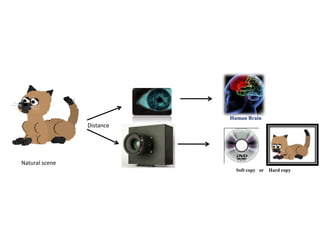
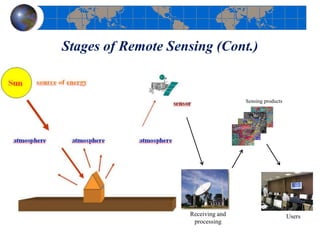
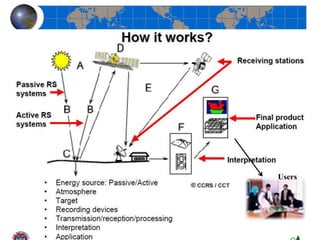
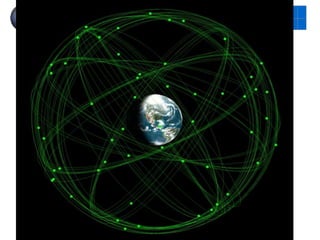
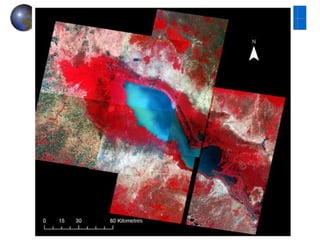
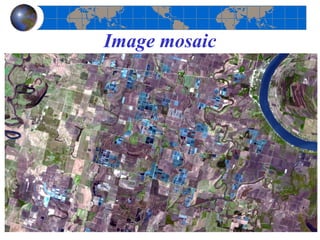
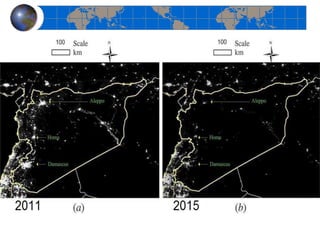
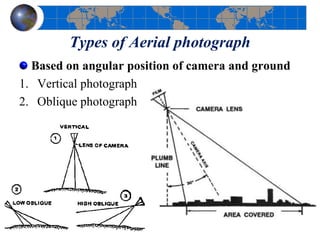
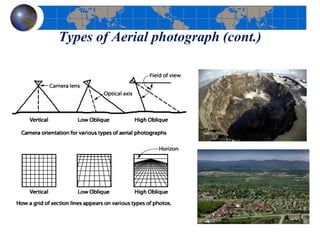
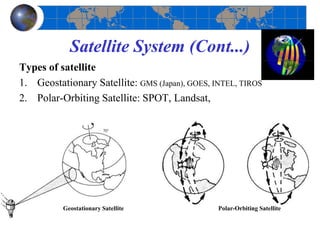
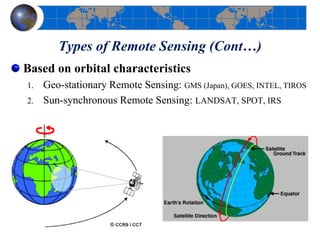
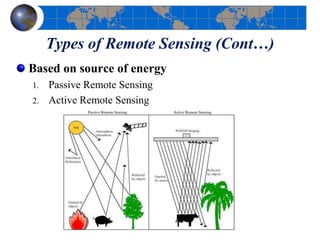
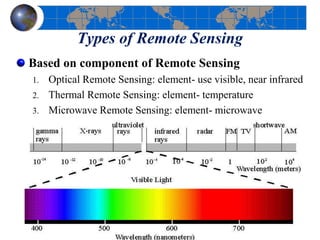
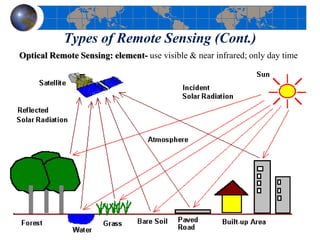
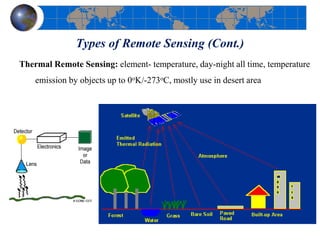
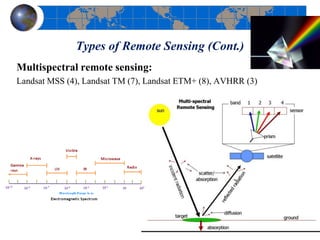
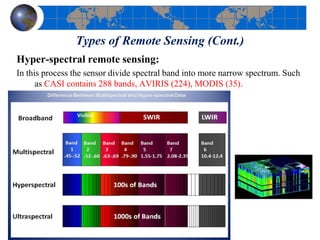
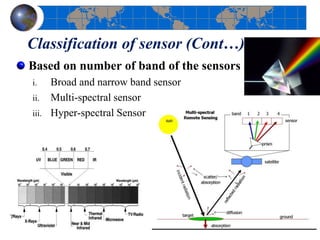
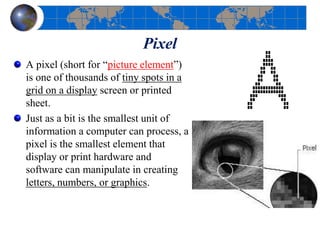
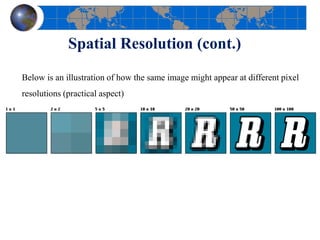
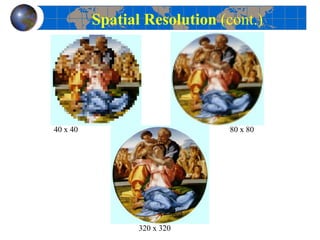
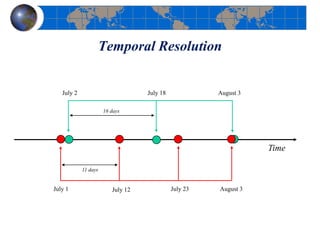
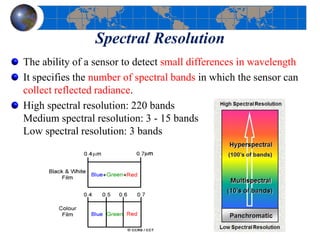
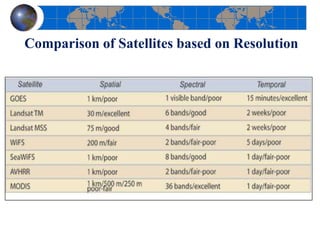
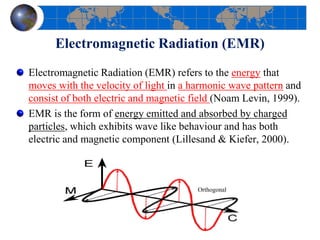
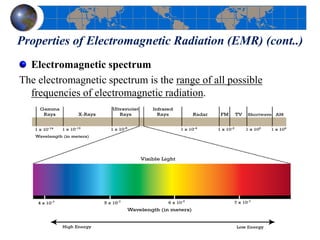
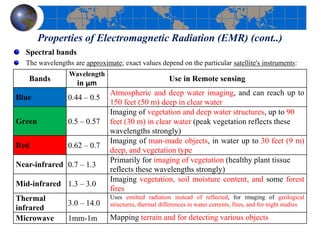
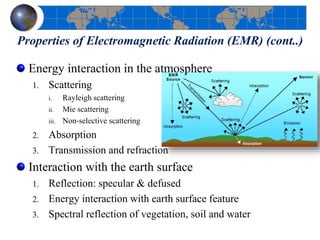
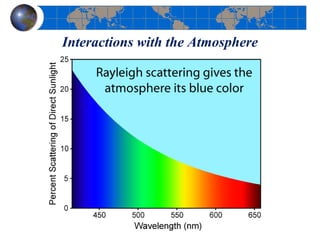
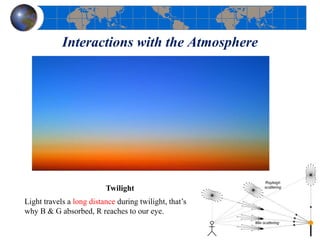
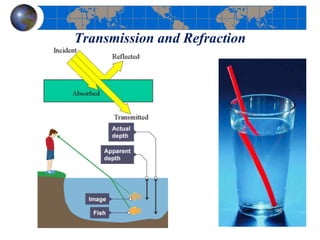
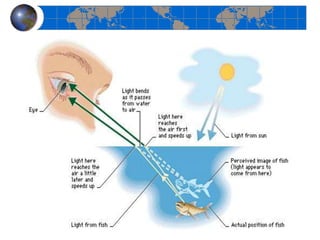
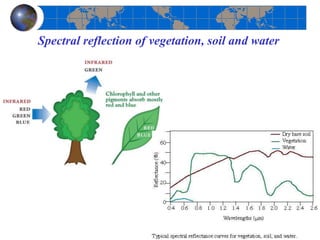
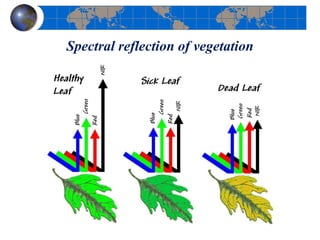
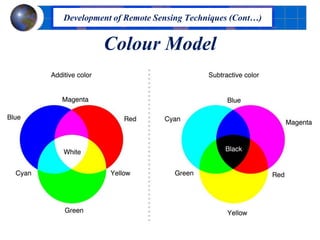
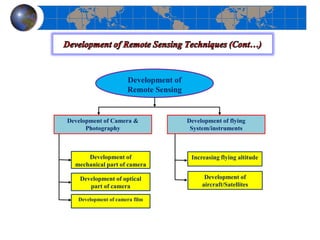
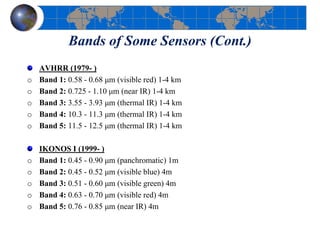
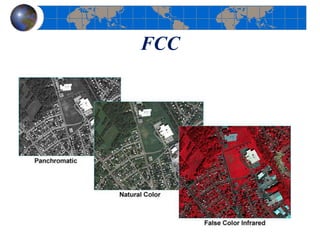
This document provides an introduction to satellite remote sensing. It discusses key topics such as the definition of remote sensing, the stages of remote sensing including energy sources, sensors, and data interpretation. It also covers different types of remote sensing based on platform, orbital characteristics, energy sources, components, and spectral characteristics. Different sensors, image resolution, electromagnetic radiation properties, and interactions with the atmosphere and earth surface are described. The history and development of remote sensing techniques are briefly mentioned. In summary, the document provides a comprehensive overview of the fundamental concepts and components of remote sensing from multiple perspectives.