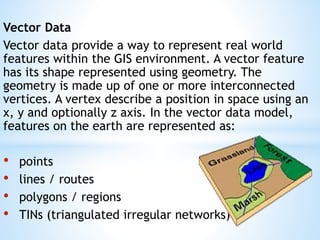
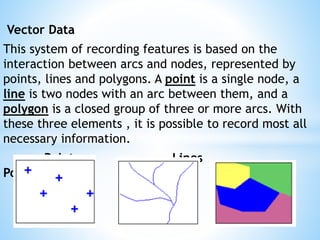
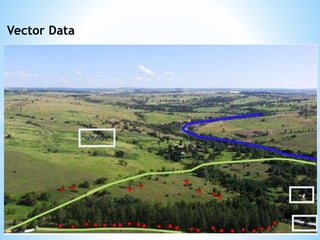
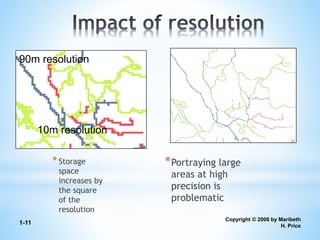
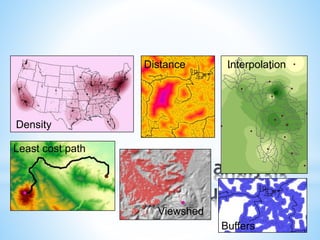
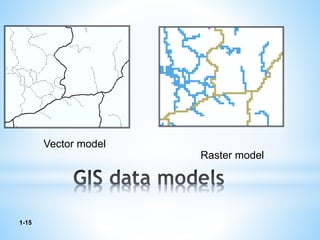
This document discusses two types of spatial data used in GIS - vector data and raster data. Vector data represents geographic features as points, lines, and polygons using vertices with x, y, and z coordinates. It allows for accurate representation of shapes and storing of attribute data but requires more processing and storage. Raster data represents geographic information through a grid of cells (pixels), with each cell storing attribute values like elevation or temperature. It is better for continuously changing data but cannot represent linear features well and has increased storage needs at higher resolutions. Both data types have advantages and disadvantages depending on the use case.