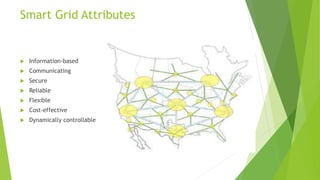
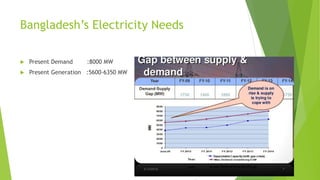
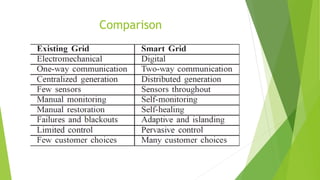
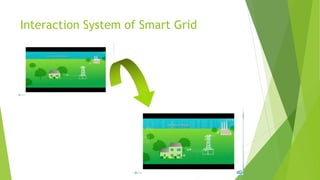
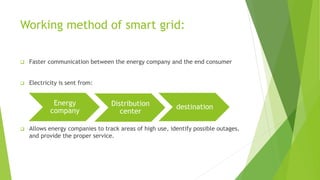
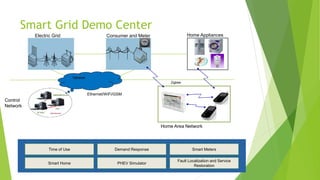
The presentation discusses smart grid technology, including its attributes, reasons for use, components, users, and how it works. A smart grid uses information technologies to improve how electricity is delivered from power plants to consumers. It allows for two-way interaction between consumers and the grid and integrates new technologies. Key benefits include reduced costs, improved reliability, efficiency and capacity, enabling predictive maintenance and automated operations. Security and privacy are main concerns due to two-way communication and potential for hacking of automated meters. The future of smart grid is uncertain but may become widely used over the long run.