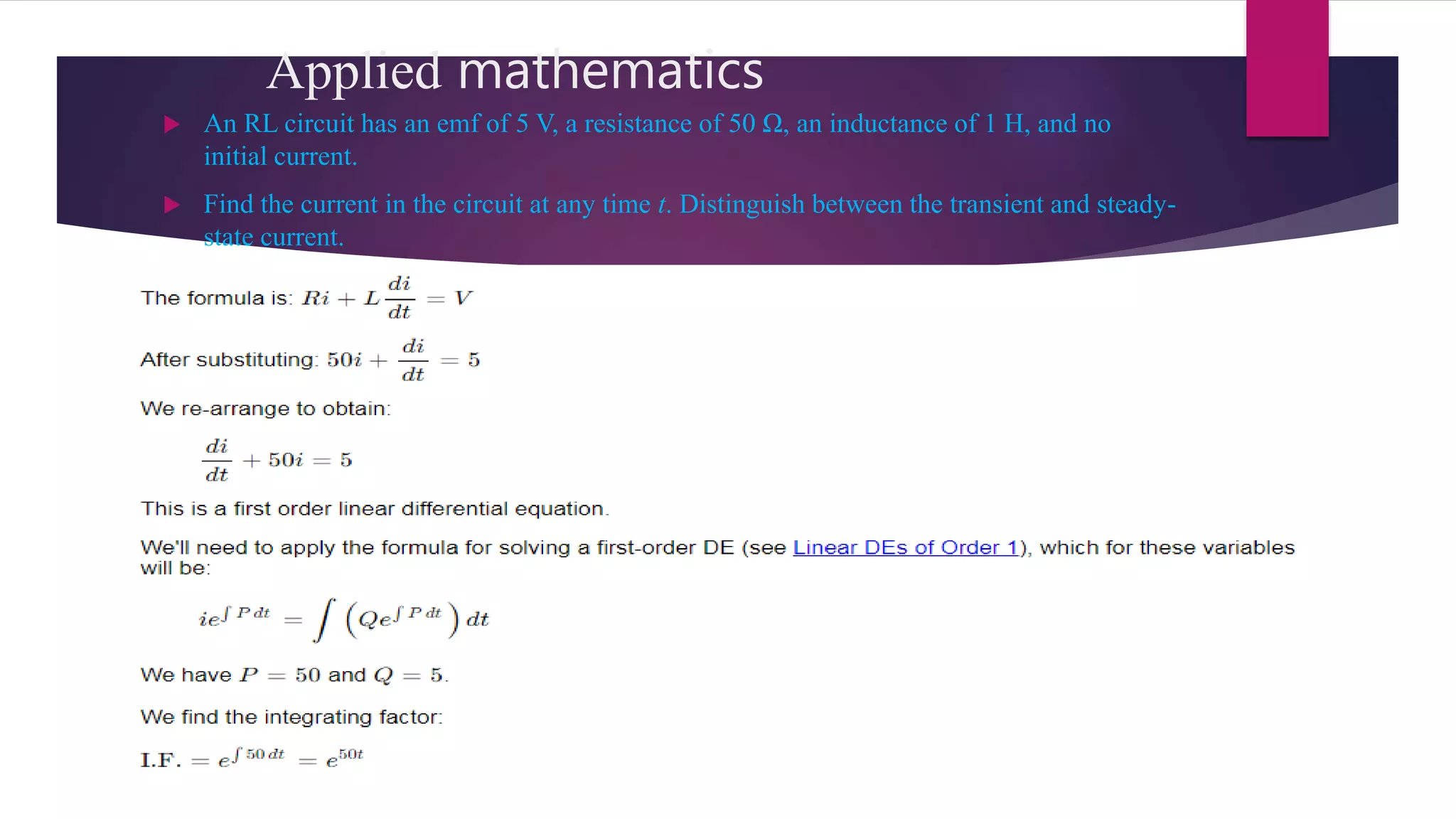
This presentation summarizes applications of differential equations in electrical and electronics engineering. It was prepared by three students for their Mathematics III course at Daffodil International University in Bangladesh. The presentation defines ordinary and partial differential equations, provides examples of each, and discusses the history and invention of differential equations by Newton, Leibniz, and others. It then outlines several applications of differential equations in areas like software, games, artificial intelligence, and physics concepts like electric circuits, cooling, decay, electromagnetism, fluids, heat, and waves. One application example calculates current in an RL circuit over time.