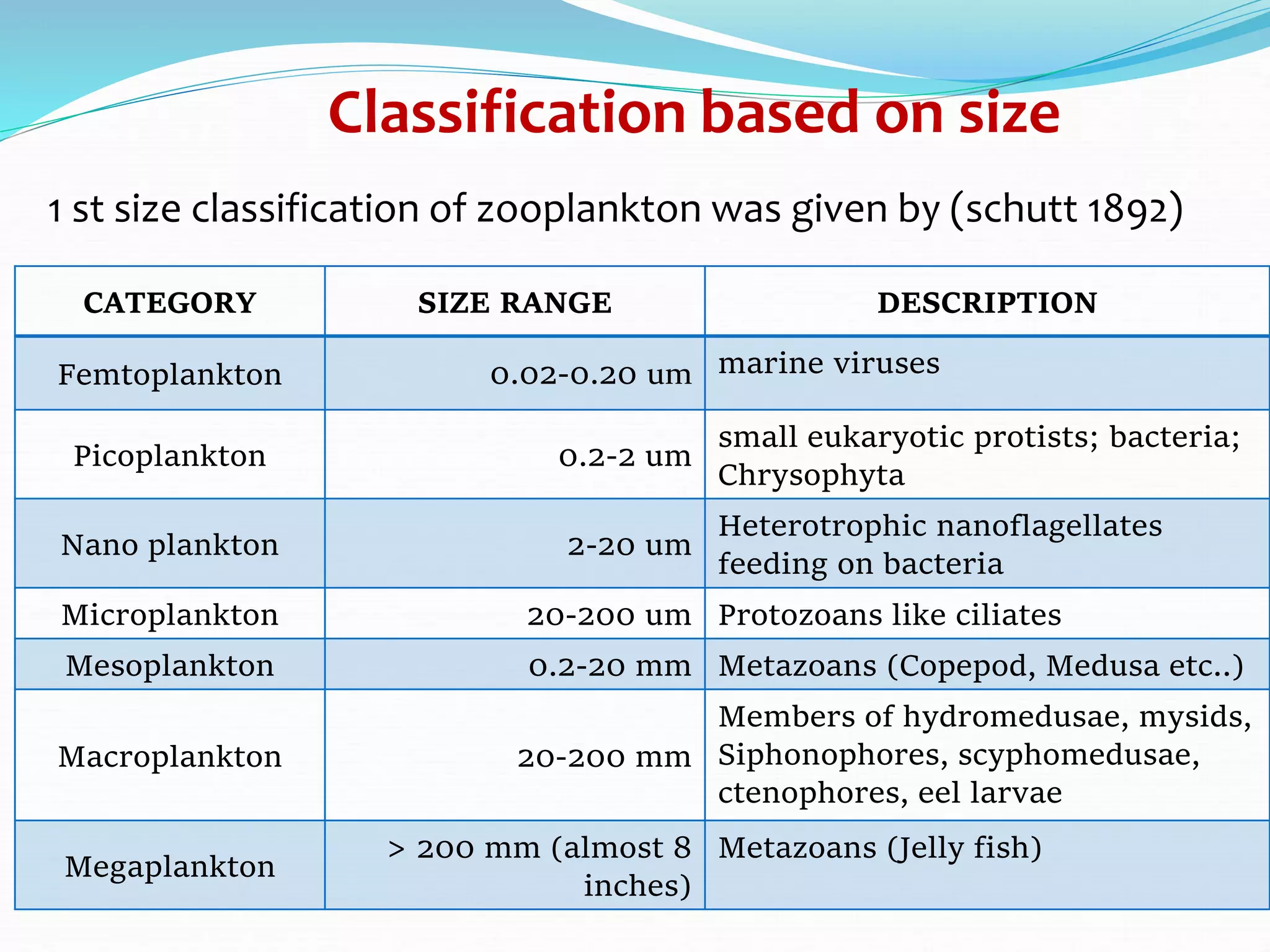
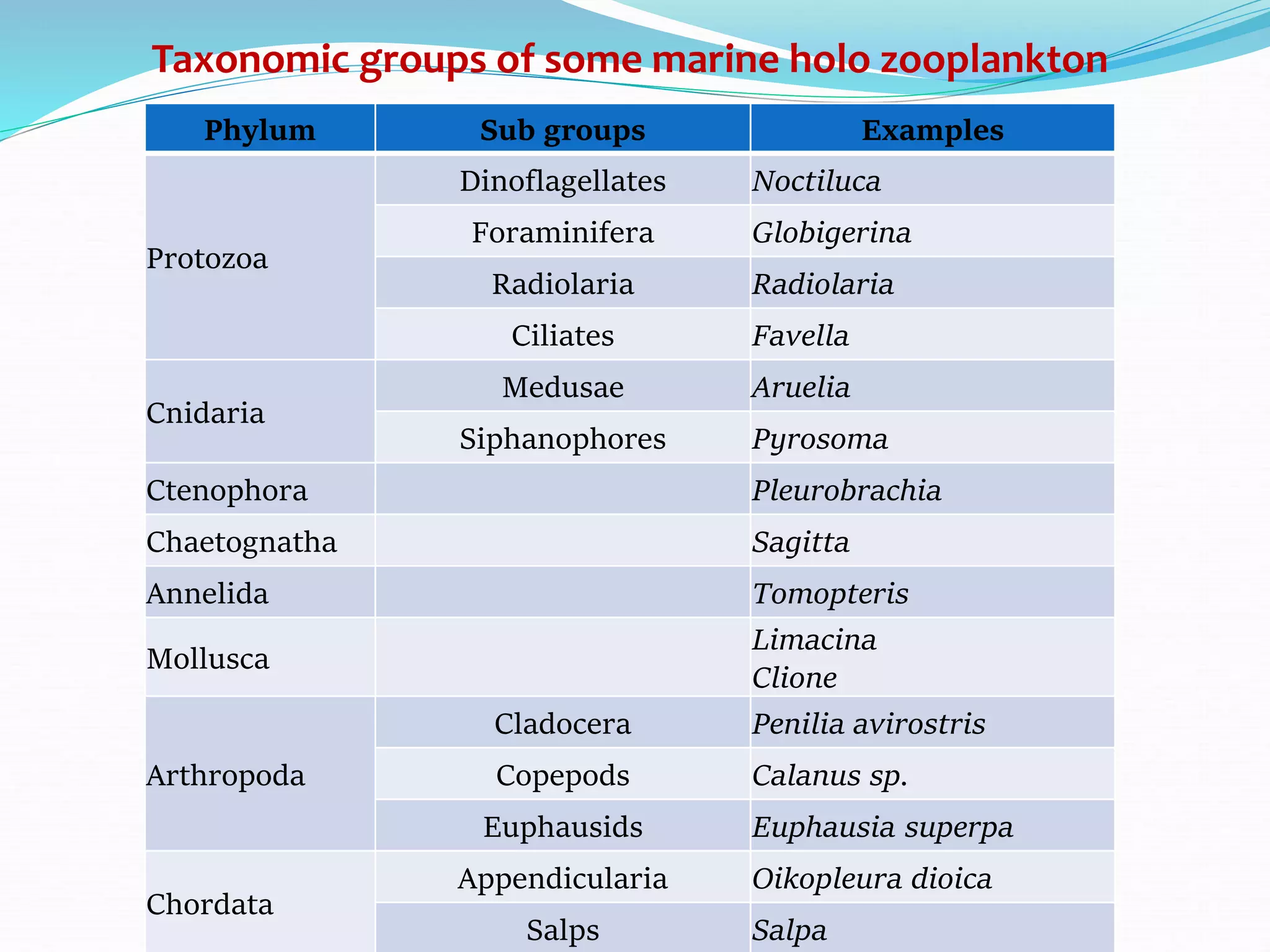
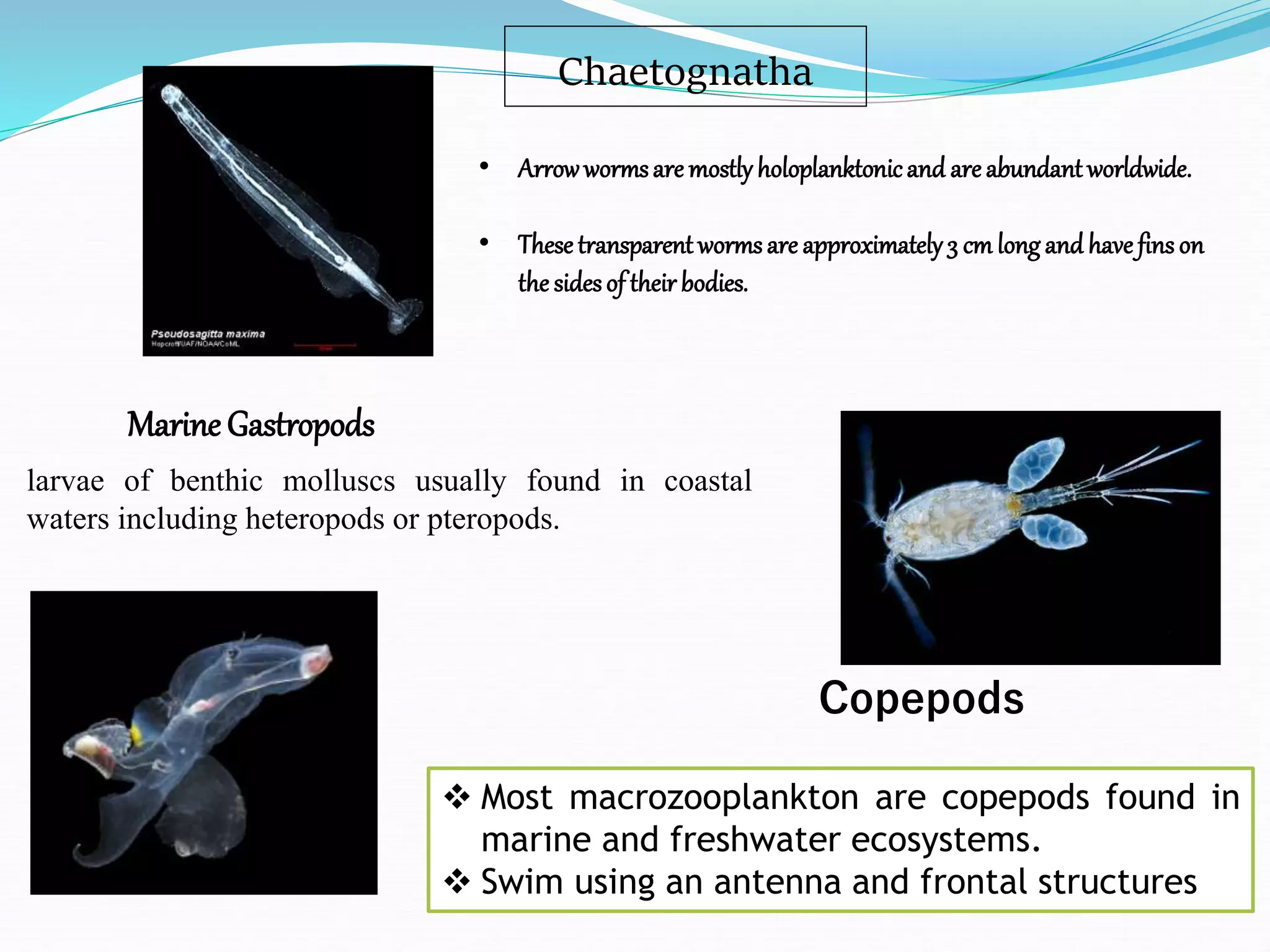
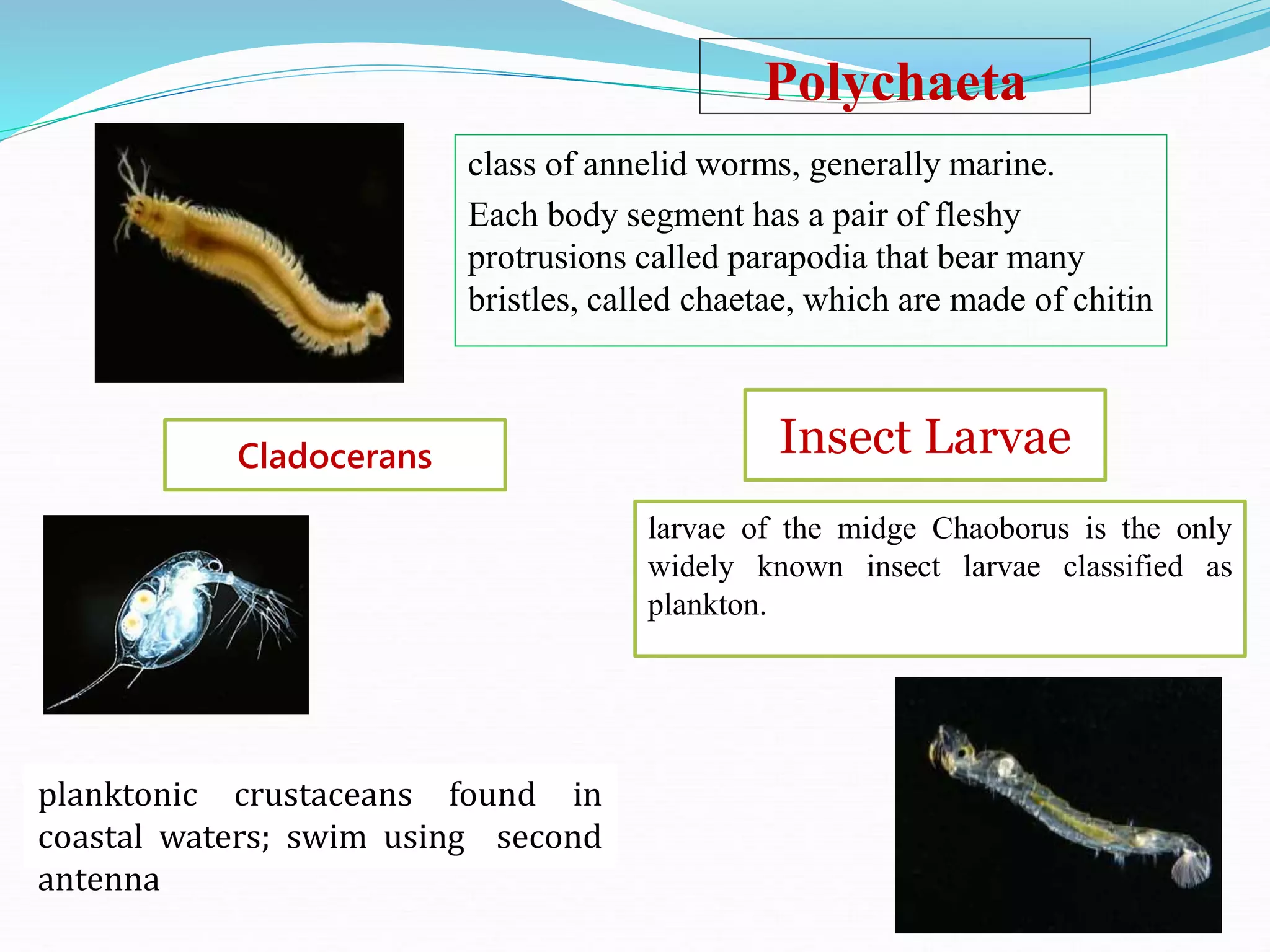
Zooplankton are small aquatic animals that drift or float in water and rely on currents for movement. Without environmental controls, the entire world could be covered by a 3-foot thick layer of zooplankton in just 130 days. Zooplankton are classified based on size from femtoplankton to megaplankton. They also have holoplankton that remain plankton their whole life and meroplankton that are partially planktonic. Common phyla include protozoa, cnidaria, chaetognatha, annelida, mollusca, arthropoda, and chordata.