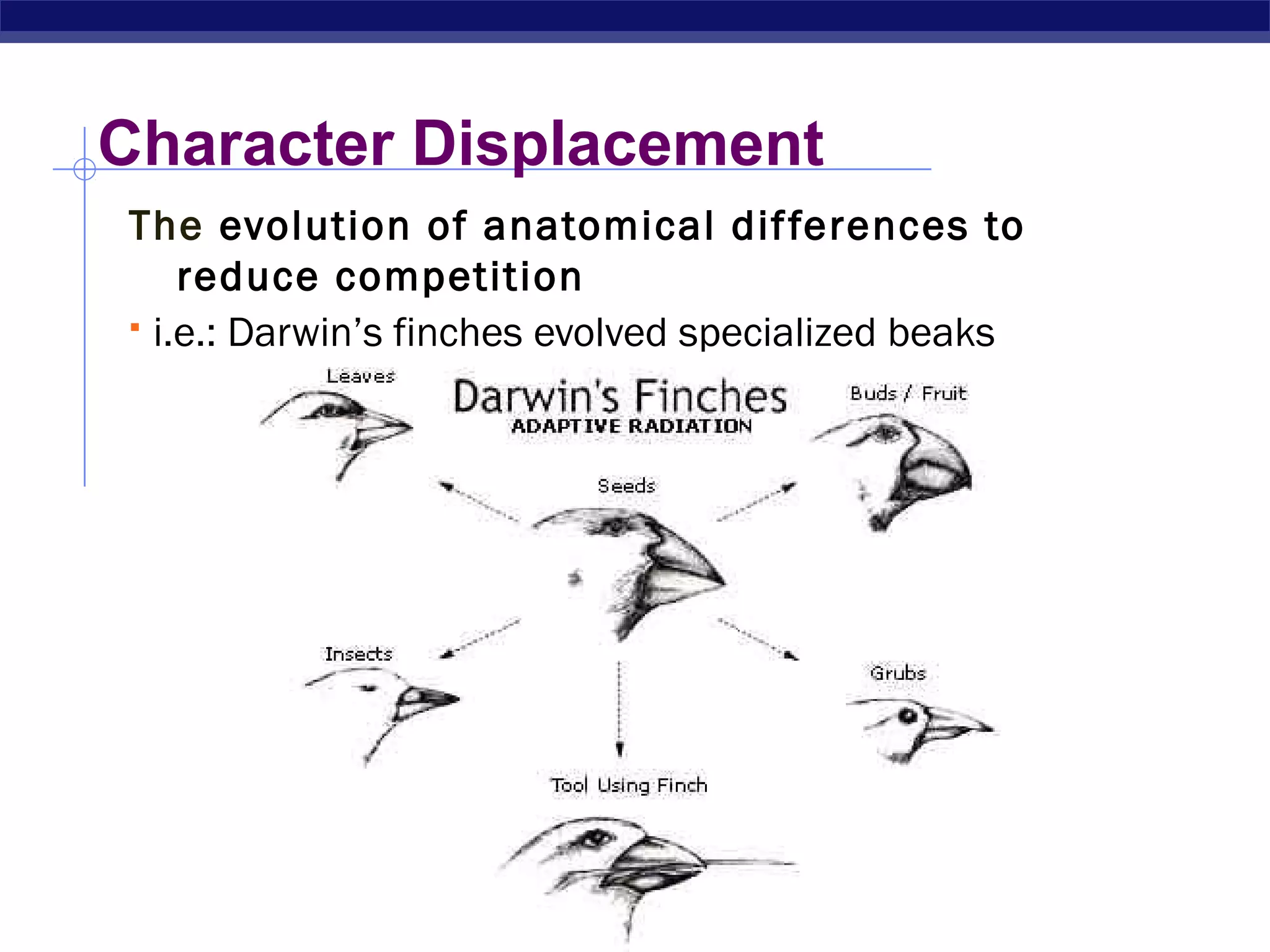
This document summarizes the five major types of species interactions: predation, competition, parasitism, mutualism, and commensalism. It defines each interaction and provides examples. Predation involves one species consuming another for food, while competition occurs when two species require the same limited resources. Parasitism benefits one species at the expense of the other. Mutualism is a cooperative relationship that benefits both species, such as pollination. In commensalism, one species benefits while the other is not affected.