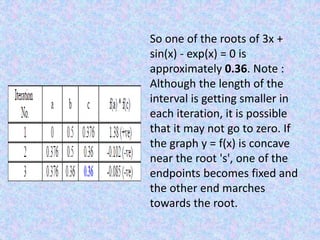
The False-Position Method is an iterative root-finding algorithm that improves upon the bisection method. It uses the slope of a line between two points to estimate a new root, rather than always bisecting the interval. Given an initial interval where the function changes sign, it calculates a new x-value at the intersection of the x-axis and a line through two existing points. It then chooses a new interval based on where the function changes sign again. The method is similar to bisection but uses a different formula to calculate the new estimate. An example finds a root of 3x + sin(x) - exp(x) = 0 between 0 and 0.5, converging to a solution of approximately 0.


![Methodology
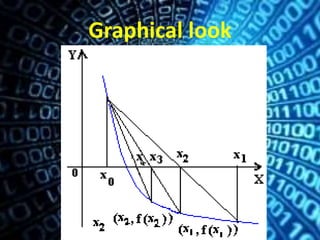
we start with an initial interval [x1,x2], and we
assume that the function changes sign only once
in this interval. Now we find an x3 in this
interval, which is given by the intersection of the
x axis and the straight line passing through
(x1,f(x1)) and (x2,f(x2)). It is easy to verify that
x3 is given by](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aa5ac394-41dc-4021-829b-cb52b82ca626-150610192307-lva1-app6891/85/The-False-Position-Method-3-320.jpg)
![Methodology
Now, we choose the new
interval from the two choices
[x1,x3] or [x3,x2] depending on in
which interval the function
changes sign.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aa5ac394-41dc-4021-829b-cb52b82ca626-150610192307-lva1-app6891/85/The-False-Position-Method-4-320.jpg)

![Numerical Example
Find a root of 3x + sin(x) - exp(x) =0. The
graph of this equation is given in the
figure.
From this it's clear that there is a
root between 0
and 0.5 and also
another root between 1.5 and
2.0. Now let us consider the function f
(x) in the
interval [0, 0.5] where f (0) * f (0.5) is
less than
zero and use the regula-falsi scheme to
obtain the
zero of f (x) = 0.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aa5ac394-41dc-4021-829b-cb52b82ca626-150610192307-lva1-app6891/85/The-False-Position-Method-7-320.jpg)