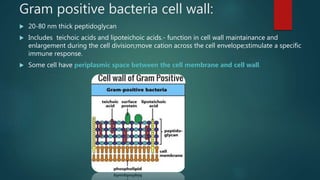
This document discusses the differences between gram positive and gram negative bacterial cell walls. Gram positive bacteria have a thick peptidoglycan layer (20-80nm) in their cell wall containing teichoic acids, while gram negative bacteria have a thinner peptidoglycan layer (10nm) sandwiched between an inner and outer membrane. Gram staining is used to differentiate the two types based on their ability to retain crystal violet dye - gram positive bacteria retain the dye due to their thick peptidoglycan layer and appear violet, while gram negative bacteria lose the dye due to their thinner peptidoglycan layer and appear red with safranin counterstain. The staining protocol involves staining


![Chemical nature of bacterial cell wall:
Peptidoglycan is a made up of 2 amino sugars.
1.N-acetyl glucosamine [NAG]
2.N- acetylmuramic acid [NAM]
NAM attached 4 amino acid chain. The four amino acids that compose the tetrapeptide are: L-
alanine, D-glutamine, L-lysine or meso-diaminopimelic acid (DPA), and D-alanine.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/grampositiveandgramnegativebacteria-200819124051/85/Gram-positive-and-gram-negative-bacteria-3-320.jpg)

![Gram negative bacteria cell wall
Inner and outer membranes and periplasmic space between them contains a thin peptidoglycan
layer.
Outer membrane contains lipopolysaccharides[LPS].
Lipid portion endotoxin may become toxic when released during infection.
Contain porin protein in upper layer – regulate molecules entering and leaving cell.
Peptidoglycan layer 10 nm thickness.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/grampositiveandgramnegativebacteria-200819124051/85/Gram-positive-and-gram-negative-bacteria-6-320.jpg)








![Microscopic images of gram positive and
gram negative bacteria.[100X oil immersion]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/grampositiveandgramnegativebacteria-200819124051/85/Gram-positive-and-gram-negative-bacteria-15-320.jpg)
