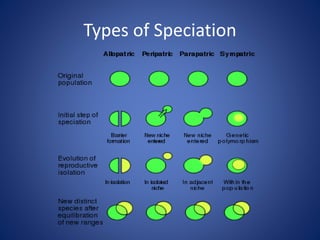
This document discusses speciation and the evolution of new species. It defines different types of speciation, including allopatric, parapatric, and sympatric speciation. Reproductive isolation is a key factor in speciation, with both prezygotic barriers that prevent interbreeding and postzygotic barriers affecting the viability of hybrid offspring. Speciation occurs over long periods of time through either gradual evolution or punctuated equilibrium. The document also covers taxonomy, phylogeny, cladistics, extinction, and adaptive radiation.