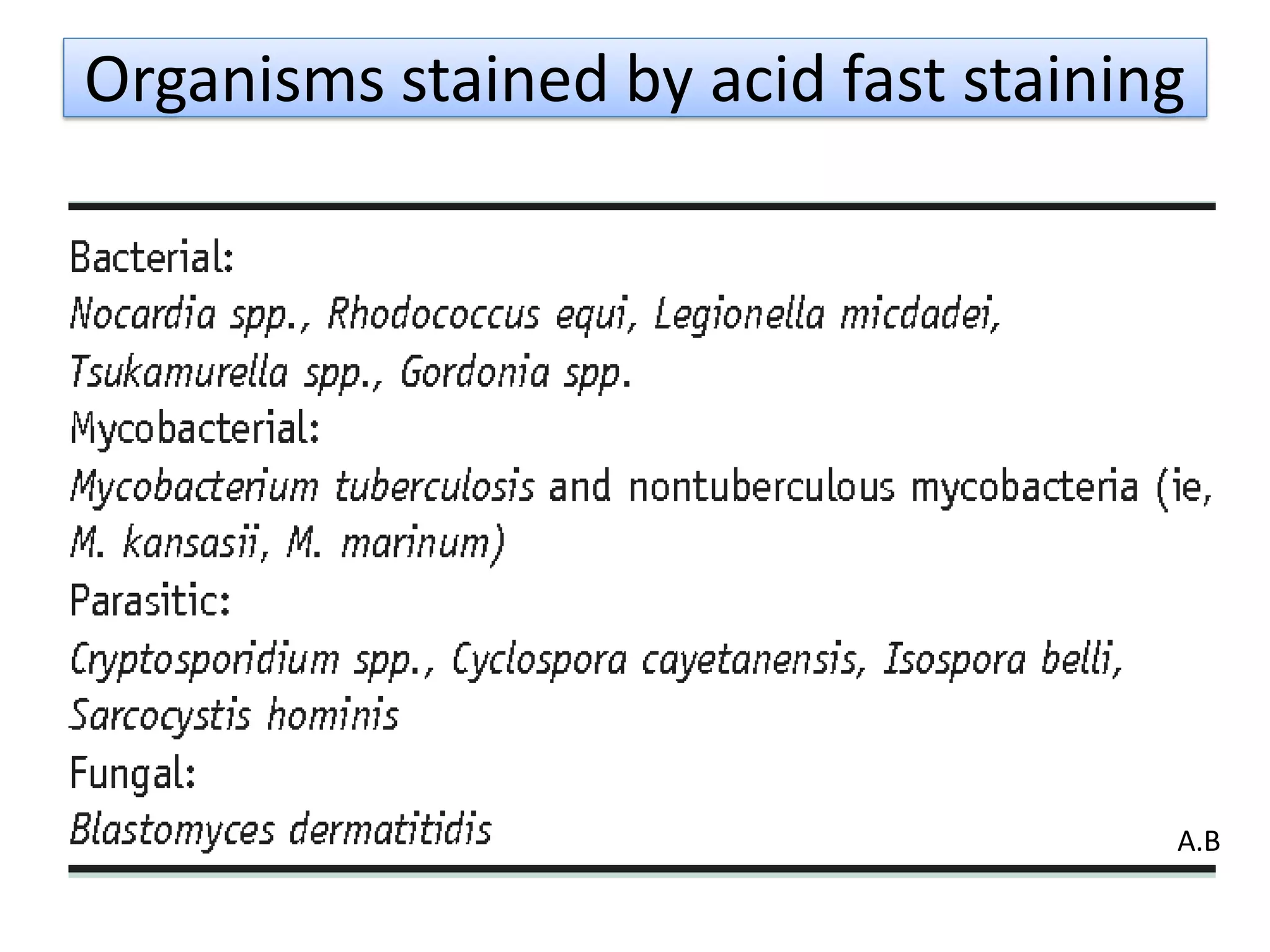
- Acid-fast staining is used to differentiate acid-fast and non-acid fast bacteria by identifying organisms like Mycobacterium that have wax-like cell walls resistant to decolorizing acids. It was developed based on techniques by Ehrlich, Ziehl, and Neelsen and involves staining with carbol fuchsin and decolorizing non-acid fast cells with acid before counterstaining.
- Mycobacterium and other acid-fast bacteria contain high amounts of mycolic acids in their cell walls, making them impermeable and resistant to drying and disinfectants. This waxy composition allows them to retain the red carbol fuchsin stain after acid treatment.
-