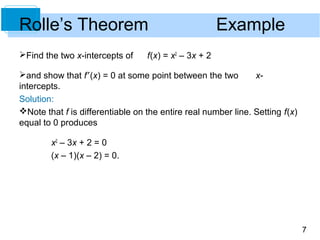
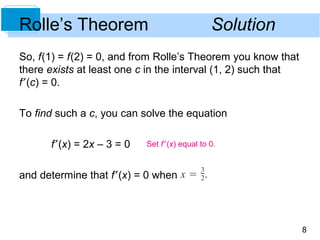
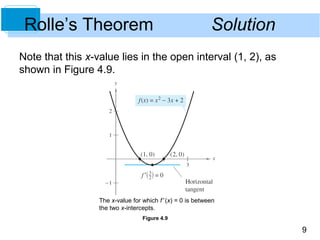
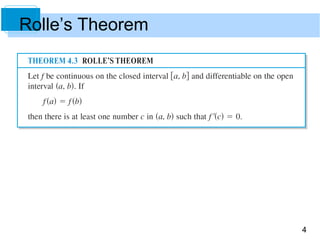
This document discusses Rolle's Theorem from calculus. Rolle's Theorem states that if a function f is continuous on a closed interval [a,b] and differentiable on the open interval (a,b), and if f(a) = f(b), then there exists at least one value c in the interval (a,b) where the derivative of f is equal to 0. The document provides an example of applying Rolle's Theorem to show that the derivative of the function f(x) = x^2 - 3x + 2 is equal to 0 at some point between the two x-intercepts of the function.


![3
Rolle’s Theorem
The Extreme Value Theorem states that a continuous
function on a closed interval [a, b] must have both a
minimum and a maximum on the interval.
Both of these values, however, can occur at the
endpoints. Rolle’s Theorem, named after the French
mathematician Michel Rolle’s, gives conditions that
guarantee the existence of an extreme value in the interior
of a closed interval.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rollstheorem-170418072516/85/Roll-s-theorem-3-320.jpg)
![5
Rolle’s Theorem
From Rolle’s Theorem, you can see that if a function f is
continuous on [a, b] and differentiable on (a, b), and if
f(a) = f(b), then there must be at least one x-value between
a and b at which the graph of f has a horizontal tangent, as
shown in Figure 4.8(a).
f is continuous on [a, b] and differentiable on (a, b).
Figure 4.8(a)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rollstheorem-170418072516/85/Roll-s-theorem-5-320.jpg)
![6
Rolle’s Theorem
If the differentiability requirement is dropped from Rolle’s
Theorem, f will still have a critical number in (a, b), but it
may not yield a horizontal tangent. Such a case is shown in
Figure 4.8(b).
f is continuous on [a,
b]. Figure 4.8(b)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rollstheorem-170418072516/85/Roll-s-theorem-6-320.jpg)