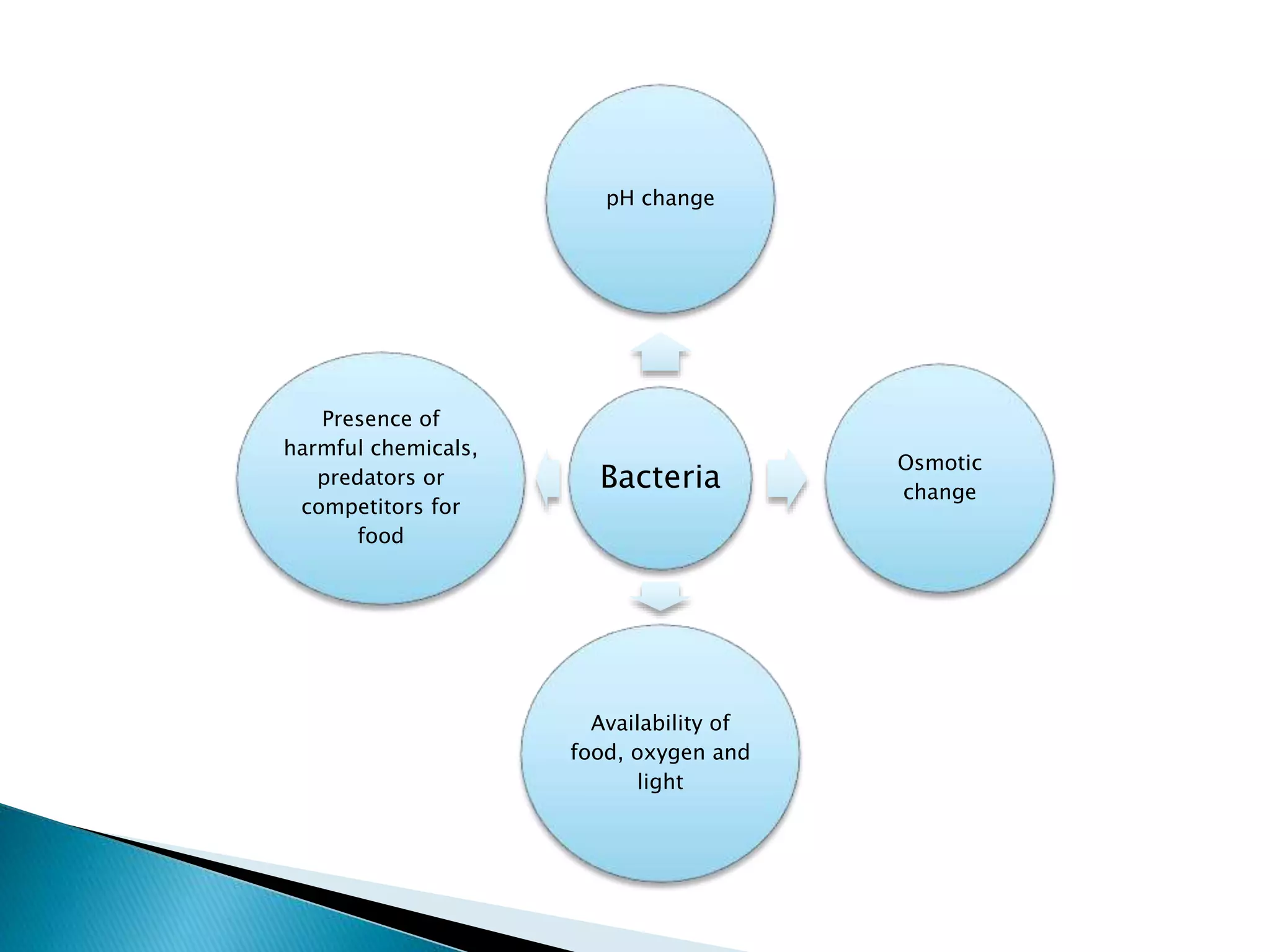
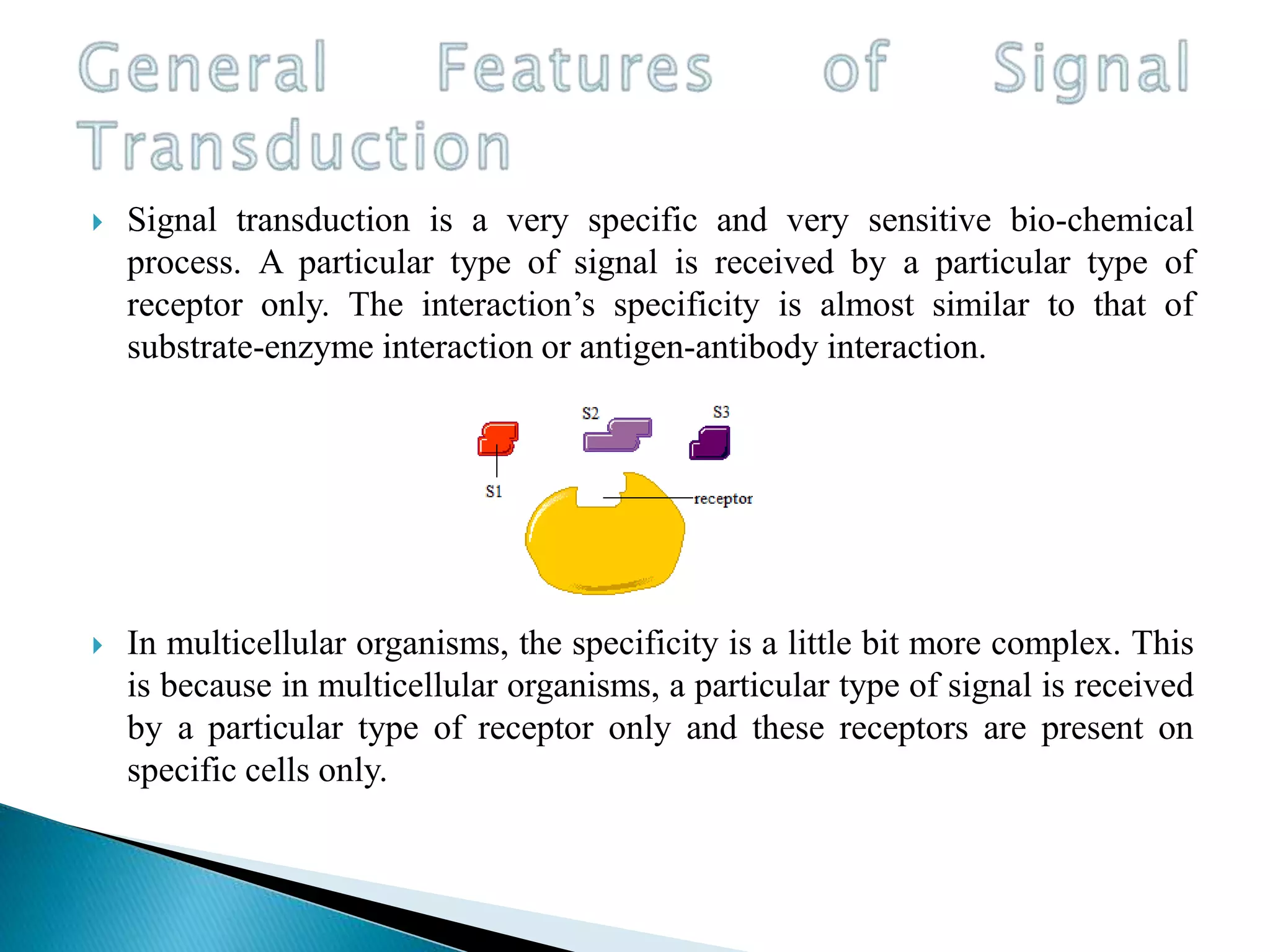
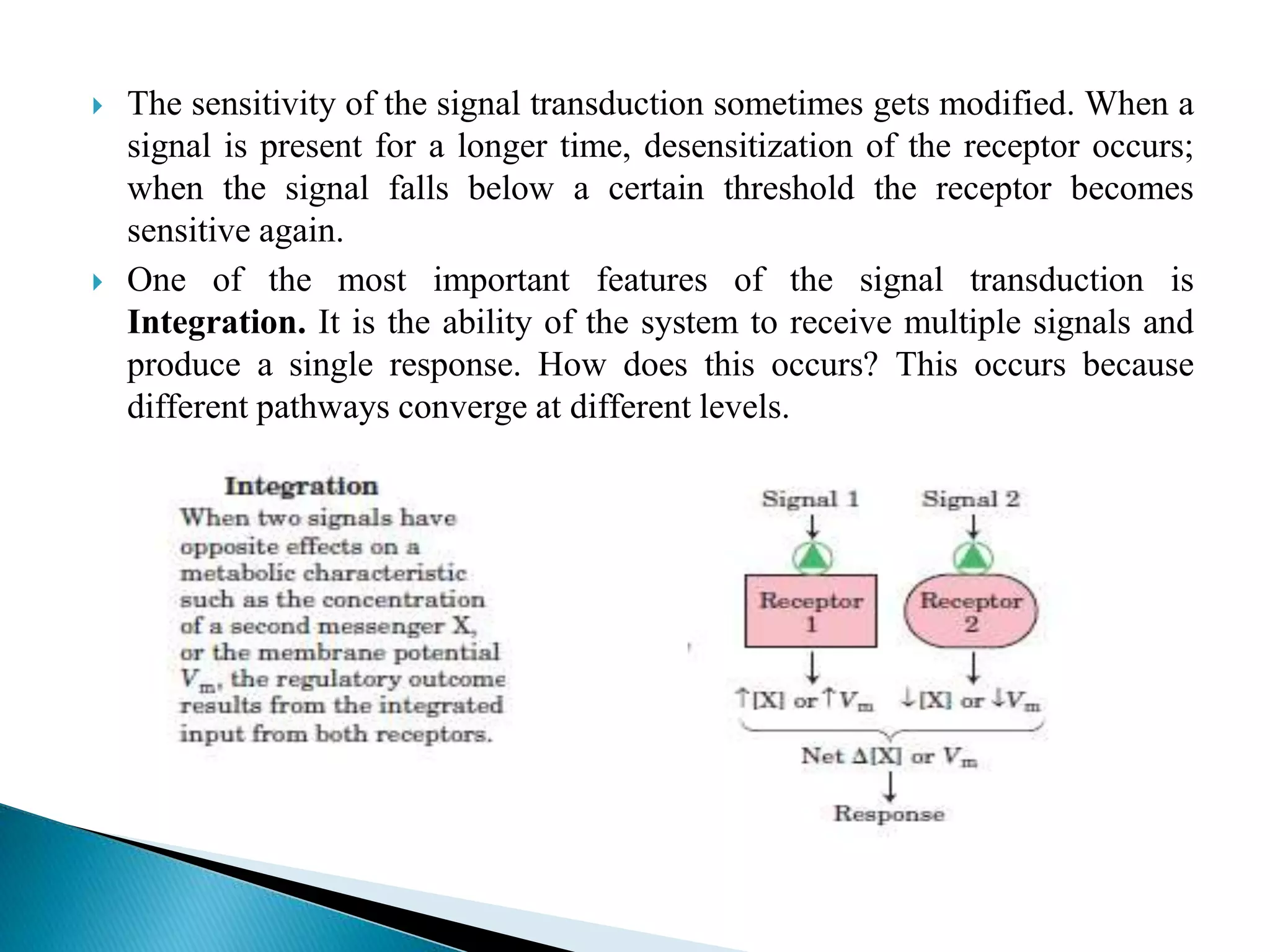
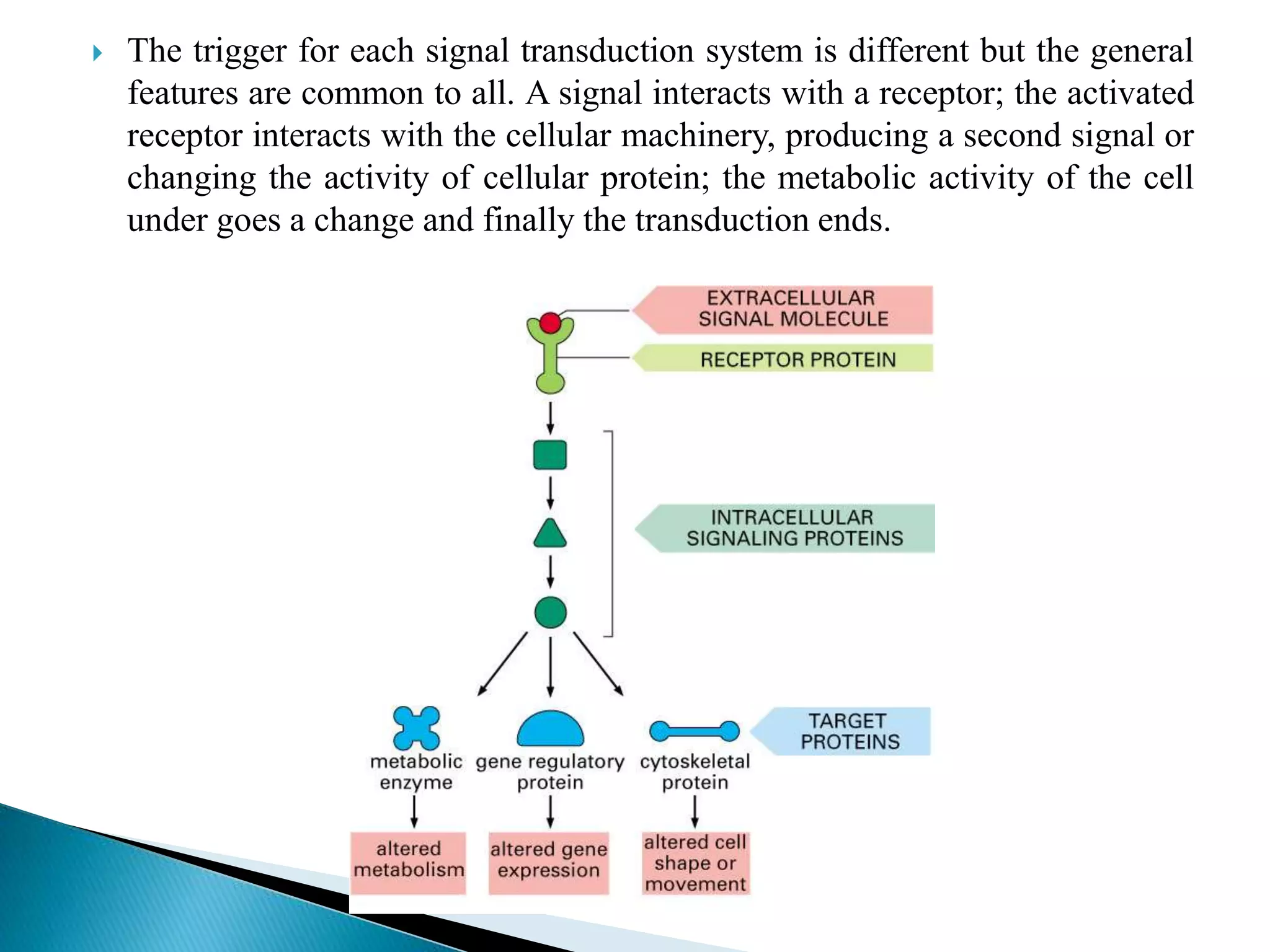
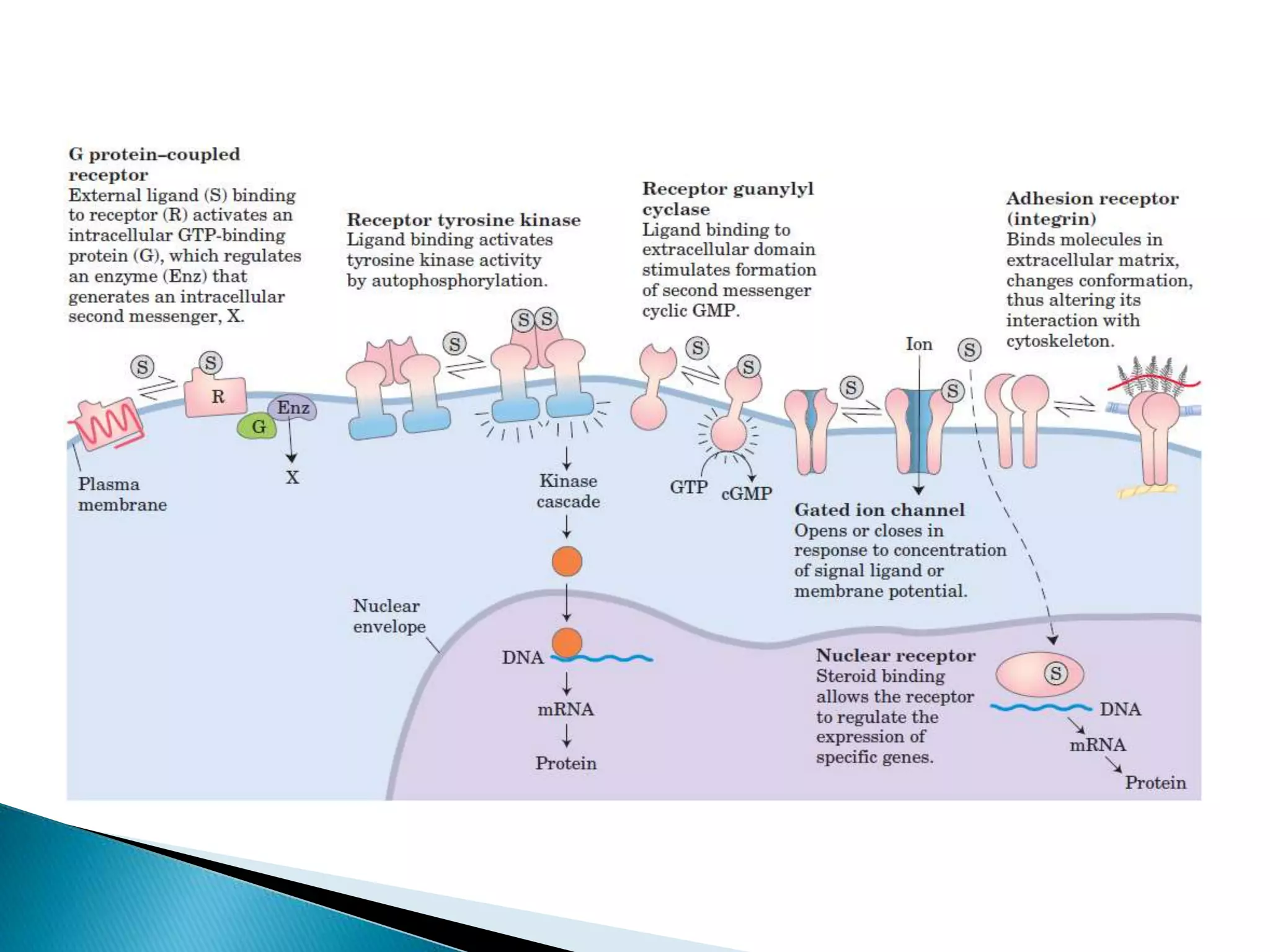
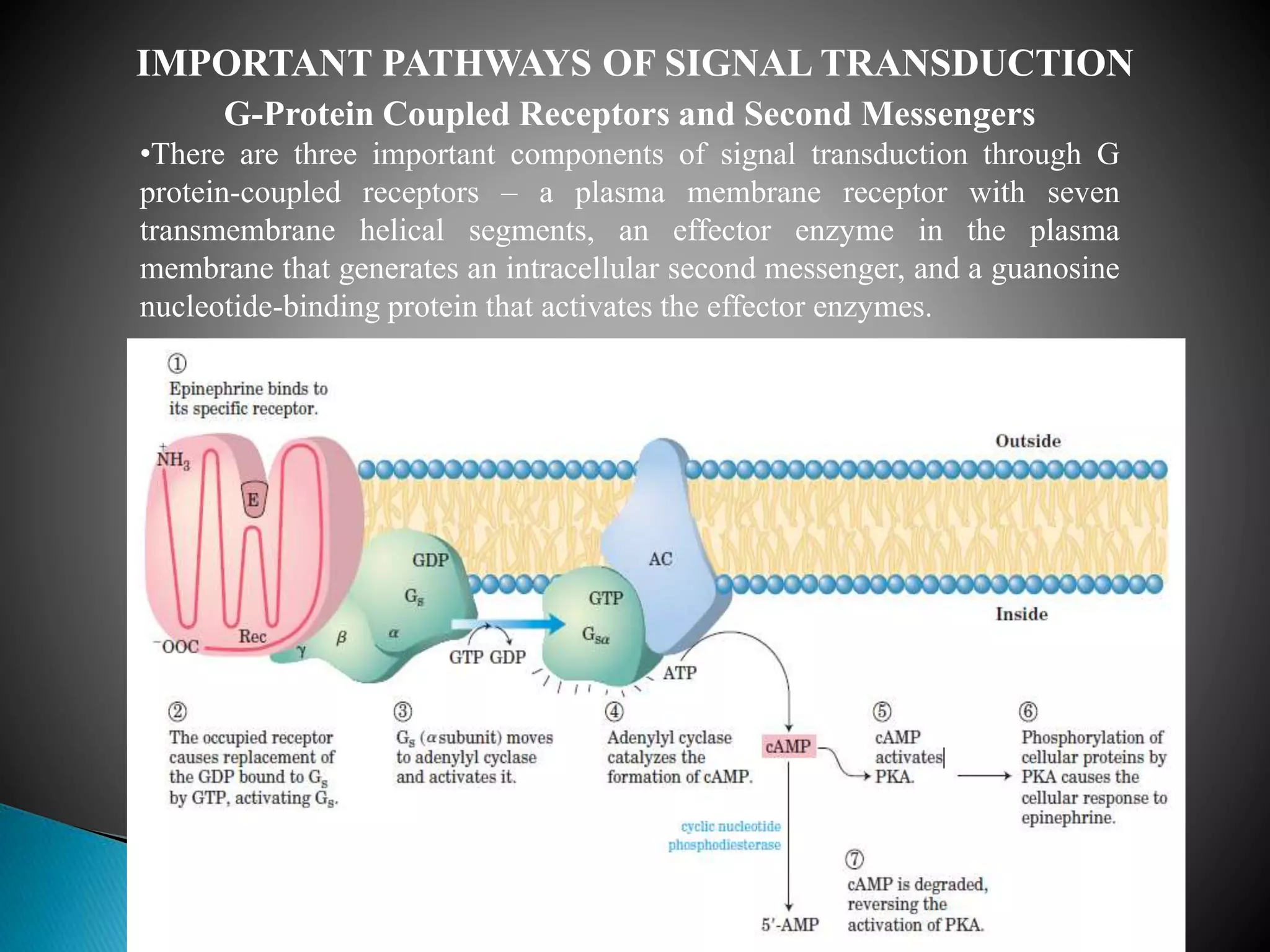
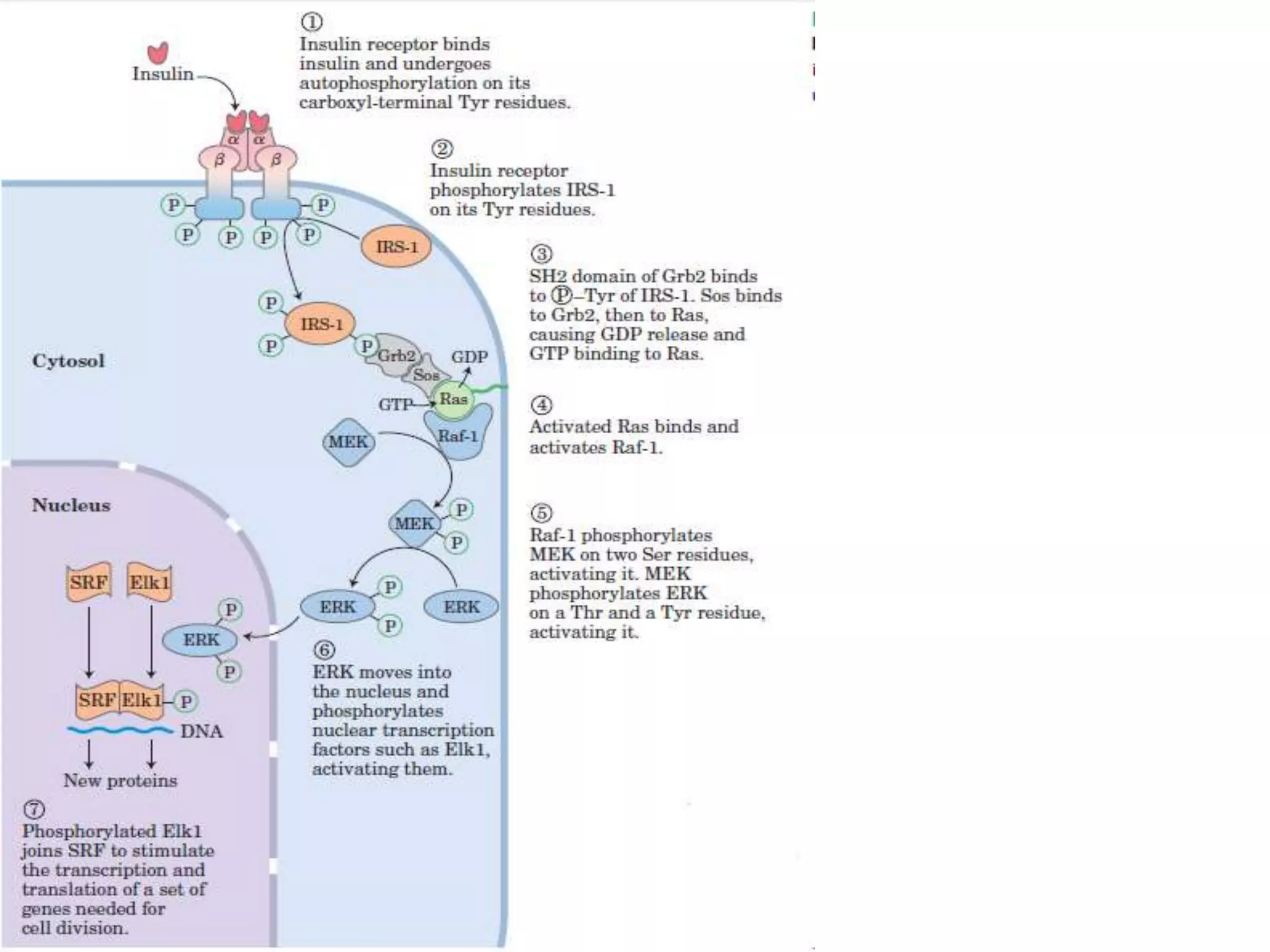
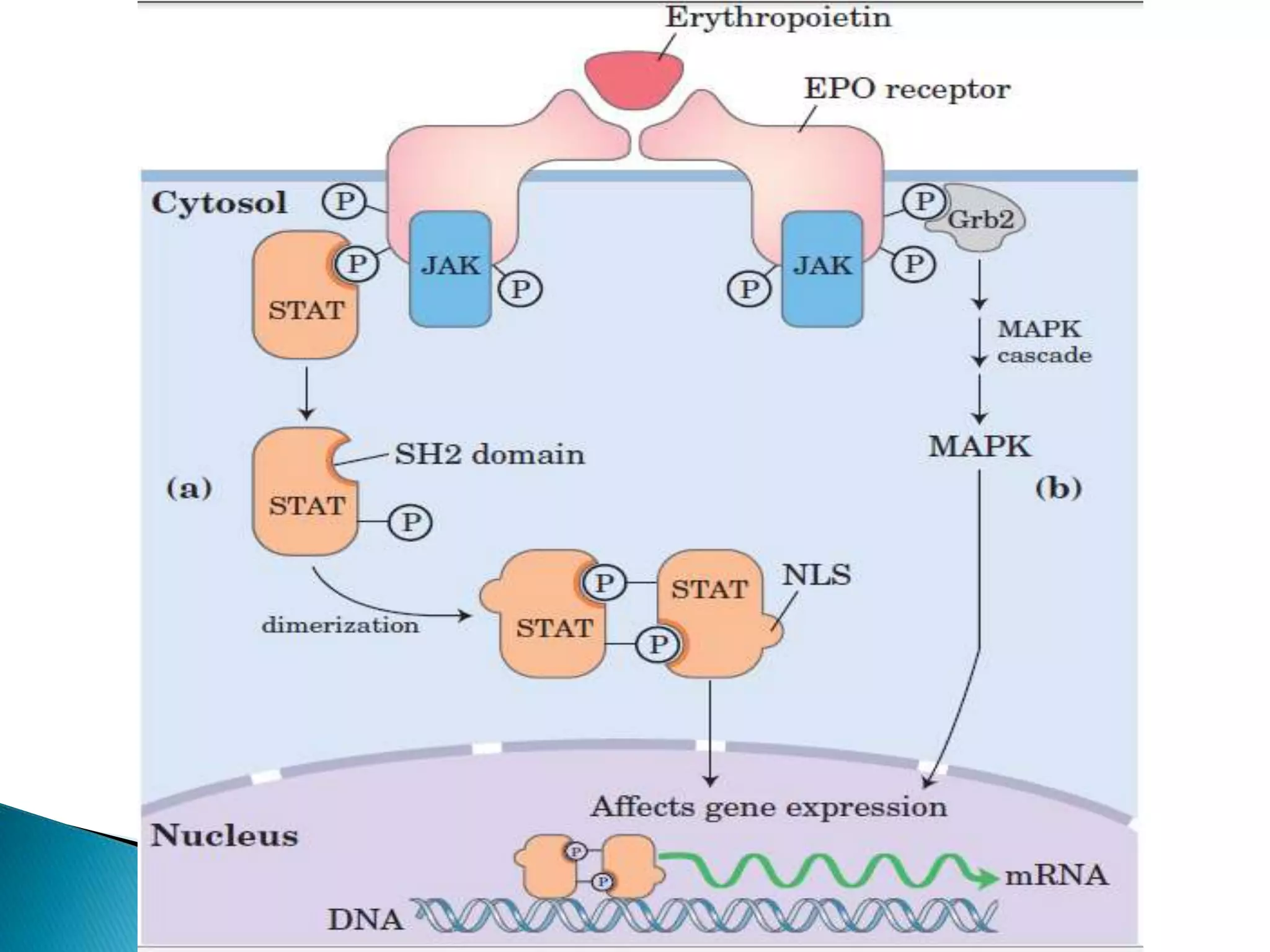
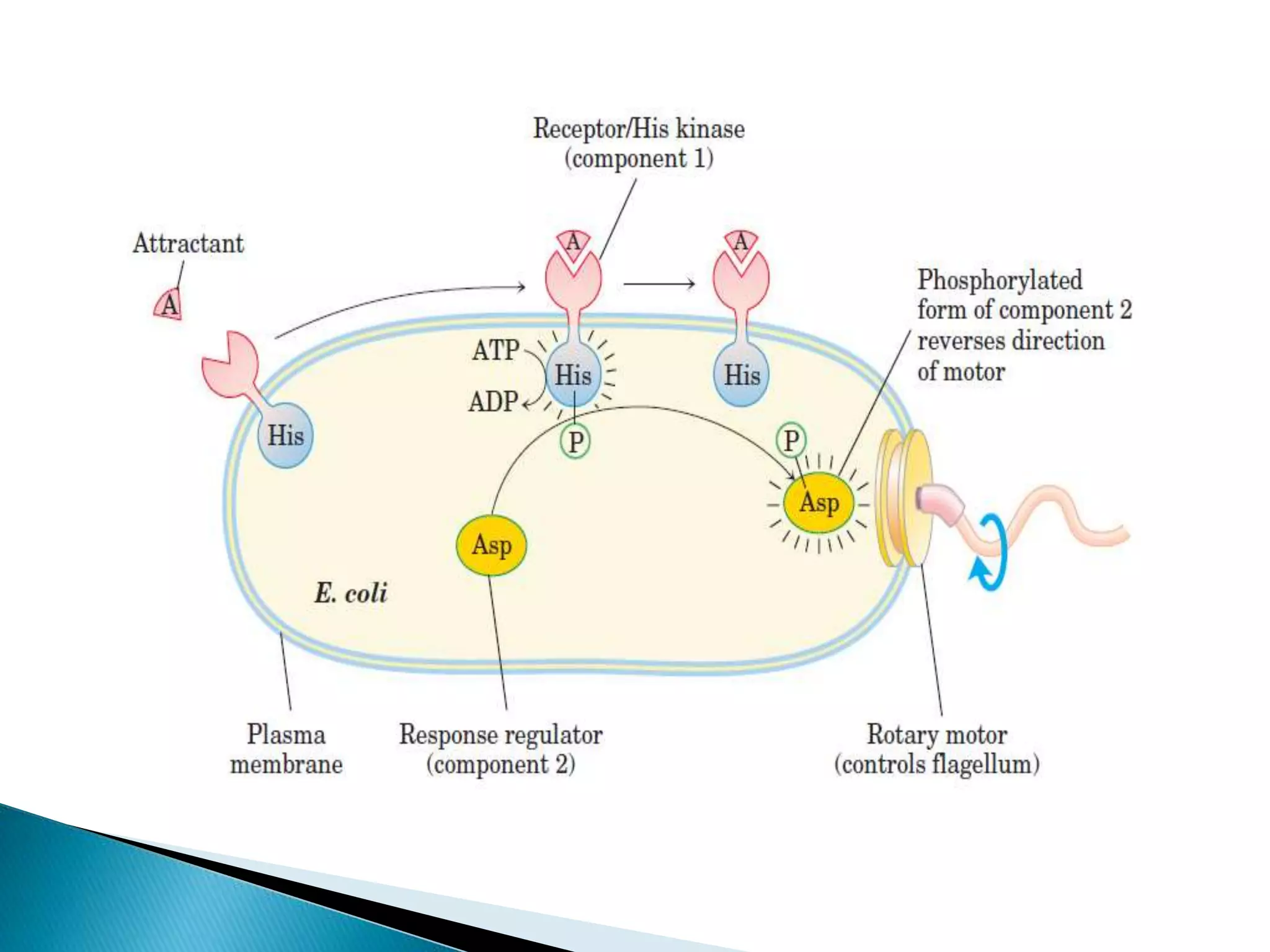
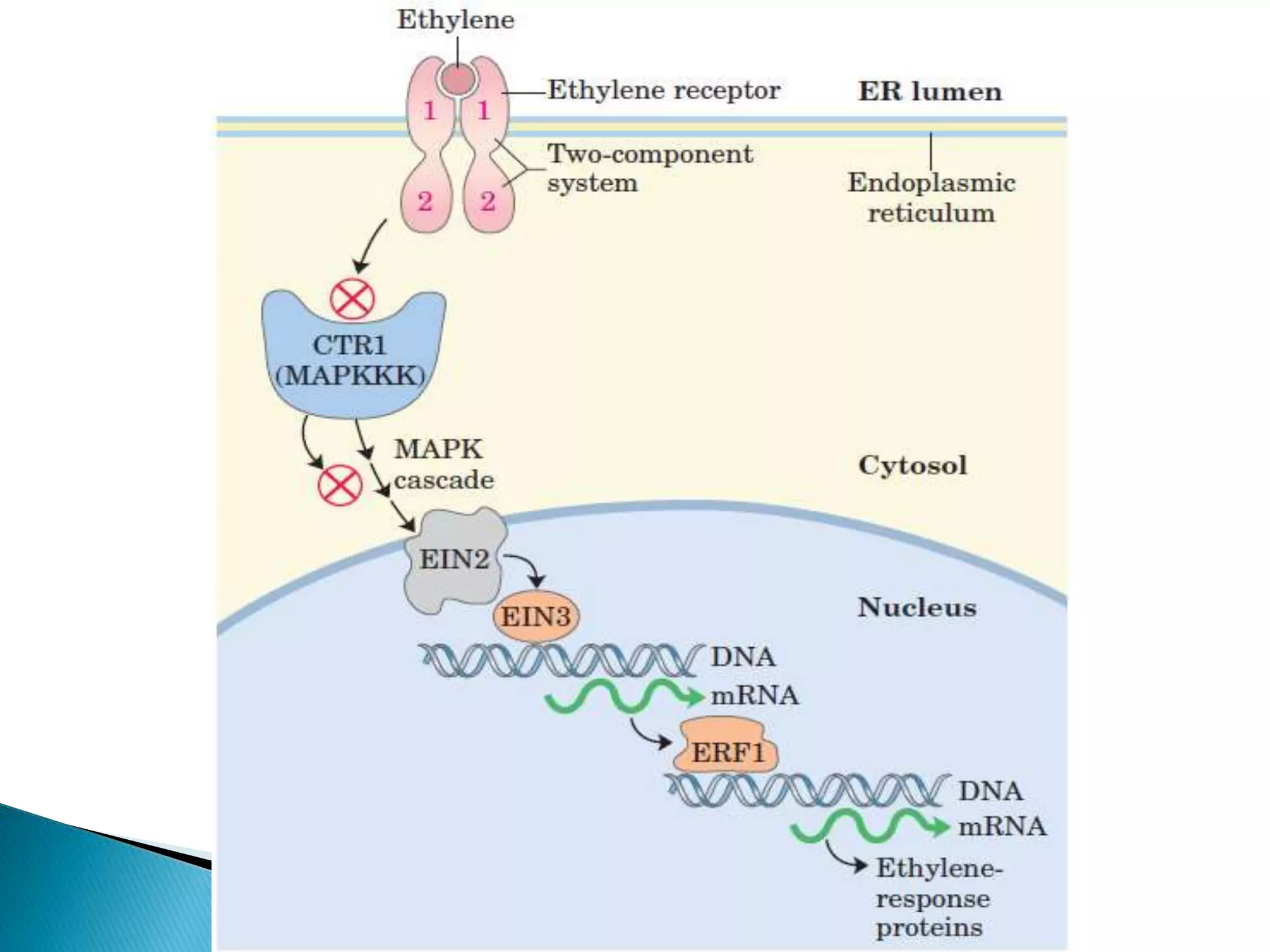
This document discusses signal transduction in cells. It explains that membrane proteins in bacterial cells detect environmental changes and generate signals to trigger responses. In multicellular organisms, cells exchange various signals, such as plant cells responding to growth hormones and sunlight. The document then provides details on the specific and sensitive nature of signal transduction pathways, including different types of receptors and some important signal transduction pathways like G protein-coupled receptors and receptor tyrosine kinases. It also discusses two-component regulatory systems in bacteria and plants.