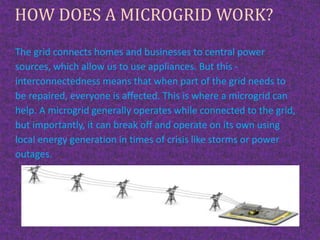
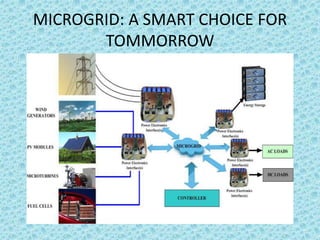
Microgrid technology allows for localized power generation and high efficiency by connecting interconnected loads and distributed energy resources. It can operate in both grid-connected and island modes, providing advantages like stability, autonomy, and support for renewable energy sources. Microgrids are positioned as a smart choice for the future, enhancing electric service reliability and reducing emissions.