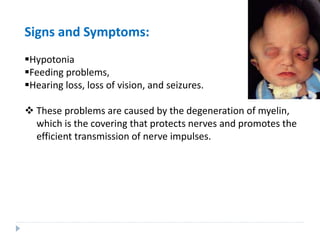
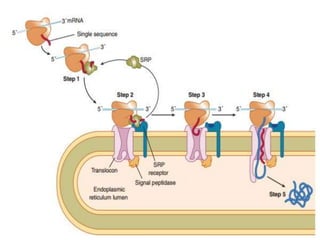
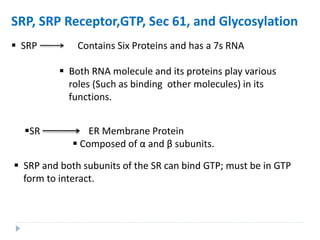
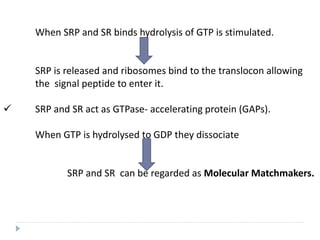
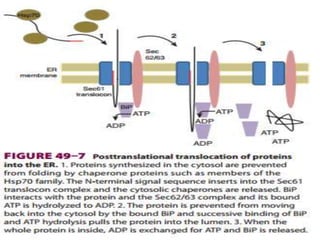
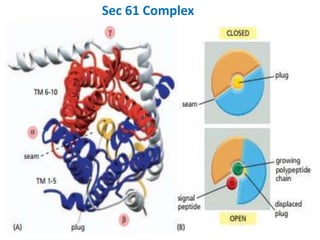
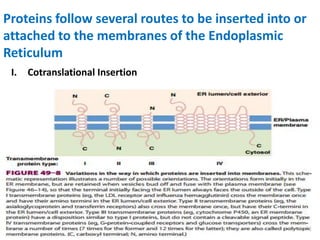
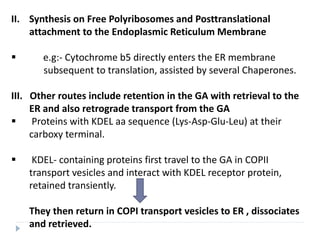
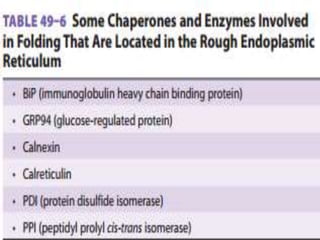
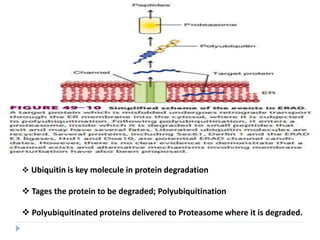
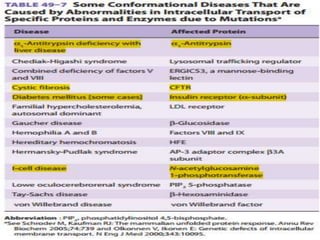
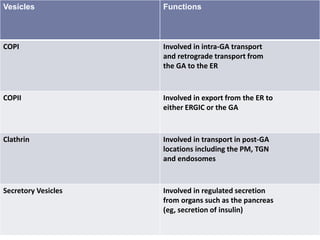
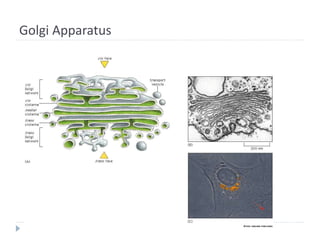
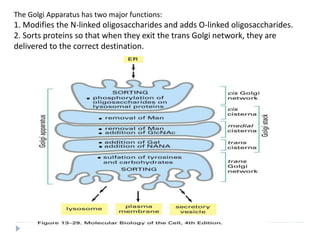
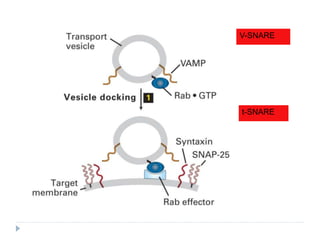
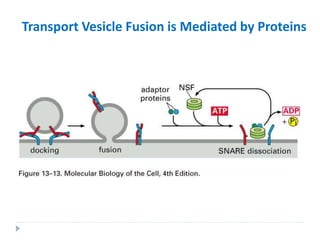
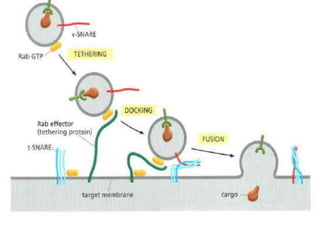
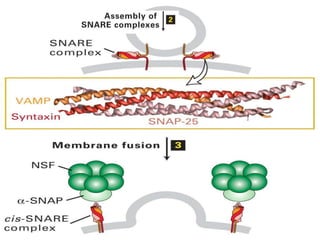
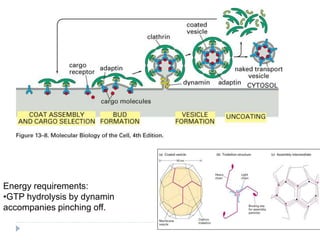
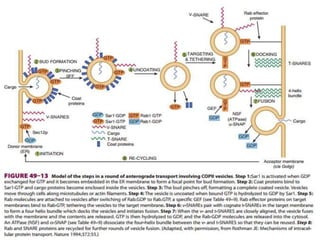
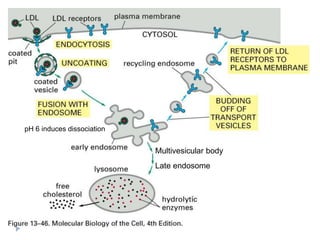
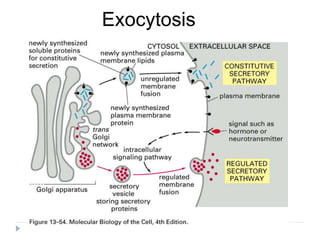
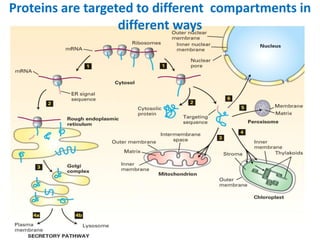
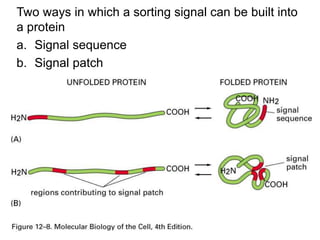
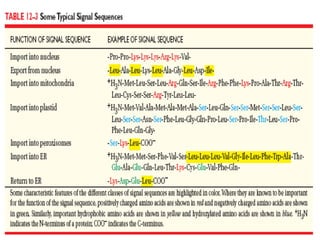
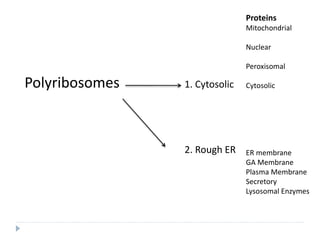
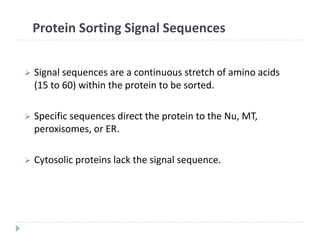
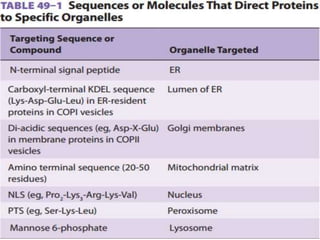
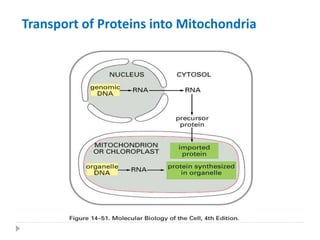
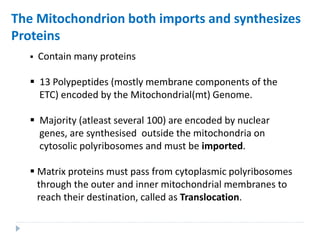
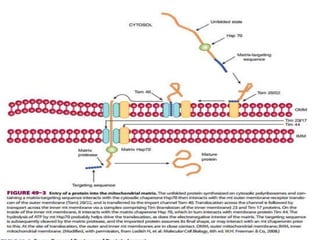
This document discusses intracellular protein trafficking and sorting. It describes how proteins contain signal sequences that target them to different organelles like the endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, peroxisomes and nucleus. It explains the roles of the signal recognition particle, translocon complex and chaperones in transporting proteins into the ER. The Ran GTPase system and importins/exportins are also summarized in their role in nuclear transport. Clinical implications of defects in peroxisome biogenesis are mentioned.

![Protein Transport Mechanisms
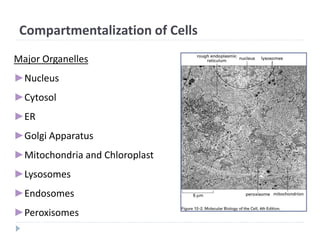
1. Transport through pores (Nucleus).
2. Transport across membranes
(Chloroplast and Mitochondria[MT]).
3. Transport by vesicles (ER and Golgi).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intracellulartraffickingandproteinsorting-200130090258/85/Intracellular-trafficking-and-protein-sorting-7-320.jpg)



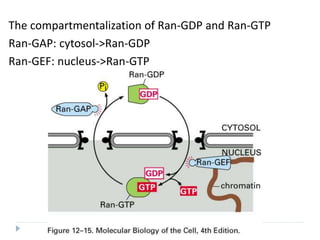
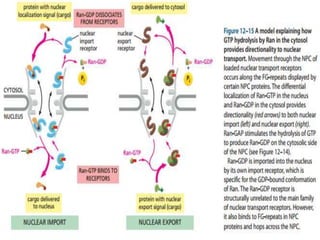
![ Depending on NLS content, a cargo molecule interacts with
one of a family of soluble proteins called IMPORTINS.
Complex docks transiently at the NPC.
Ran Plays a key critical regulatory role in the interaction
of the complex with the NPC and its translocation
through the NPC.
Ran proteins Small monomeric nuclear GTPases
Exist in either GTP bound or GDP bound
states.
Regulated by Guanine Nucleotide Exchange
Factors(GEFs), located in Nucleus and Ran
GTPase accelerating proteins (GAPs)
[Cytosolic].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intracellulartraffickingandproteinsorting-200130090258/85/Intracellular-trafficking-and-protein-sorting-25-320.jpg)
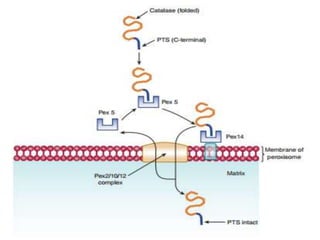
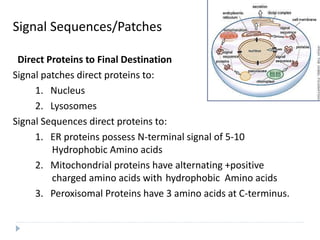
![Import of Proteins into Peroxisomes
Carry Unique targeting sequences.
Peroxisome Important organelle involved in aspects of the metabolism
of molecules ( FA, Cholesterol, Bile Acids, Plasmalogens,
Purines, Amino Acids).
Bound by a single membrane and contains more than 50
Enzymes : Catalase and Urate Oxidase Marker
Enzymes for Peroxisome.
Two Peroxisomal-matrix targeting sequences (PTSs) have been discovered.
I. PTS1 = Tripeptide; (Ser-Lys-Leu) [SKL] located at the Carboxy
terminal of the matrix proteins including Catalase.
Form complex with Pex5 (Cytosolic receptor).
II. PTS II = at the N-Terminus; has been found in atleast four matrix
proteins (e.g: Thiolase).
These two sequences are not cleaved after entry into the matrix.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intracellulartraffickingandproteinsorting-200130090258/85/Intracellular-trafficking-and-protein-sorting-29-320.jpg)