Embed presentation
Downloaded 374 times




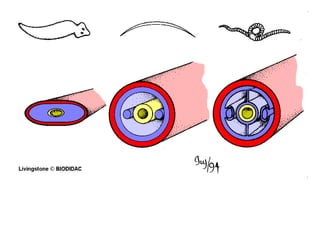
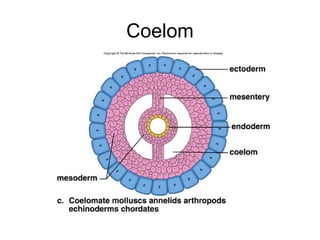

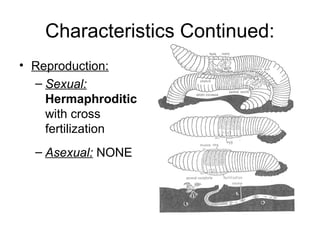
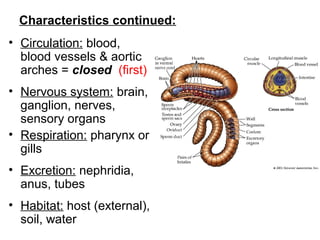
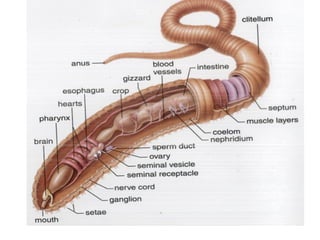
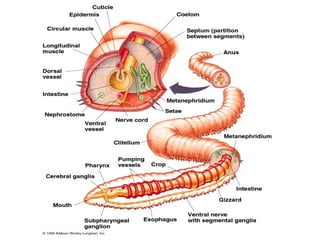
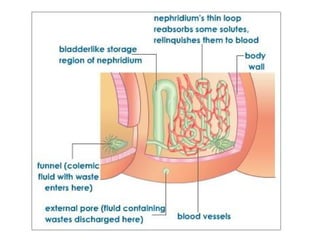

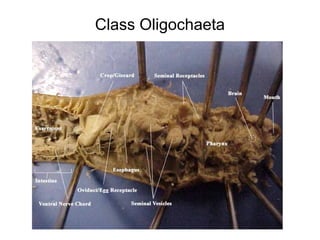

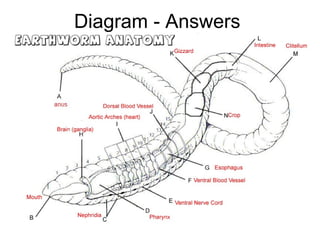

Phylum Annelida includes segmented worms such as earthworms, leeches, and polychaete worms. Their bodies are divided into many segments separated by internal walls. They play important ecological roles such as aerating soil, being a food source, and breaking down material. Their bodies have three layers, a coelom body cavity, complete digestive system, and sexual reproduction through cross-fertilization. They also have a closed circulatory system, nervous system, respiratory organs, excretory organs, and can live in soil, water, or as parasites on hosts. The three main classes are Oligochaeta (earthworms), Polychaeta (marine worms), and Hirudinea (lee

















