1. Species diversity refers to the number and variety of species in a given region. It takes into account both the number of species and how evenly abundant they are.
2. There are three main types of species: endemic, exotic, and cosmopolitan. Endemic species are restricted to a particular area while exotic species have been transported by humans.
3. Factors that affect species diversity include speciation, extinction, migration, habitat destruction, and the introduction of invasive species. Speciation occurs through geographic isolation or reductions in gene flow. Extinction can be caused by overharvesting, pollution, and habitat loss.










































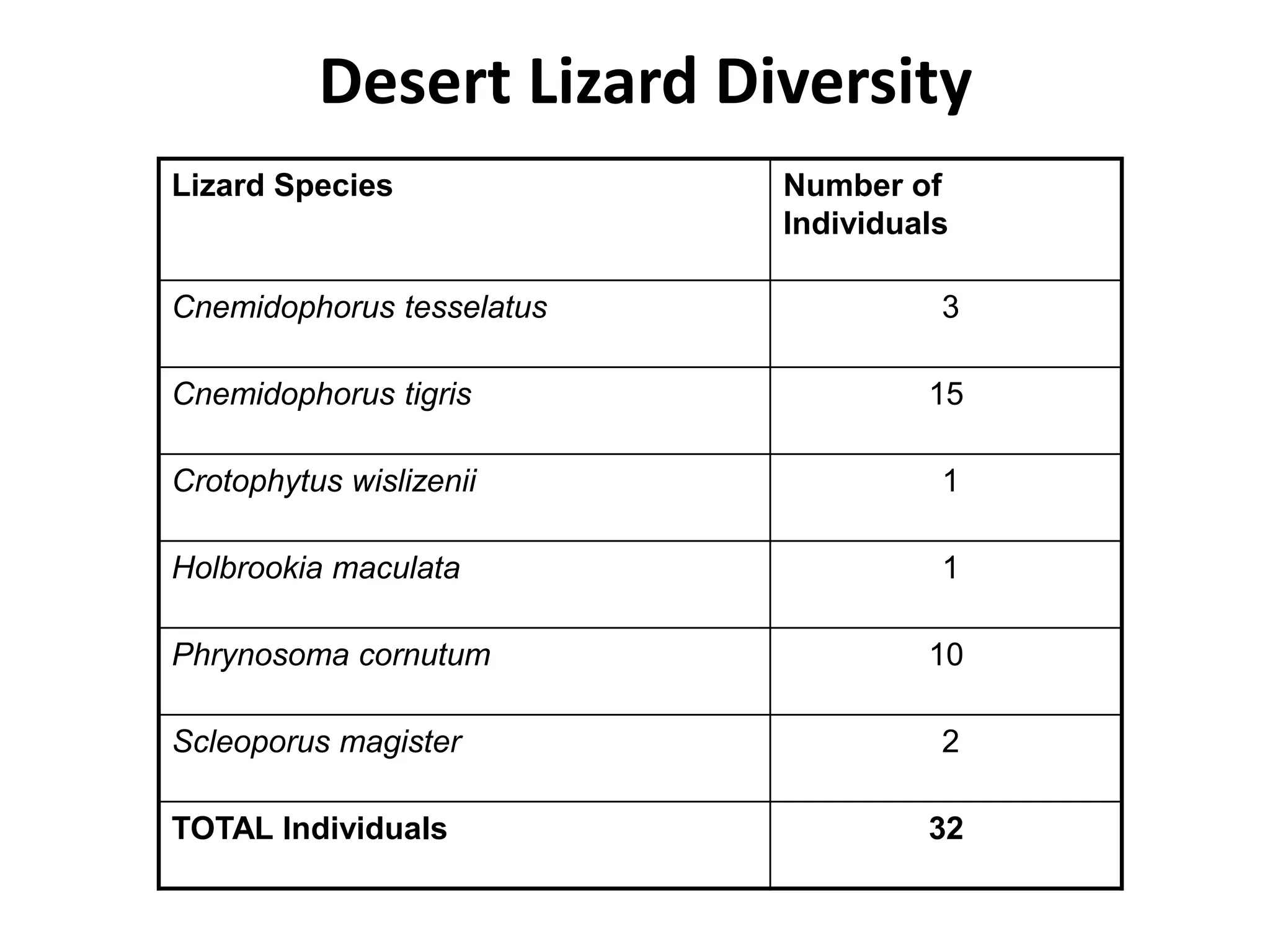
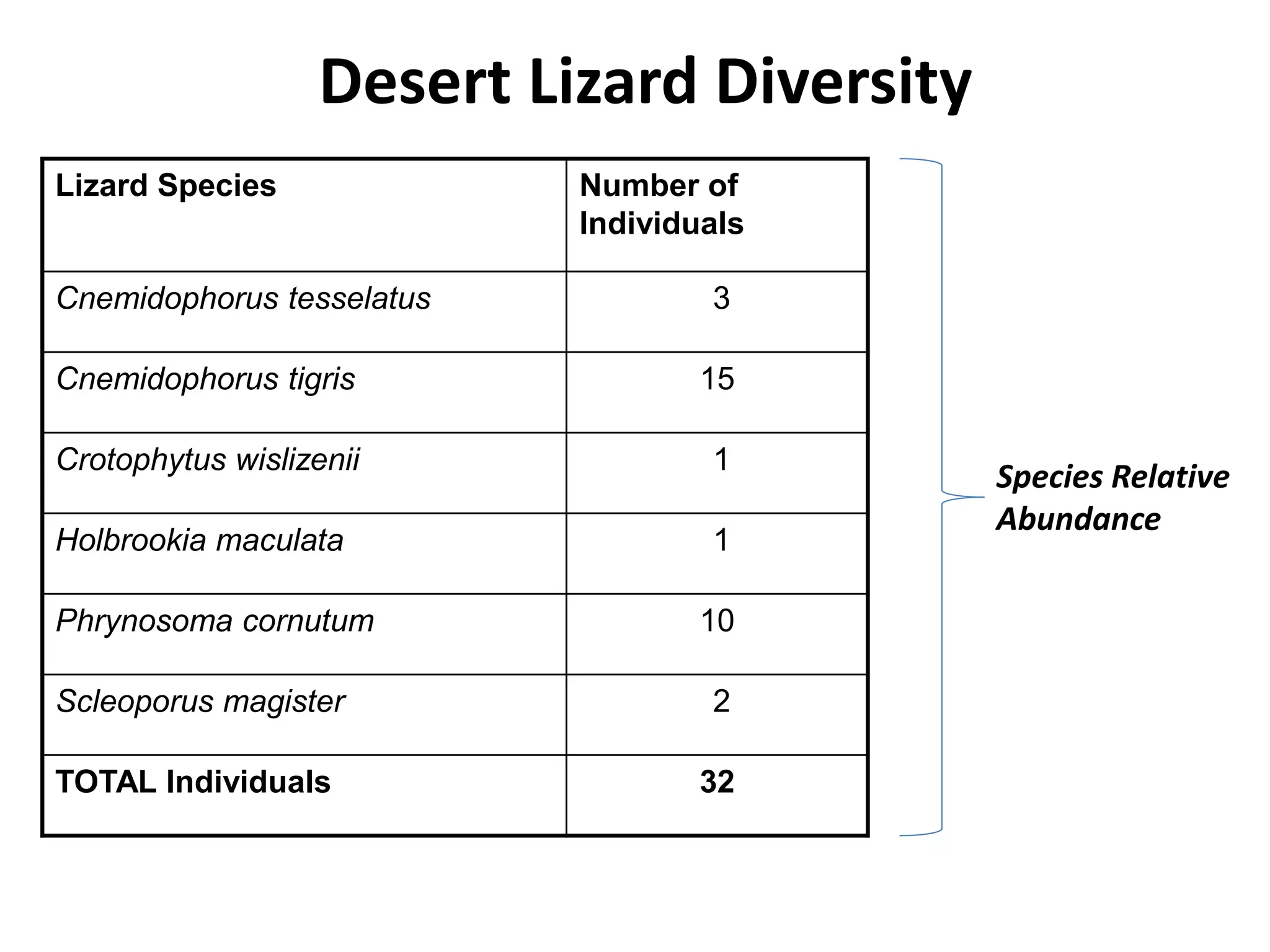

![• Shannon-Wiener diversity function
H' = - (pi) [ln(pi)]
H’ = Shannon-Wiener index of species diversity
s = number of species in community
pi = proportion of total abundance represented
by ith species
Species diversity](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/speciesdiversity-150221155236-conversion-gate02/75/Species-diversity-46-2048.jpg)
