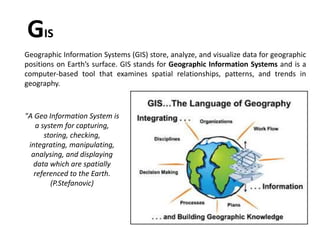
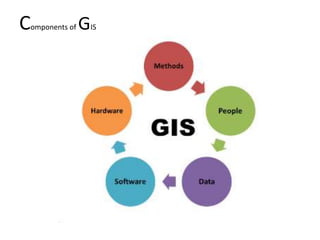
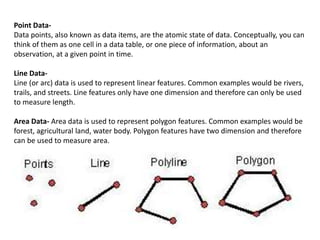
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) store, analyze, and visualize spatial data referenced to Earth's surface. GIS integrates hardware, software, data, and personnel to capture, store, update, manipulate, analyze and display geographic information efficiently. Key components include GIS software that provides tools to work with spatial data stored in a database, as well as spatial data like vectors and rasters, and associated attribute data. GIS relies on both technical specialists to design and maintain the system and end users to apply it to problems.