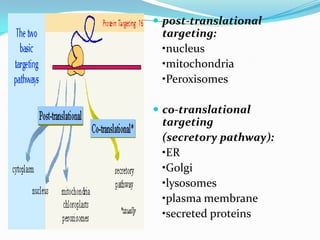
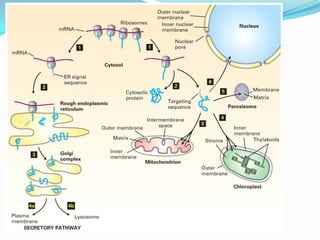
Protein targeting involves transporting proteins to their proper destinations after synthesis so they can perform their functions. There are two main pathways: co-translational targeting transports proteins during translation to the ER, Golgi and secretory pathway, while post-translational targeting transports proteins after translation to the nucleus, mitochondria and peroxisomes. Targeting sequences on the protein interact with receptors to mediate transport through membrane channels using energy from GTP or ATP hydrolysis. Defects in protein targeting can cause diseases like Zellweger syndrome, primary hyperoxaluria and cystic fibrosis.