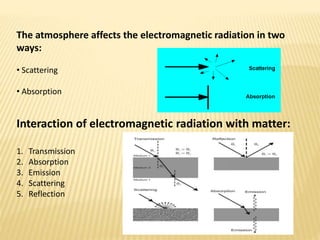
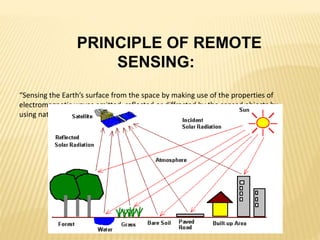
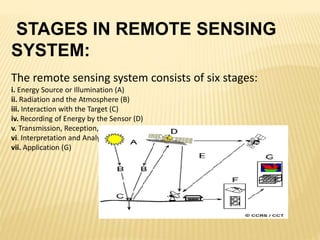
This document discusses remote sensing and geographic information systems (GIS). Remote sensing involves collecting data about objects from a distance using electromagnetic energy and sensors. It works through various stages including energy source, interaction with the target, sensor recording, processing, and interpretation. Remote sensing has applications in resource exploration, environmental monitoring, and land use analysis. GIS integrates spatial data using computer hardware, software, and trained personnel. It has advantages like visualization and modeling capabilities, and disadvantages like high costs and data errors. The future of remote sensing and GIS is promising as more industries adopt these technologies.