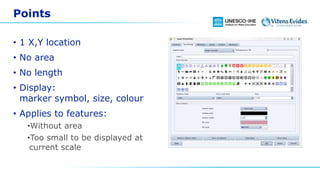
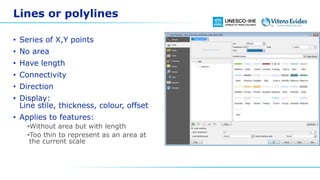
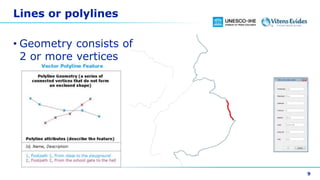
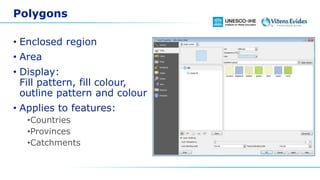
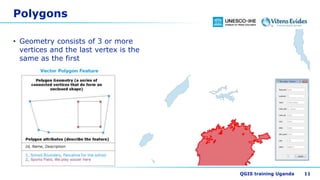
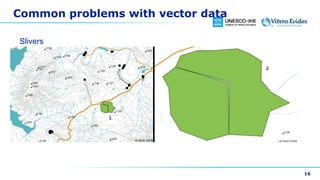
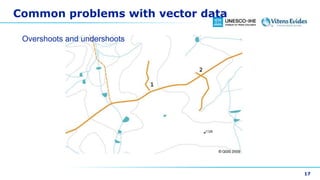
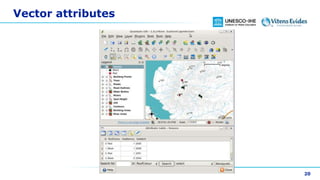
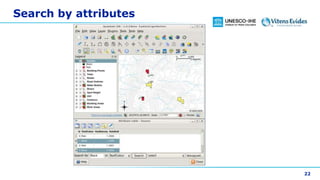
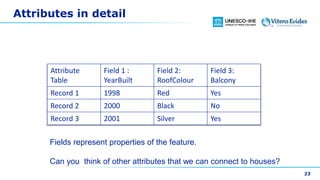
This document discusses vector data in GIS. It begins by defining vector data as representing real-world features using points, lines, and polygons. It then describes the three vector types - points as single X,Y coordinates with no area or length, lines/polylines as a series of points with length but no area, and polygons as enclosed areas formed by connecting three or more points. The document provides examples of each vector type and how they can represent different landscape features. It also discusses attributes associated with vector data, common problems like slivers and overshoots/undershoots, and how vector data can be queried and symbolized based on attributes.