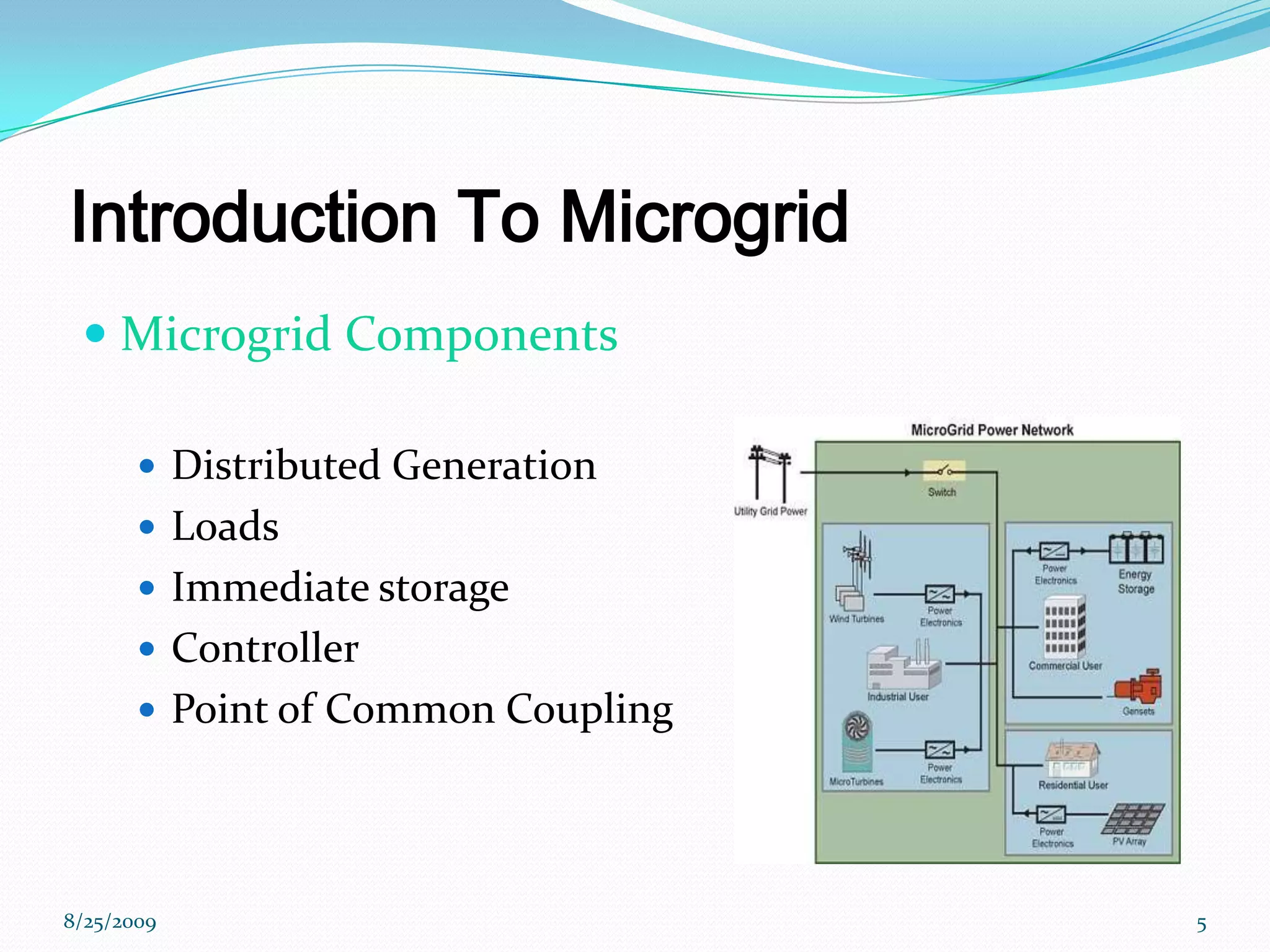
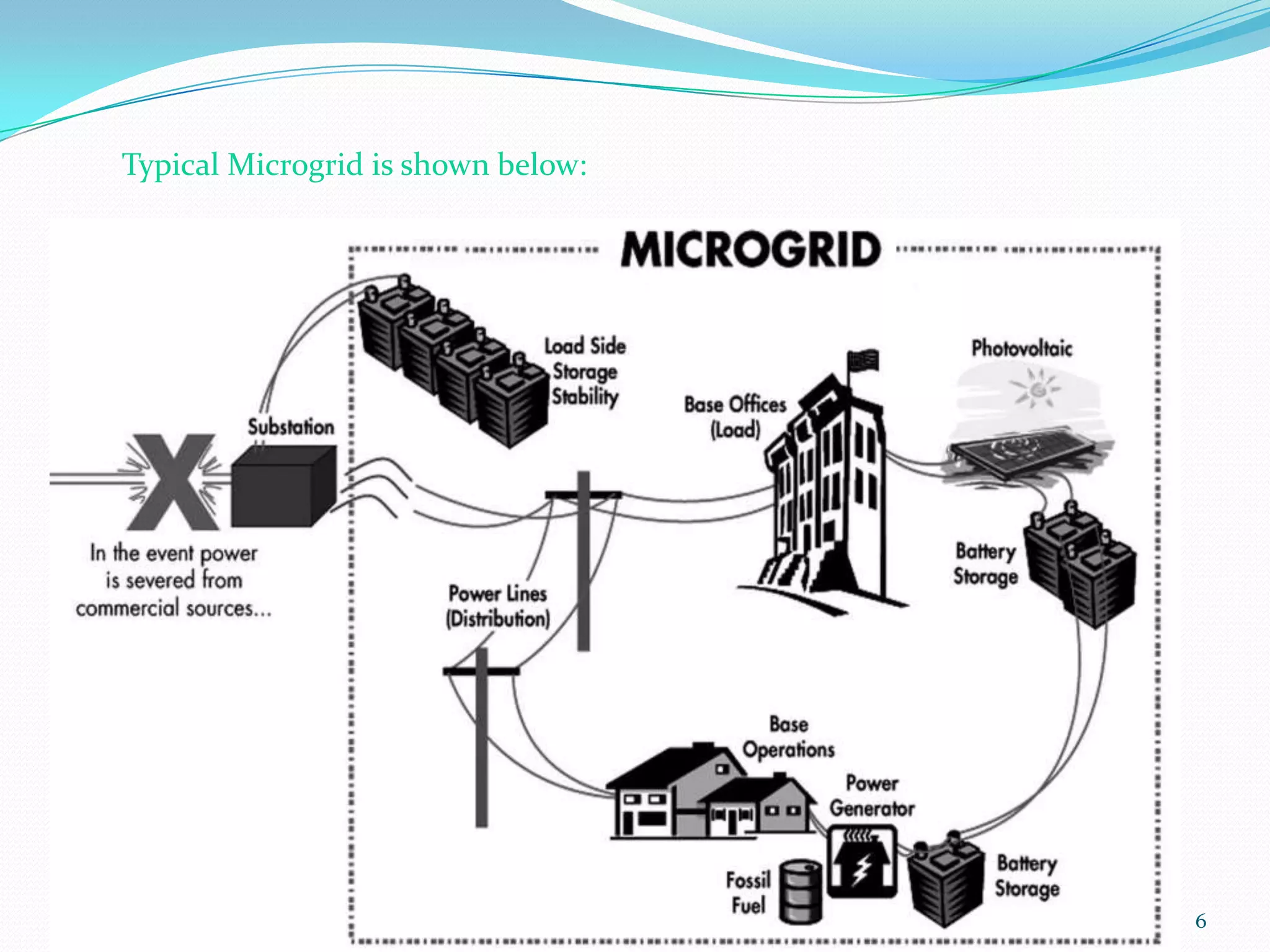
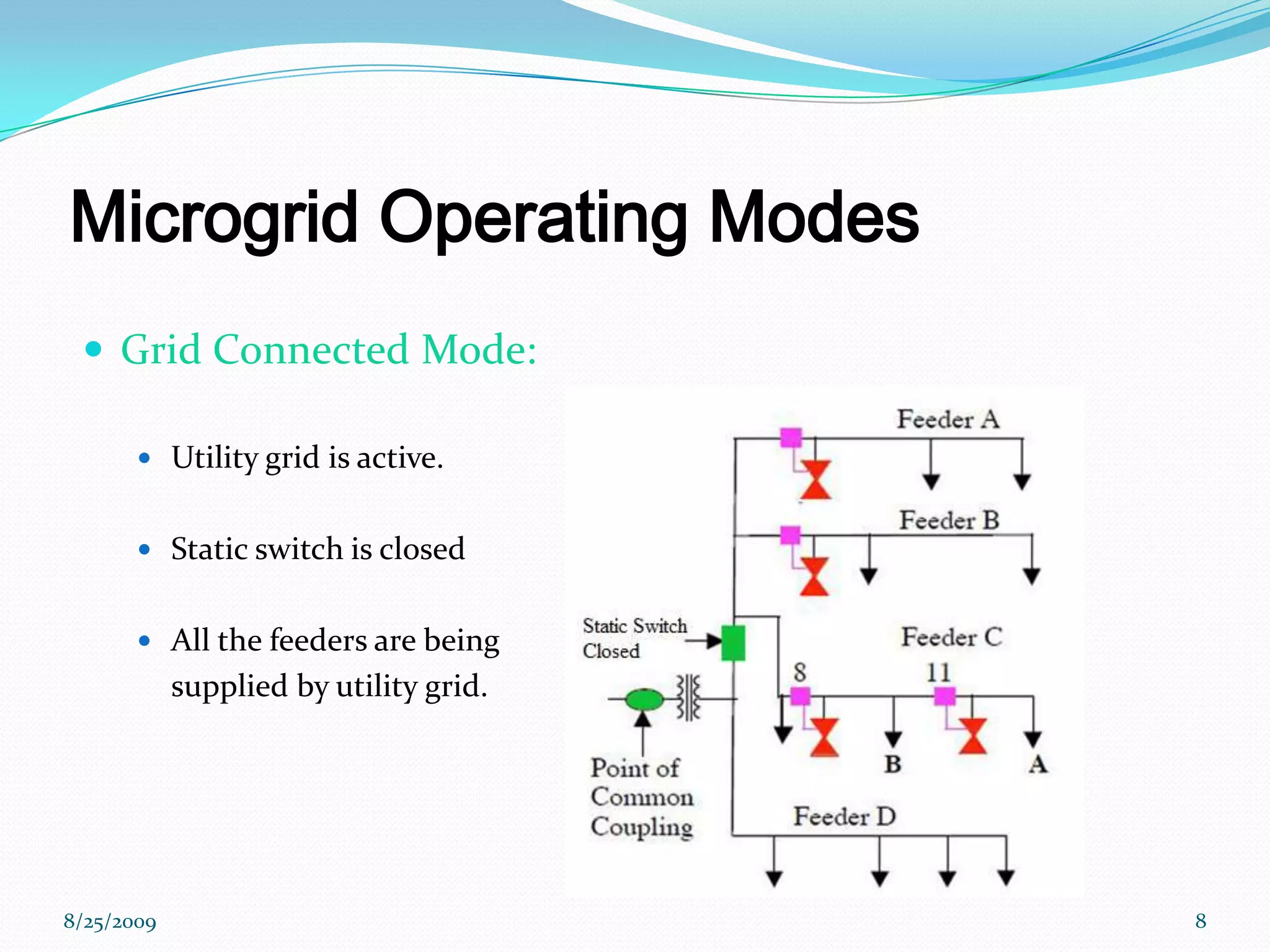
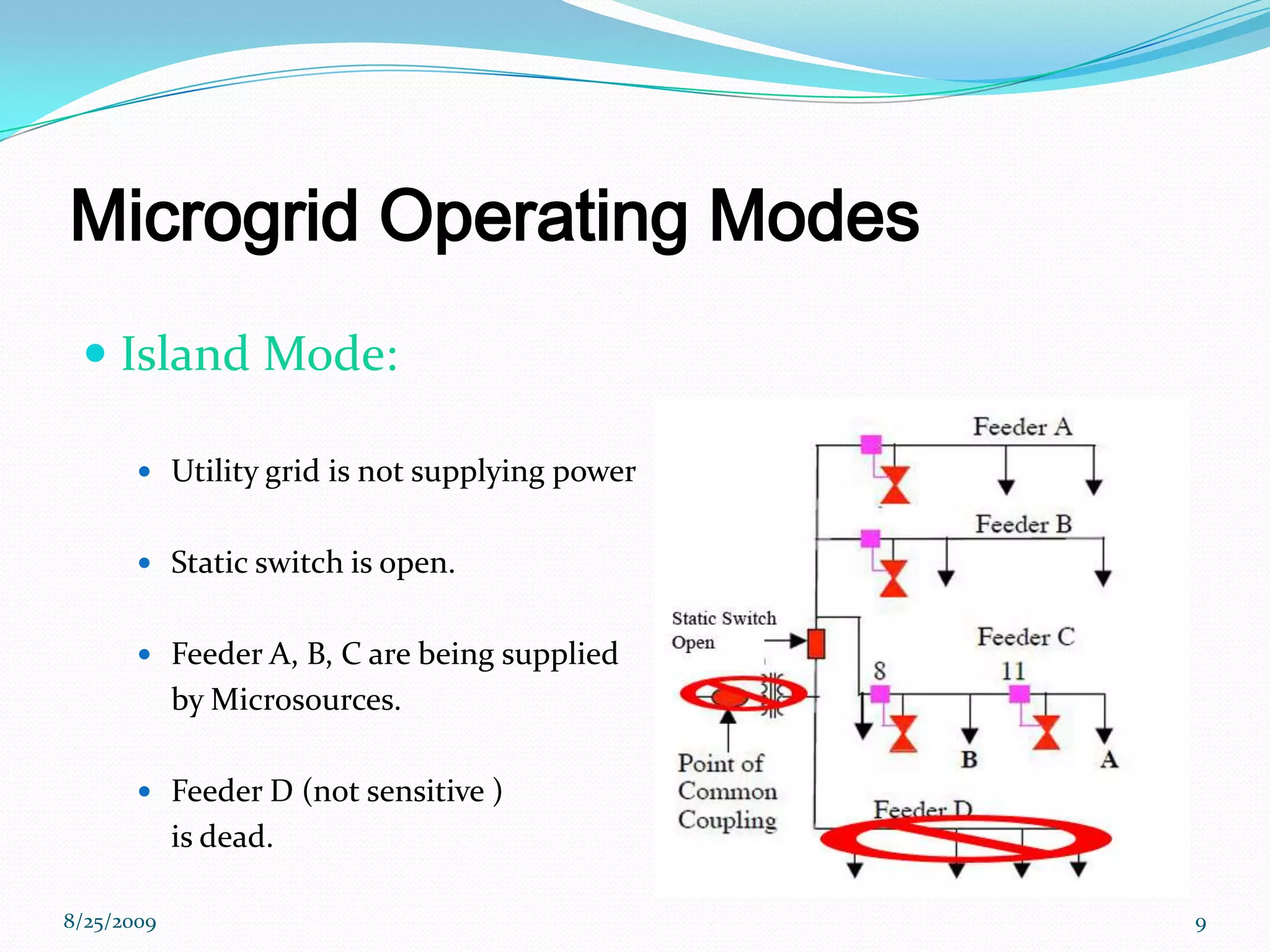
The document provides an introduction to microgrids, highlighting their role as small-scale power networks that enable local power generation and enhance energy reliability. It discusses the operational modes, advantages, disadvantages, and environmental benefits of microgrids compared to conventional grids. Future directions for research in microgrid technology are also outlined, emphasizing improvements in reliability and energy delivery systems.