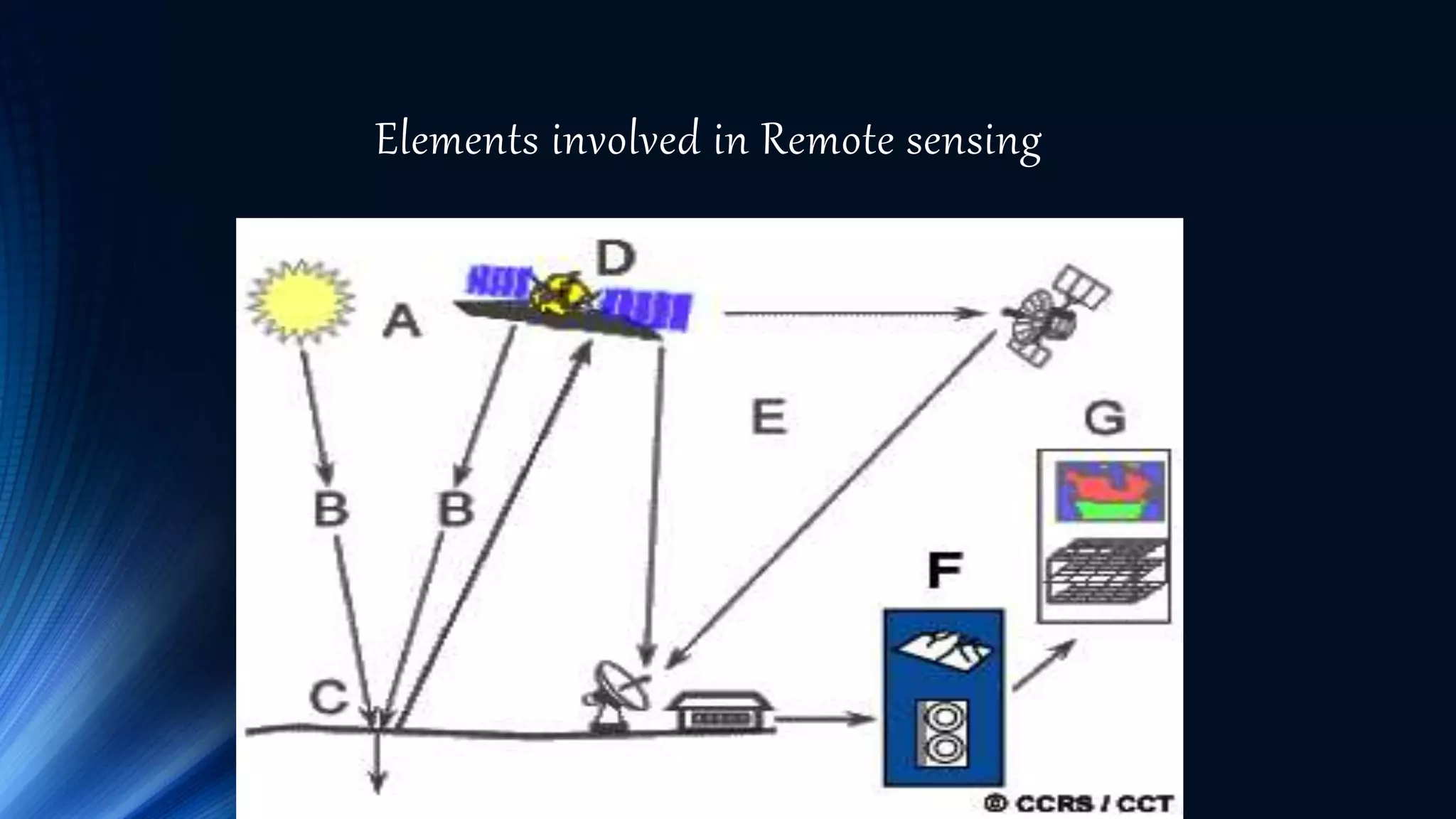
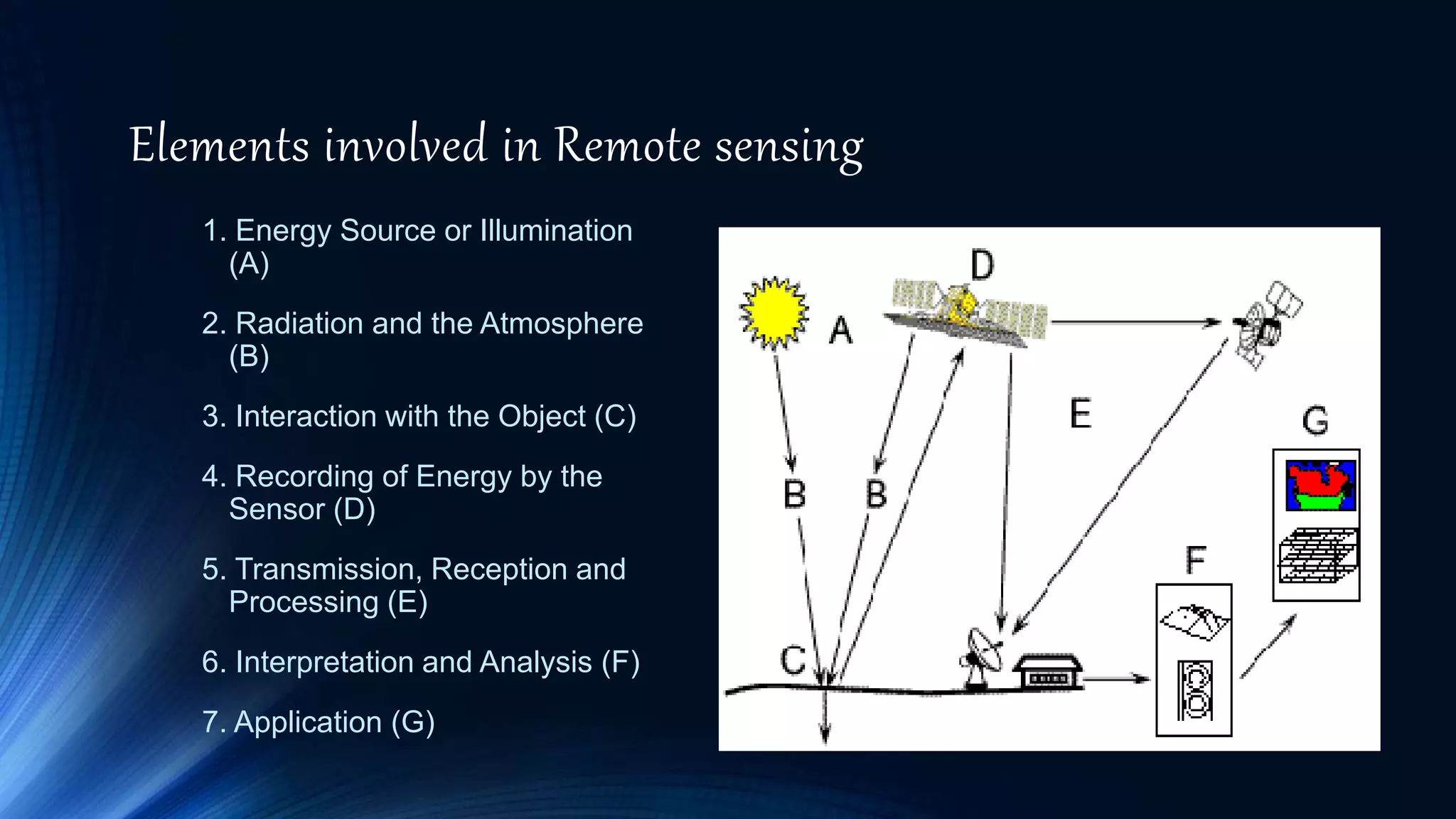
Remote sensing involves obtaining information about objects through analysis of data collected by instruments without physical contact. It uses electromagnetic radiation as a physical carrier to transmit information from objects to sensors through an intervening medium. The output is usually an image representing the observed scene. Remote sensing has a long history dating back to the 1840s with cameras on balloons, and emerged in the 1950s as a technique using various sensors on spacecraft. It involves an energy source, radiation interaction with the object, sensor recording, transmission and processing, interpretation and applications. Active sensors use artificial sources while passive sensors rely on natural sources like the sun. Platforms include ground, airborne and spaceborne. Applications are in meteorology, oceanography, geology, agriculture,