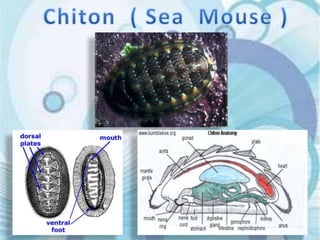
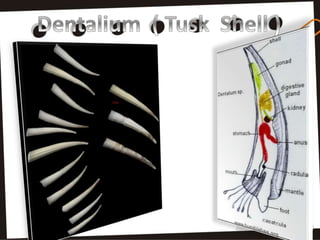
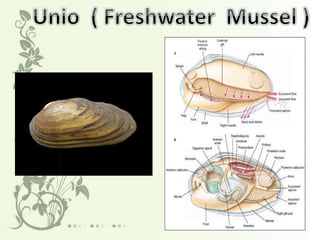
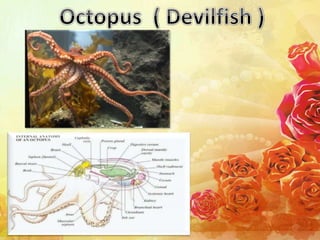
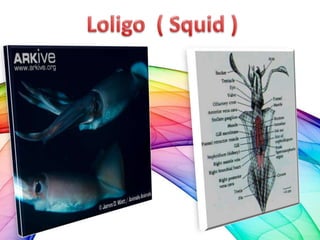
This document summarizes the characteristics of the phylum Mollusca. It describes their soft unsegmented bodies, bilaterally symmetrical structure, and hard calcareous shells. It divides the body into a head, mantle, visceral mass, and foot. It provides details on their digestive, respiratory, circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems. It lists the six major mollusc classes and provides one example for each: Monoplacophora, Amphineura, Scaphopoda, Gastropoda, Pelecypoda/Bivalvia, and Cephalopoda.



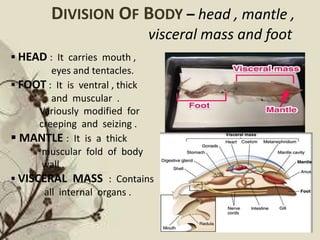
![GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS [visceral mass ]
DIGESTIVE ORGANS :
Alimentary canal is
well developed and coiled .
RESPIRATION :
Respiration by gills
enclosed in mantle cavity .
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM :
It is of lacunar type
with dorsal heart & few
blood vessels .
EXCRETORY ORGANS :
One or two pairs of kidney .
NERVOUS SYSTEM :
Comprises of paired cerebral ,
plural , pedal and visceral ganglia .
REPRODUCTION :
Sexes are usually separate
but may be united .
Gonads are usually unpaired .
Fertilisation can be either
external or internal .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/umaseminar-160509140210/85/Phylum-Mollusca-5-320.jpg)