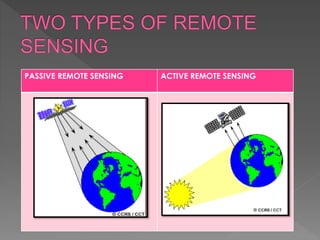
Remote sensing involves collecting and interpreting data about the Earth from various distances, significantly enhancing our environmental and geographical understanding. It utilizes both passive and active sensors to measure electromagnetic radiation, with applications across geology, agriculture, and resource management. The technology is vital for efficient data collection, especially in inaccessible areas, and supports global positioning and geographic information systems.