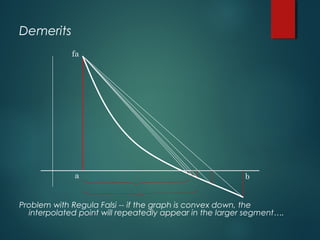
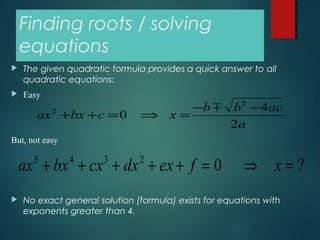
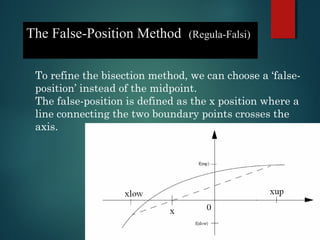
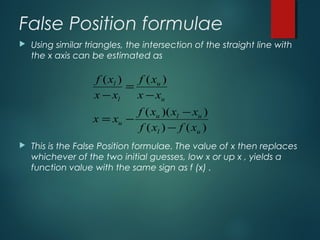
This document describes the False Position Method for finding the roots of equations. The method uses linear interpolation to estimate the root between two initial guesses that bracket it. It improves on the bisection method by choosing a "false position" where the line between the guesses crosses the x-axis, rather than the midpoint. The false position formula is derived using similar triangles. An example applying the method to find a root of x^3 - 2x - 3 = 0 is shown. The merits of the false position method are faster convergence compared to bisection, while the demirits are possible non-monotonic convergence and lack of precision guarantee.





![Example
Lets look for a solution to the equation x3
-2x-3=0.
We consider the function f(x)=x3
-2x-3
On the interval [0,2] the function is negative at 0 and positive at 2. This
means that a=0 and b=2 (i.e. f(0)f(2)=(-3)(1)=-3<0, this means we can
apply the algorithm).
( )
2
3
4
6
31
)2(3
)0()2(
02)0(
0 =
−
−=
−−
−
−=
−
−
−=
ff
f
xrfp
8
21
2
3
)(
−
=
= fxf rfp
This is negative and we will make the a
=3/2 and b is the same and apply the
same thing to the interval [3/2,2].
( )( )
( )
( )
29
54
58
21
2
3
12
3
)2(
2
2
3
8
21
2
1
8
21
2
3
2
3
2
3
=+=
−
−=
−
−
−= −
−
ff
f
xrfp
267785.0
29
54
)( −=
= fxf rfp
This is negative and we will make the a
=54/29 and b is the same and apply the
same thing to the interval [54/29,2].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/regulafalsi1603216026-150426045300-conversion-gate01/85/Regulafalsi_bydinesh-9-320.jpg)