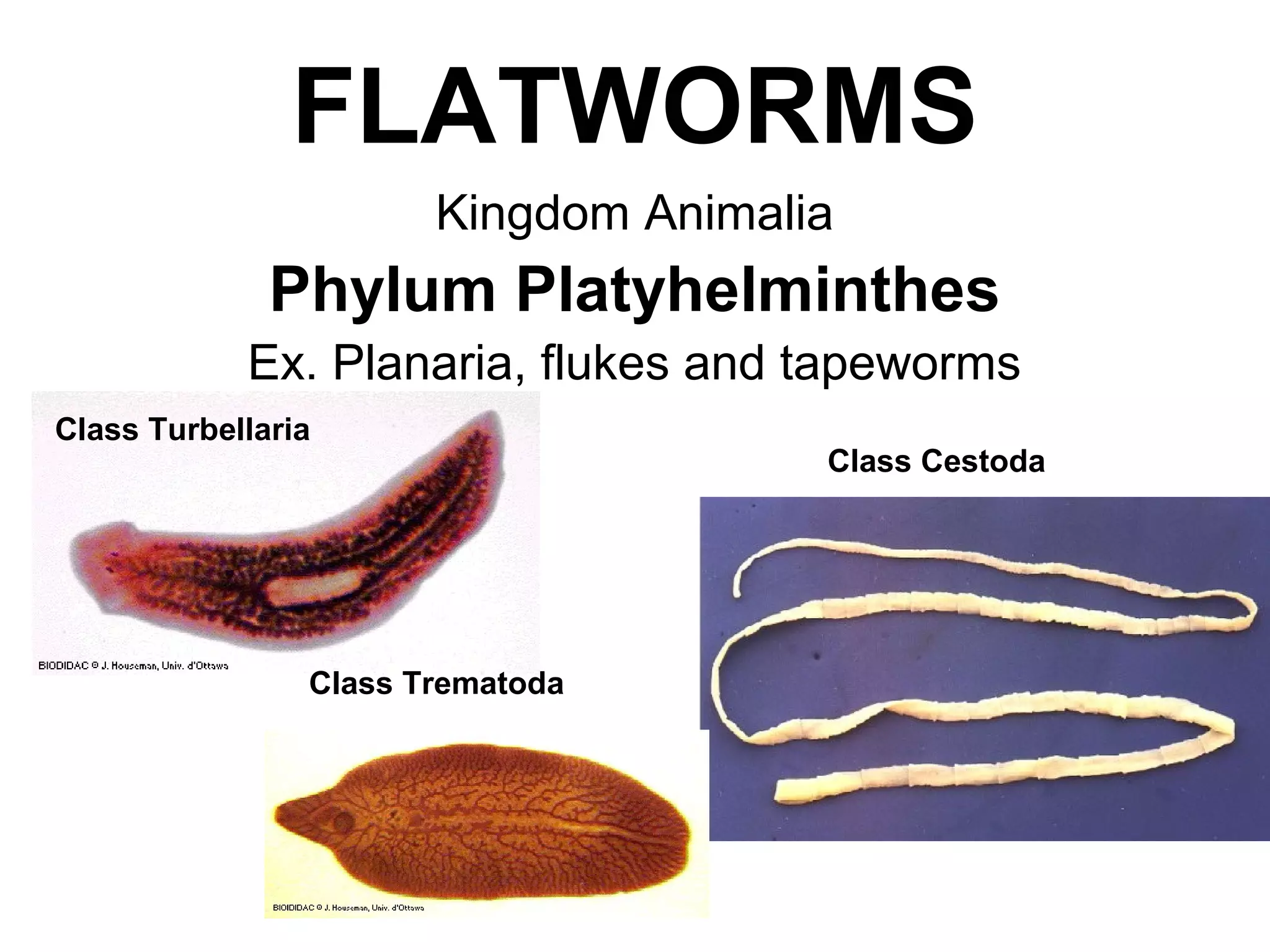
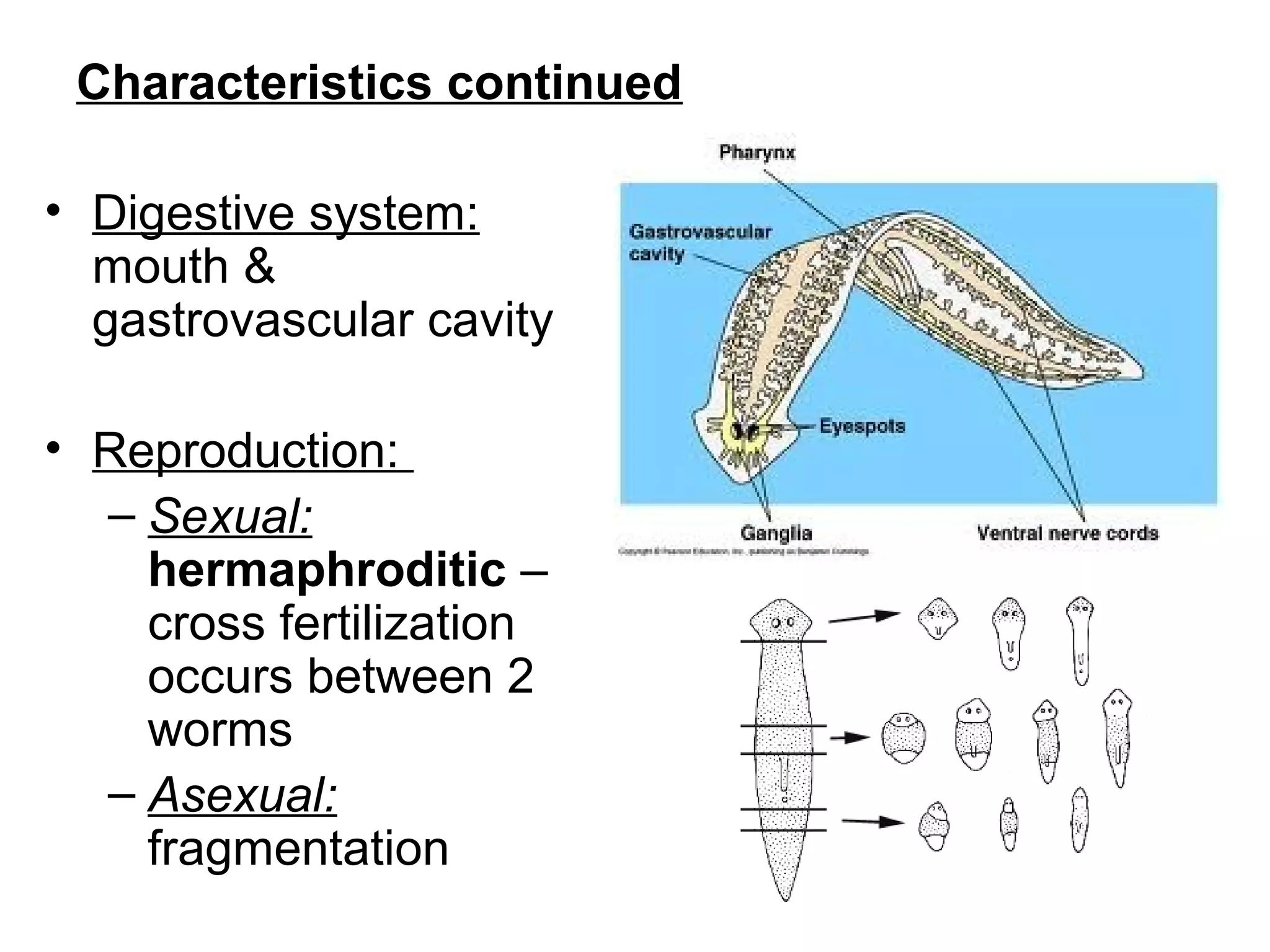
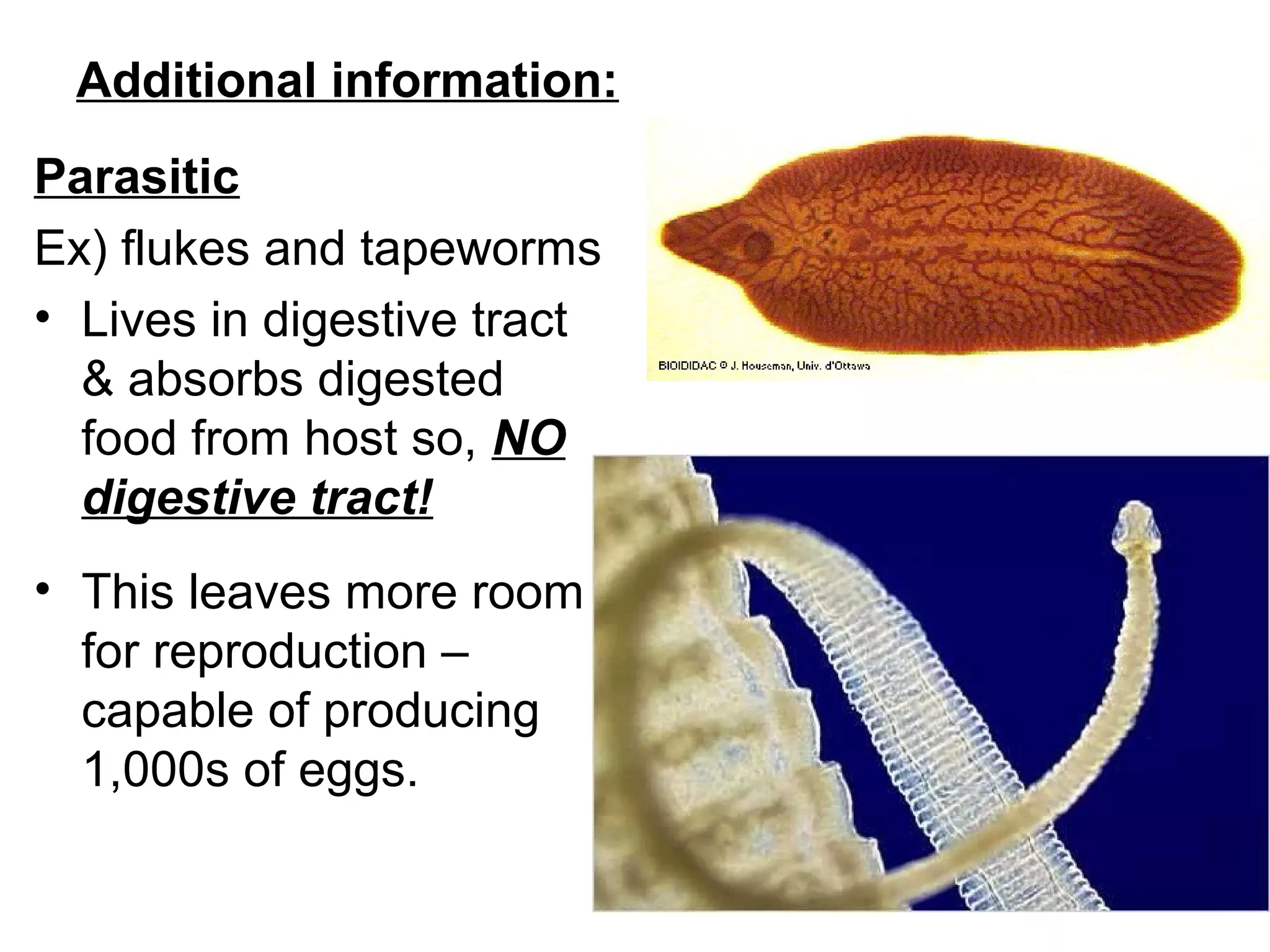
Flatworms are a phylum of soft-bodied invertebrates that include parasitic tapeworms and flukes as well as free-living planaria. They have a triploblastic structure with three germ layers and acoelomate body plan lacking a body cavity. Flatworms reproduce sexually through cross-fertilization or asexually through fragmentation. Parasitic species like tapeworms and flukes have complex lifecycles involving multiple hosts. Tapeworms are hermaphroditic and release proglottid segments containing eggs, while flukes develop through larval stages that infect intermediate hosts.