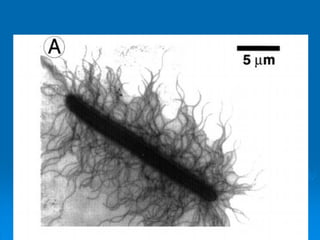
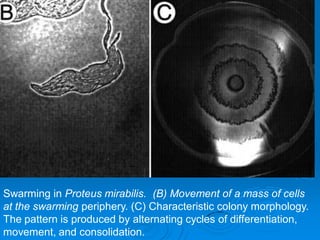
Proteus are Gram-negative, motile bacilli that are commonly found in the environment and intestines. The two main species are P. mirabilis and P. vulgaris. They are characterized by swarming growth on agar plates and being positive for urease, motility, and H2S production. Proteus can cause opportunistic infections like UTIs and wound infections. Identification involves culture, biochemical tests, and Dienes phenomenon for differentiation of species. Antibiotics effective against Proteus include cephalosporins and aminoglycosides.