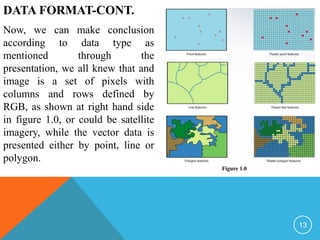
The document provides an overview of types of geographic data within Geographic Information Systems (GIS), focusing on data modeling and distinguishing between vector and raster data models. It details various data formats, such as shape-files, coverages, geodatabases, and grids, along with their characteristics and usage. Additionally, it discusses the sources of GIS data and the advantages and disadvantages of different data types.