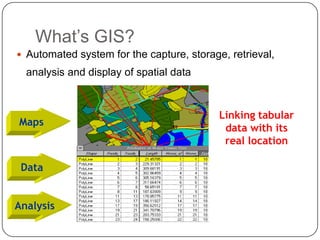
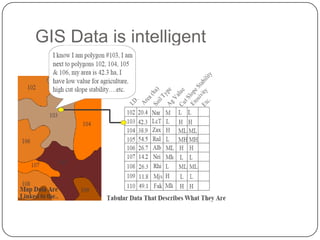
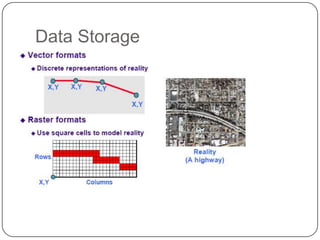
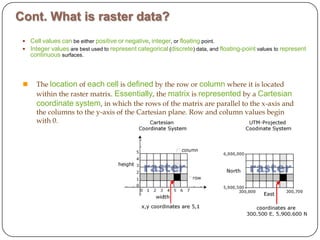
This document provides an overview of GIS, raster data formats, and spatial analysis tools. It defines GIS as an automated system for capturing, storing, analyzing and displaying spatial data linked to tabular data on maps. Raster data represents real-world phenomena through a matrix of cells, with each cell storing a value like elevation or satellite imagery. Spatial analysis tools in GIS like Euclidean distance and point density perform cell-based raster analyses, calculating distances from raster cells to points or densities of points within neighborhoods.