1. Chromatin remodeling is the process by which chromatin structure is dynamically modified to allow access of DNA for processes like transcription.
2. There are two main types of chromatin remodeling - covalent histone modification and ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling complexes.
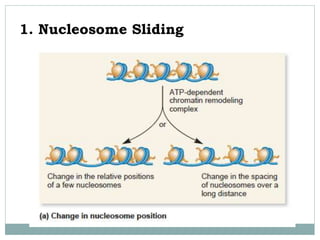
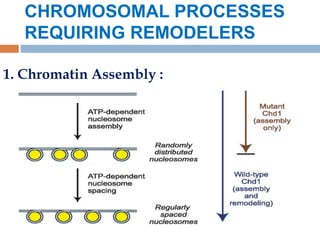
3. ATP-dependent complexes use energy from ATP hydrolysis to move, eject, or restructure nucleosomes, allowing access to DNA.
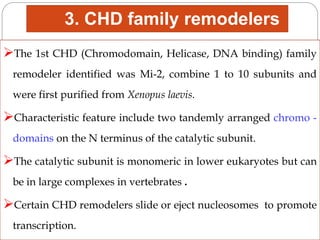
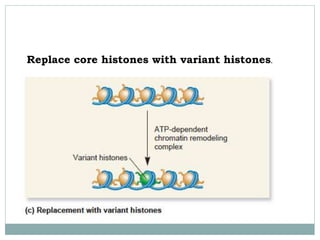
4. Examples of chromatin remodeling complexes include SWI/SNF, ISWI, CHD, and INO80 families, which have different activities like nucleosome sliding or histone variant exchange.