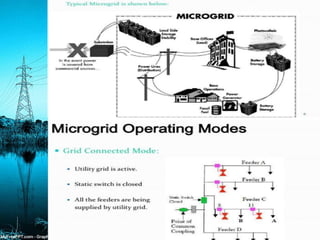
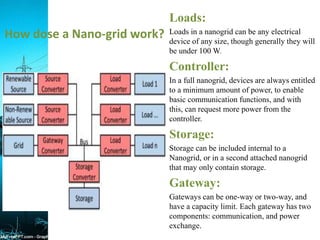
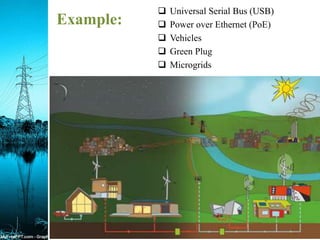
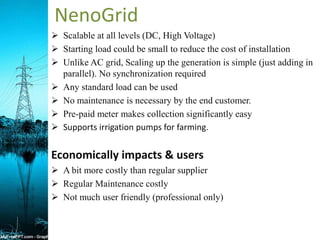
A mini-grid, micro-grid, and nano-grid are small-scale power grids that can operate independently or connect to larger grids. A mini-grid supplies electricity to a localized group, a micro-grid can be as small as a single building, and a nano-grid is typically under 100 kW and serves a single load. They use solar energy and storage to provide power in rural areas without access to main grids. These distributed energy systems improve reliability, lower costs, and have environmental benefits over traditional centralized grids.