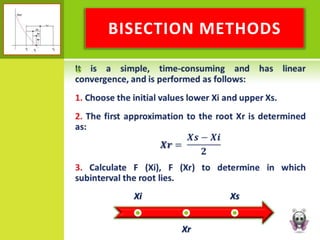
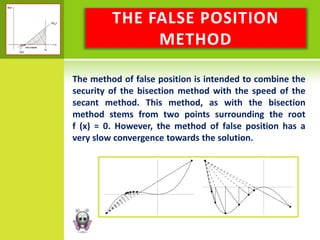
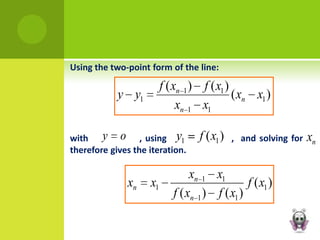
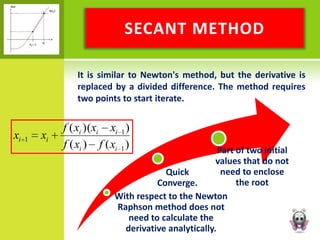
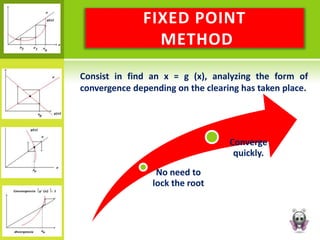
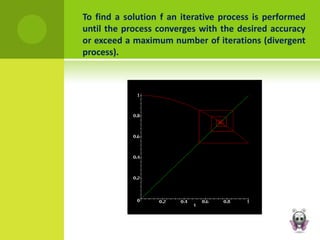
This document discusses various graphical and numerical methods for finding the roots or zeros of equations, including interval methods like bisection, the false position method, open methods like Newton-Raphson and secant methods, and fixed point methods. Interval methods use initial lower and upper bounds to repeatedly narrow the range containing the root. Open methods take initial values and generate successive approximations converging on the root through techniques like drawing tangents or divided differences. Fixed point methods analyze convergence based on the form of iteration used to find a solution.