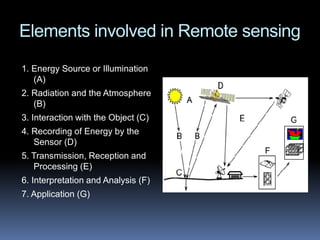
Remote sensing involves obtaining information about objects through analysis of sensor data without physical contact. It uses electromagnetic radiation as an information carrier. Key elements include an energy source, sensors to record energy interactions with objects, and transmission/processing of sensor data. Platforms can be ground, airborne, or space-based. Remote sensing provides regional views over broad portions of the electromagnetic spectrum and geo-referenced digital data. Applications include weather forecasting, mapping, monitoring vegetation/soils in agriculture, assessing water resources, and disaster control.