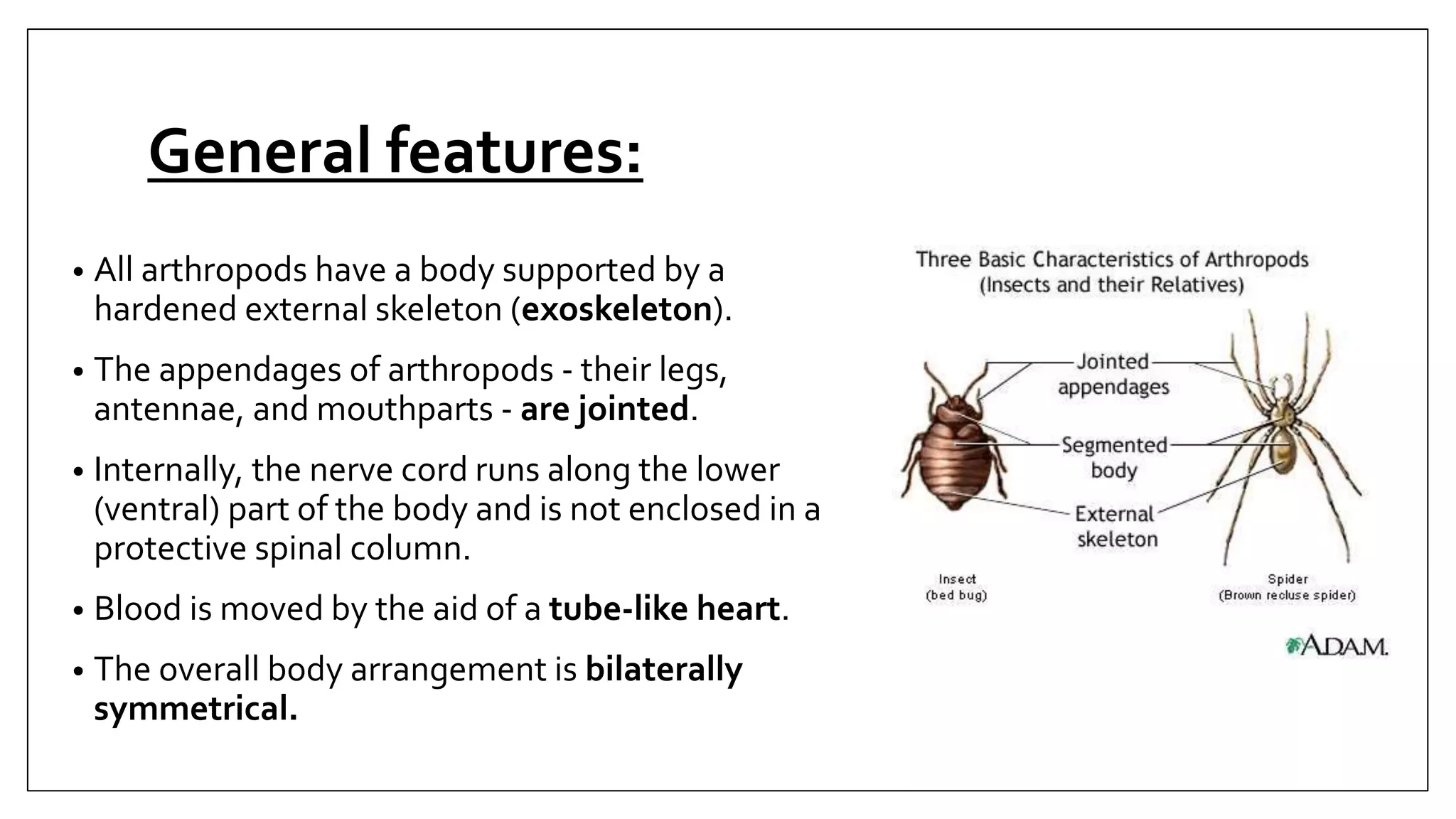
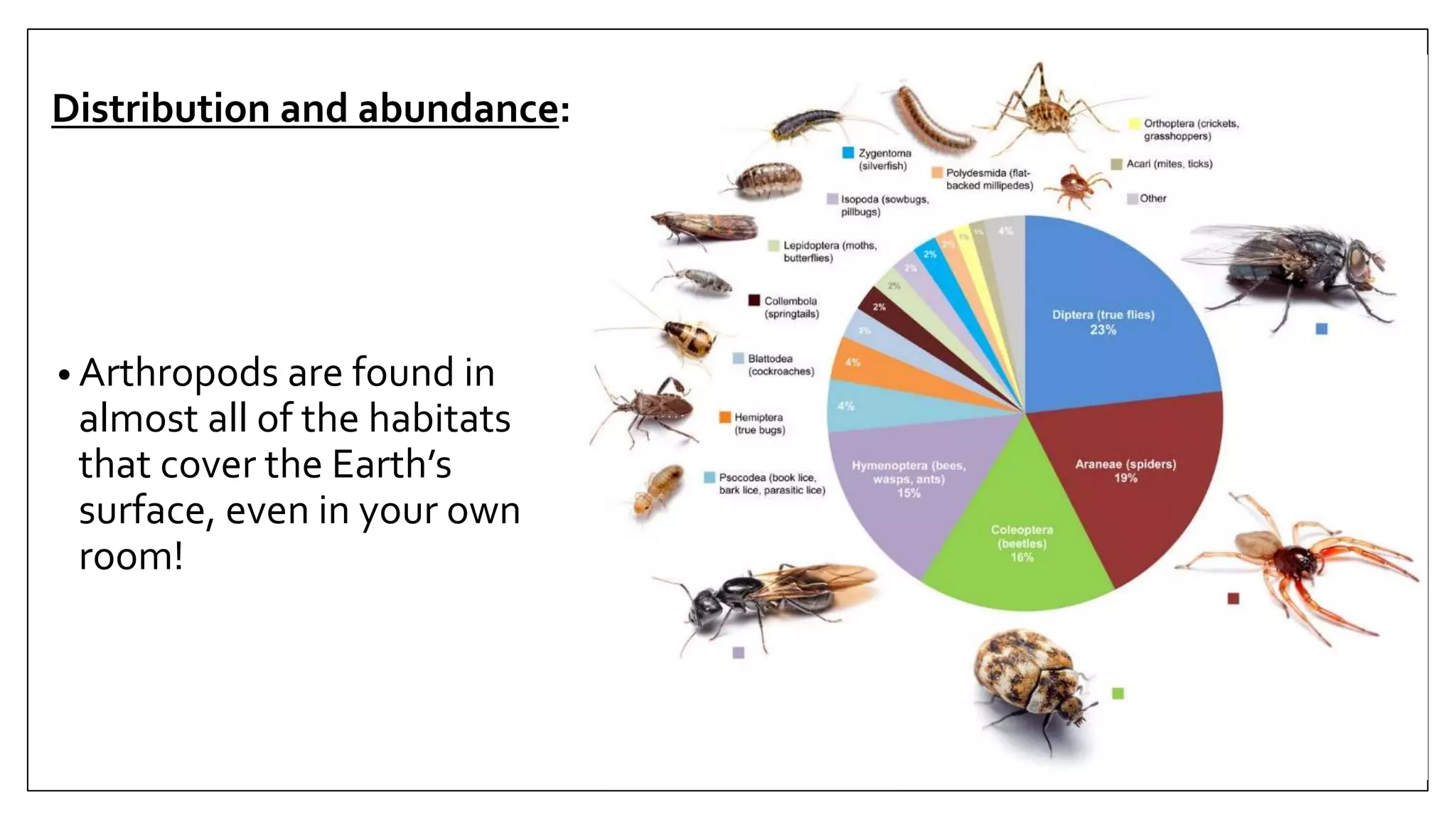
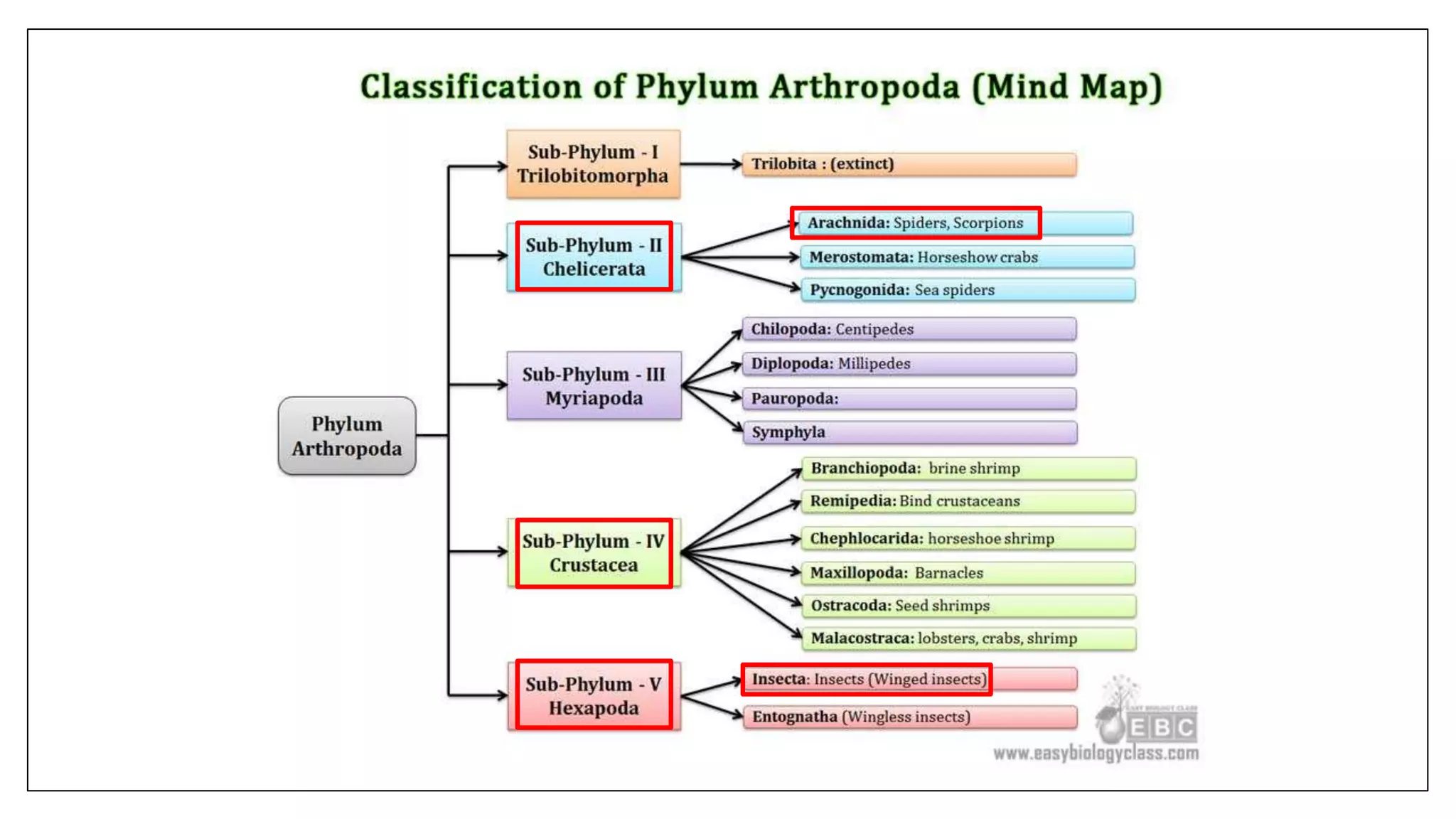
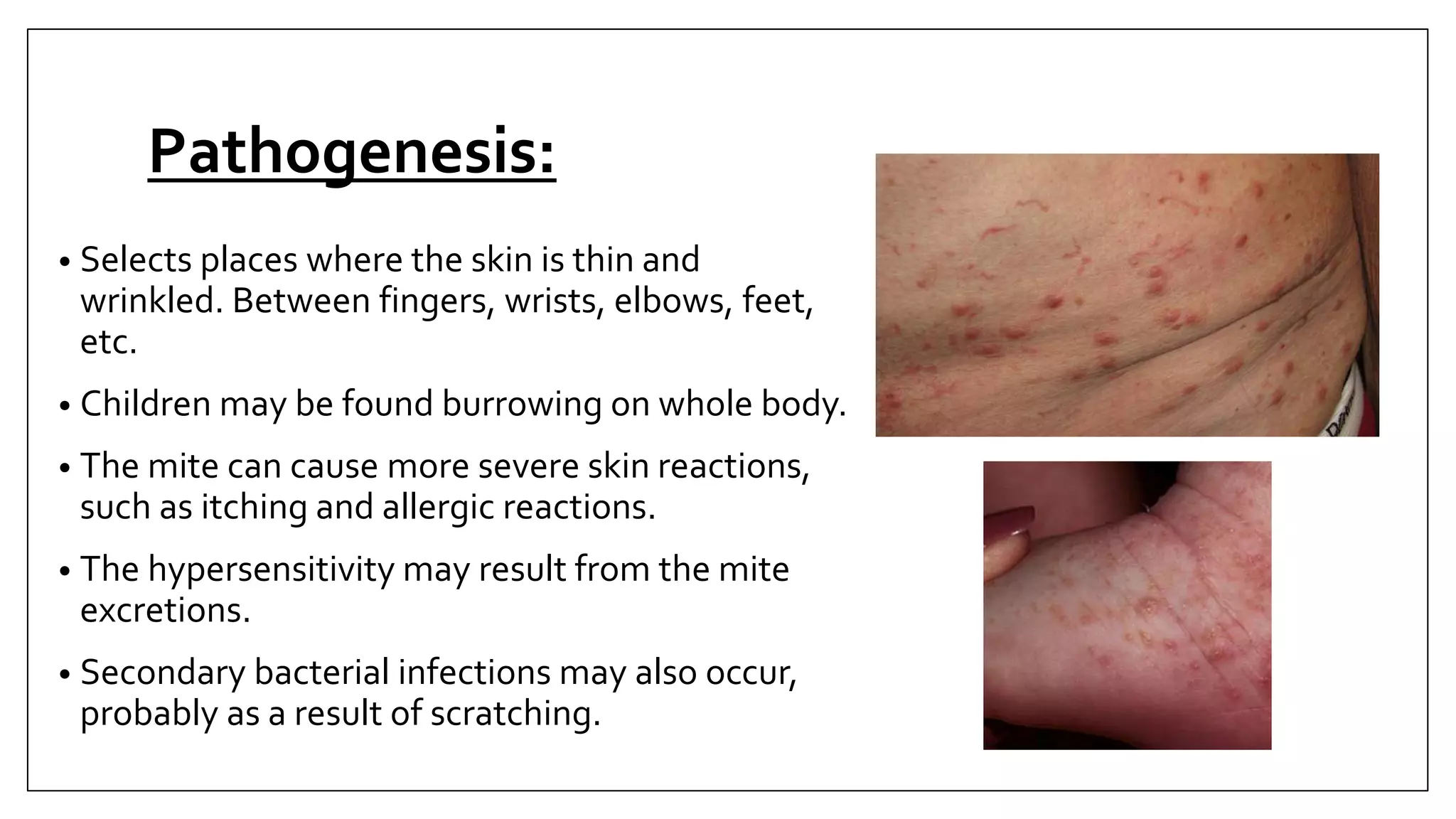
Arthropods are a phylum that includes insects, arachnids, crustaceans and others. They have an exoskeleton, jointed appendages and a tube-like heart. Some arthropods are medically important as vectors of diseases. The document discusses the characteristics and classification of arthropods, focusing on orders and species that can transmit pathogens like ticks that carry Lyme disease, fleas that transmit plague, and mosquitoes that transmit malaria. Prevention methods against arthropod bites are also outlined.