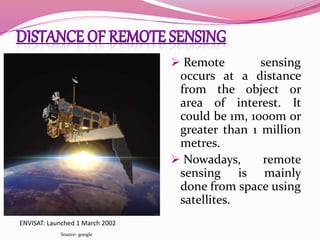
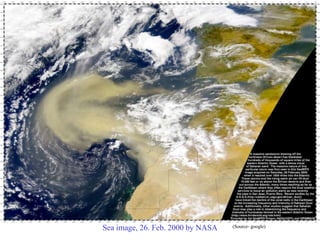
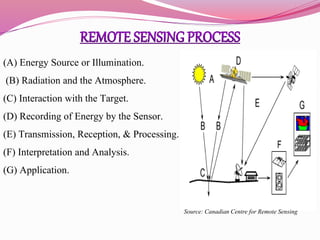
Remote sensing is the acquisition of information about objects from a distance using various sensors, primarily from satellites in space. It employs different parts of the electromagnetic spectrum for various applications, including agriculture, forestry, geology, and hydrology, enabling tasks such as crop monitoring, land use assessment, and environmental management. The field has evolved significantly since its inception, transitioning from aerial photography to advanced satellite-based systems used today.