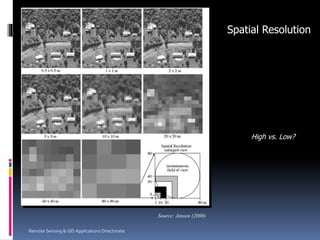
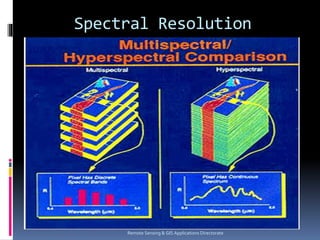
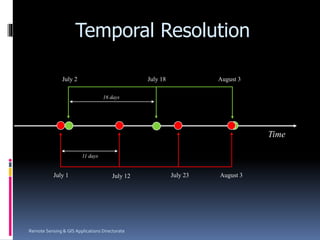
Remote sensing involves collecting information about objects without physical contact. It was first defined in the 1960s and the first earth observation satellite, Landsat-1, was launched in 1972. Remote sensing uses sensors on airborne and spaceborne platforms to detect electromagnetic radiation reflected or emitted from the object of interest. Common platforms include aircraft, balloons, and satellites. Satellites provide global coverage and frequent revisits. Remote sensing data has various applications such as agriculture, forestry, and soil mapping.