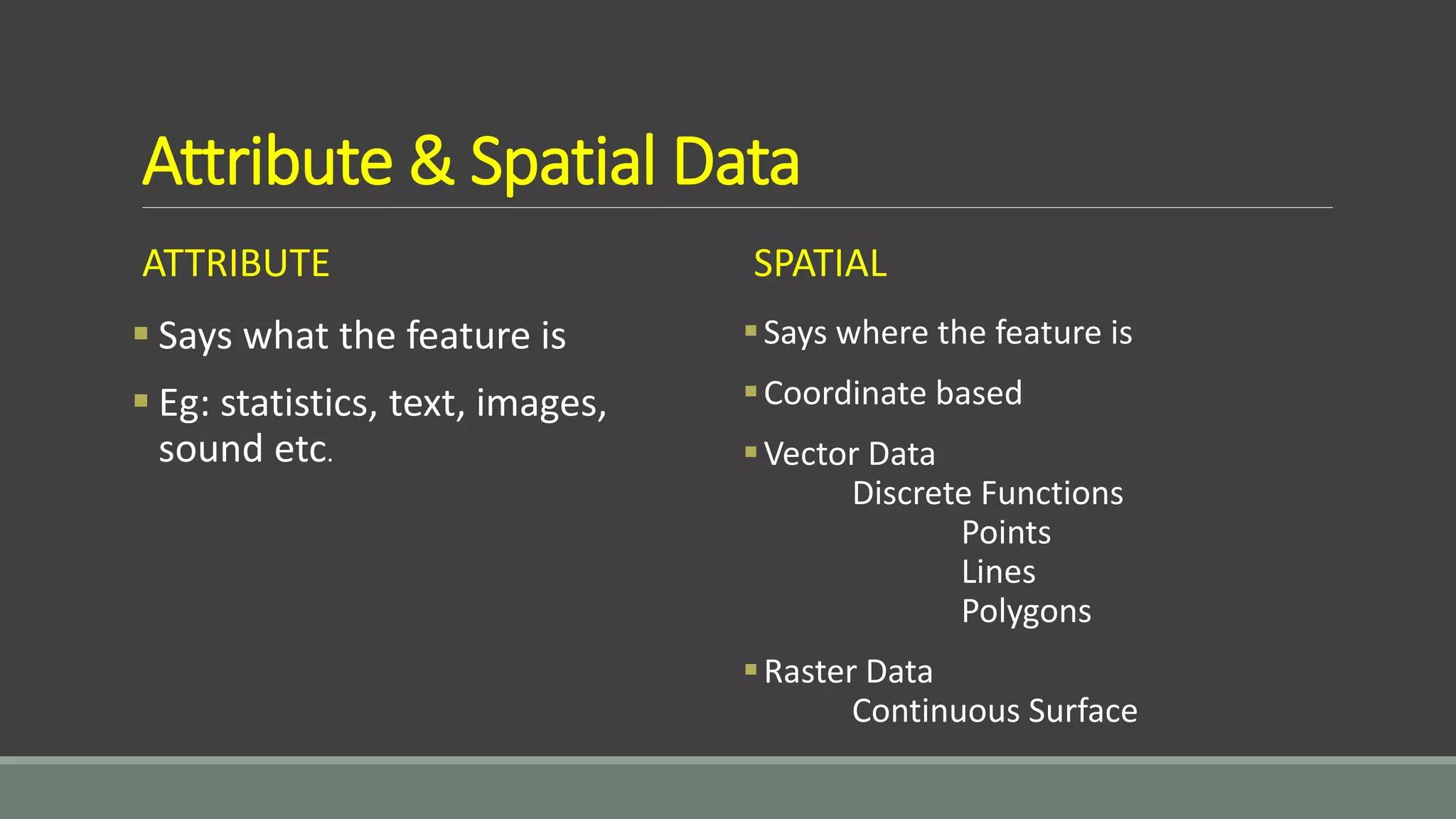
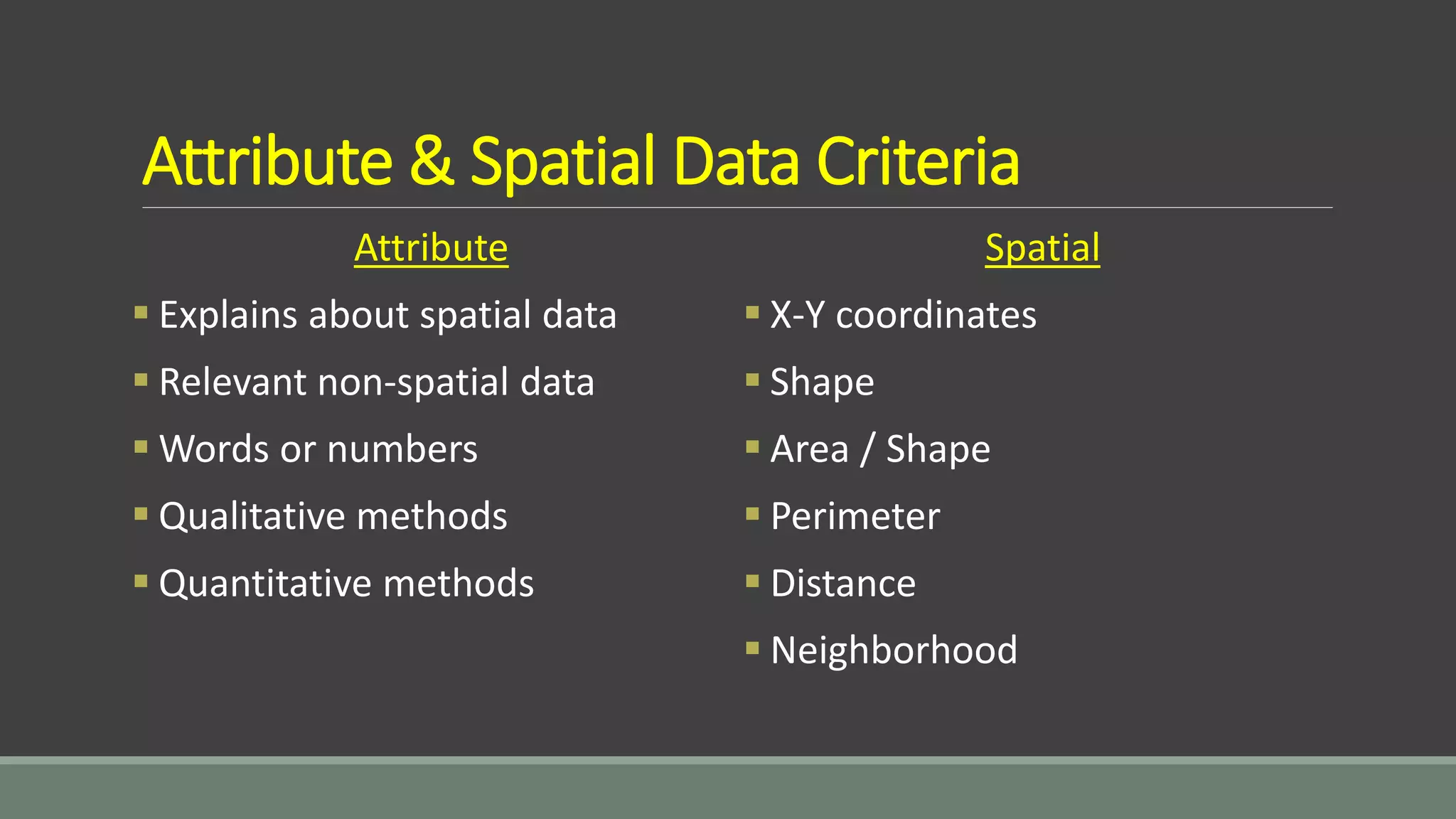
This document discusses key concepts related to data in GIS systems. It describes the different types of spatial and attribute data as well as vector and raster data formats. It explains how data is organized into layers and how those layers can be queried and overlaid to integrate information from different sources and analyze spatial patterns in the data.