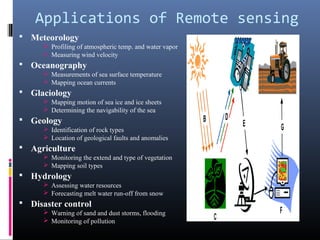
This document provides an overview of remote sensing including its history, sensors, platforms, applications, software, and use in Pakistan. Remote sensing allows obtaining information about objects through analysis of data collected by instruments without physical contact. It uses electromagnetic radiation as an information carrier. Common sensors are active like LIDAR and RADAR, or passive. Platforms include ground, airborne, and spaceborne. Applications span meteorology, oceanography, geology, agriculture, and more. Popular software for analysis includes ERDAS, ENVI, and ESRI. Pakistan is developing its own remote sensing satellite called PRSS and using the technology to improve flood management.