This document discusses numerical methods for solving nonlinear equations. It describes two types of methods - bracket/close methods which include bisection and false position, and open methods which include fixed point iteration and Newton-Raphson. For each method, it provides the algorithm, works through an example problem, and discusses advantages and disadvantages. The document was presented by three students at North Western University, Khulna on the topic of numerical methods for solving nonlinear equations.



![Algorithm of Bisection method
Bisection method Steps (Rule)
Step-1: Find points a and b such that a<b and f(a)⋅f(b)<0.
Step-2: Take the interval [a,b] and find mid value c=(a+b)/2Step-2: Take the interval [a,b] and find mid value c=(a+b)/2
Step-3: If f(c)=0 then c is an exact root and stop
the algorithm.
else if f(a)⋅f(c)<0 then the root lies between a and c, so update b=c and a=a.
else if f(a)⋅f(c)>0 then the root lies between c and b, so update a=c and b=b.
Step-4: Repeat steps 2 & 3 until f(xi)=0 or |f(xi)|≤Accuracy.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/numericalmethodforsolvingnon-linearequations-201007151011/85/Numerical-method-for-solving-non-linear-equations-4-320.jpg)
![The absolute relative approximate error:
Error = |[(new value of c – old value of c)/ new value of c]| *100%
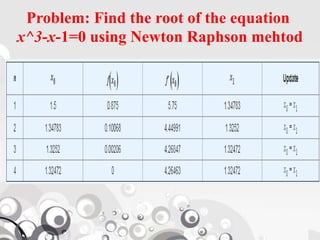
Problem: Find the root of f(x)=x^2-3 using bisection method
with interval [1,2].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/numericalmethodforsolvingnon-linearequations-201007151011/85/Numerical-method-for-solving-non-linear-equations-5-320.jpg)

![(b)False Position method
The poor convergence of the bisection
method motivate the use of better
techniques. One such method is
the Method of False Position.
Here, we start with an initial interval [a,
b], and we assume that the function
changes sign only once in this interval.changes sign only once in this interval.
Now we find 'c' in this interval, which is
given by the intersection of the x axis
and the straight line passing
through (a, f(a)) and (b, f(b)).
C =](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/numericalmethodforsolvingnon-linearequations-201007151011/85/Numerical-method-for-solving-non-linear-equations-7-320.jpg)
![Algorithm for False Position method
False Position method Steps (Rule)
Step-1:Find points a and b such that a<b and f(a)⋅f(b)<0.
Step-2: Take the interval [a, b] and find next valueStep-2: Take the interval [a, b] and find next value
c=[{a f(a)-b f(b)}/{f(b)-f(a)}]
Step-3: If f(c)=0 then c is an exact root, else if f(a)⋅f(c)<0 then update
b=c and a=a, else if f(a)⋅f(c)>0 then update a=c and b=b.
Step-4: Repeat steps 2 & 3 until f(xi)=0 or |f(xi)|≤Accuracy.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/numericalmethodforsolvingnon-linearequations-201007151011/85/Numerical-method-for-solving-non-linear-equations-8-320.jpg)
![The absolute relative approximate error
Error=|[(new value of c – old value of c)/ new value of c]|*100%
Problem: Find the root of f(x)=x^2-3 using False Position
method with interval [1,2].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/numericalmethodforsolvingnon-linearequations-201007151011/85/Numerical-method-for-solving-non-linear-equations-9-320.jpg)



![(b) Newton - Raphson method
Newton - Raphson method is a
widely-used classical method for
finding the solution to a
nonlinear univariate function
of f(x) on the interval [a,b]. It is
also referred to as the Newton-also referred to as the Newton-
Raphson method.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/numericalmethodforsolvingnon-linearequations-201007151011/85/Numerical-method-for-solving-non-linear-equations-14-320.jpg)
![Algorithm for Newton Raphson method
Newton Raphson method Steps (Rule)
Step-1:Find points a and b such that a<b and f(a)⋅f(b)<0.
Step-2:Take the interval [a,b] and find next value x0=(a+b)/2Step-2:Take the interval [a,b] and find next value x0=(a+b)/2
Step-3:Find f(x0) and f′(x0)
x1=x0-(f(x0)/f′(x0))
Step-4:If f(x1)=0 then x1 is an exact root, else x0=x1
Step-5:Repeat steps 2 to 4 until f(xi)=0 or |f(xi)|≤Accuracy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/numericalmethodforsolvingnon-linearequations-201007151011/85/Numerical-method-for-solving-non-linear-equations-15-320.jpg)