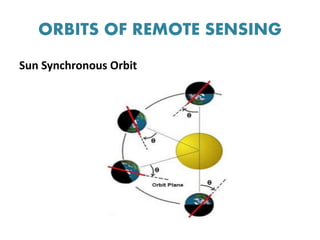
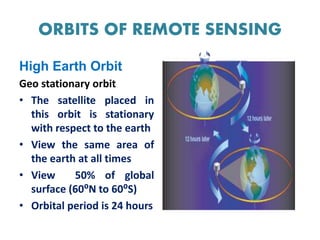
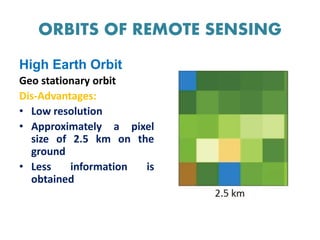
This document discusses remote sensing platforms and sensors. It describes the different types of orbits used by remote sensing satellites, including low Earth orbit, sun synchronous orbit, and geostationary orbit. It also outlines the various platforms that can be used, such as ground-based, airborne, and space-borne. Finally, it examines the characteristics of remote sensing sensors, including spatial, spectral, radiometric, and temporal resolution.