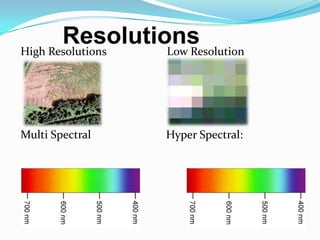
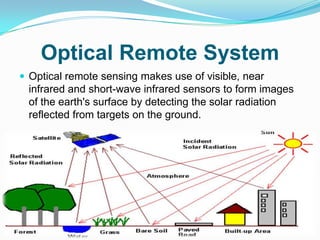
This document discusses remote sensing systems. It begins with an introduction to remote sensing as gathering information from objects without direct contact. It then covers the history of remote sensing from early aerial photography to modern satellite systems. The document outlines different types of remote sensing including passive methods like photography and radiometers and active methods like RADAR and LiDAR. It provides examples of remote sensing applications and techniques. Finally, it describes different optical, RADAR, and LiDAR remote sensing systems and how they work.