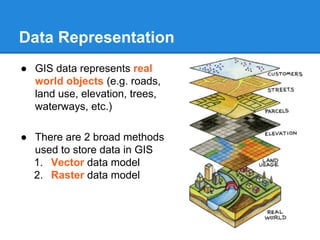
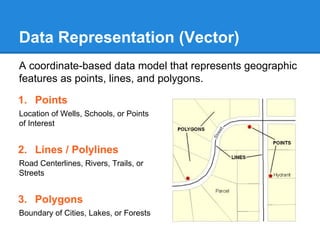
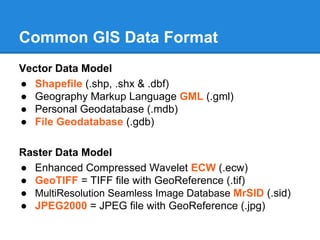
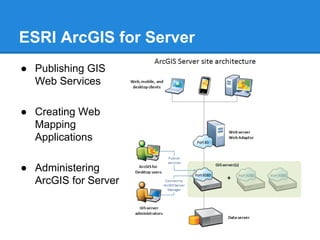
GIS is a system for managing and analyzing geographic data. It uses two main data models: vector, representing points, lines and polygons; and raster, representing data as a grid of cells. Common file formats include shapefiles for vector data and GeoTIFF and MrSID for raster. GIS data is referenced using coordinate systems like WGS84 for global latitude/longitude or HK80Grid for Hong Kong. ESRI's ArcGIS software allows viewing, editing, and publishing this geospatial data for mapping and analysis.