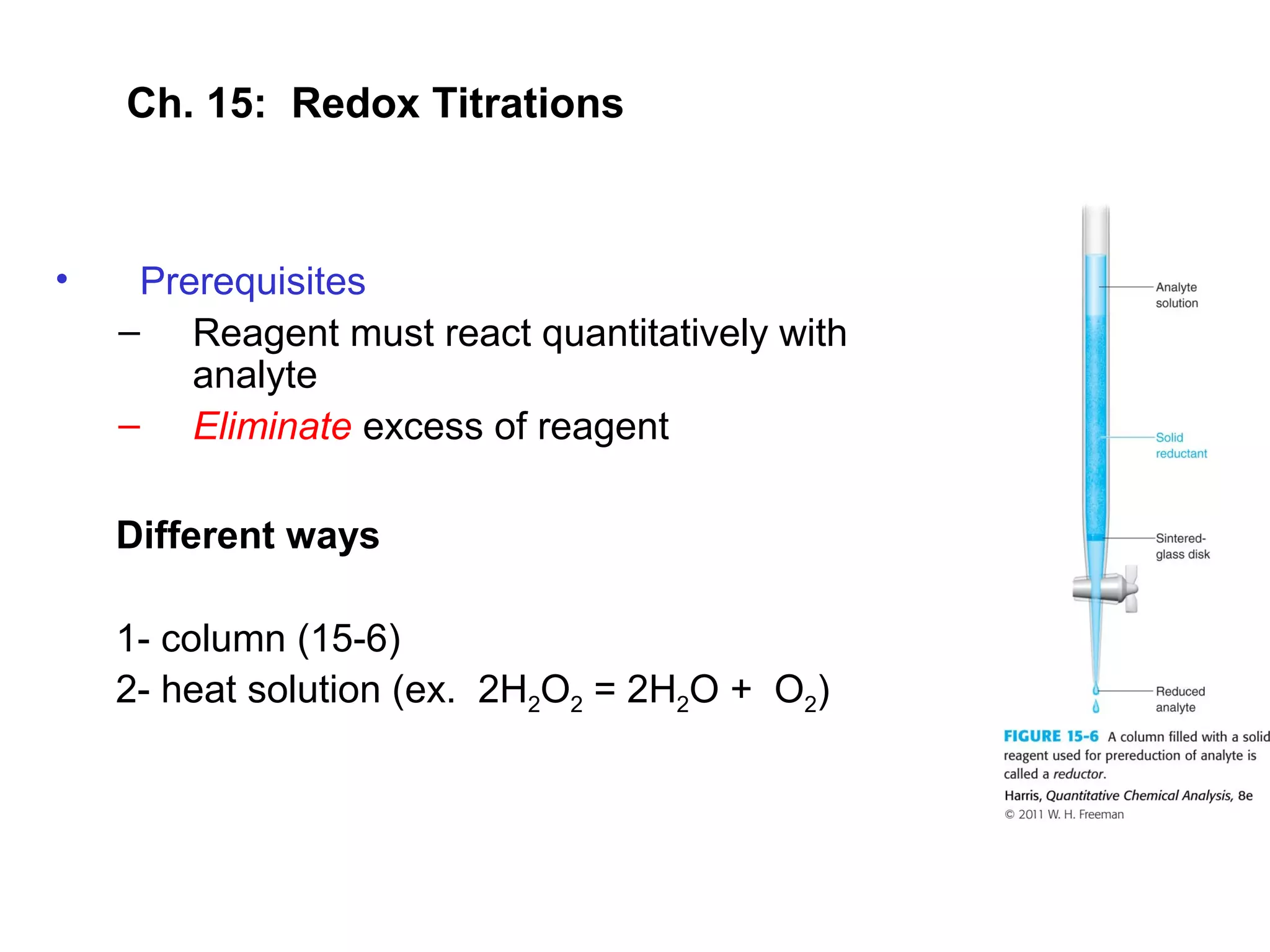
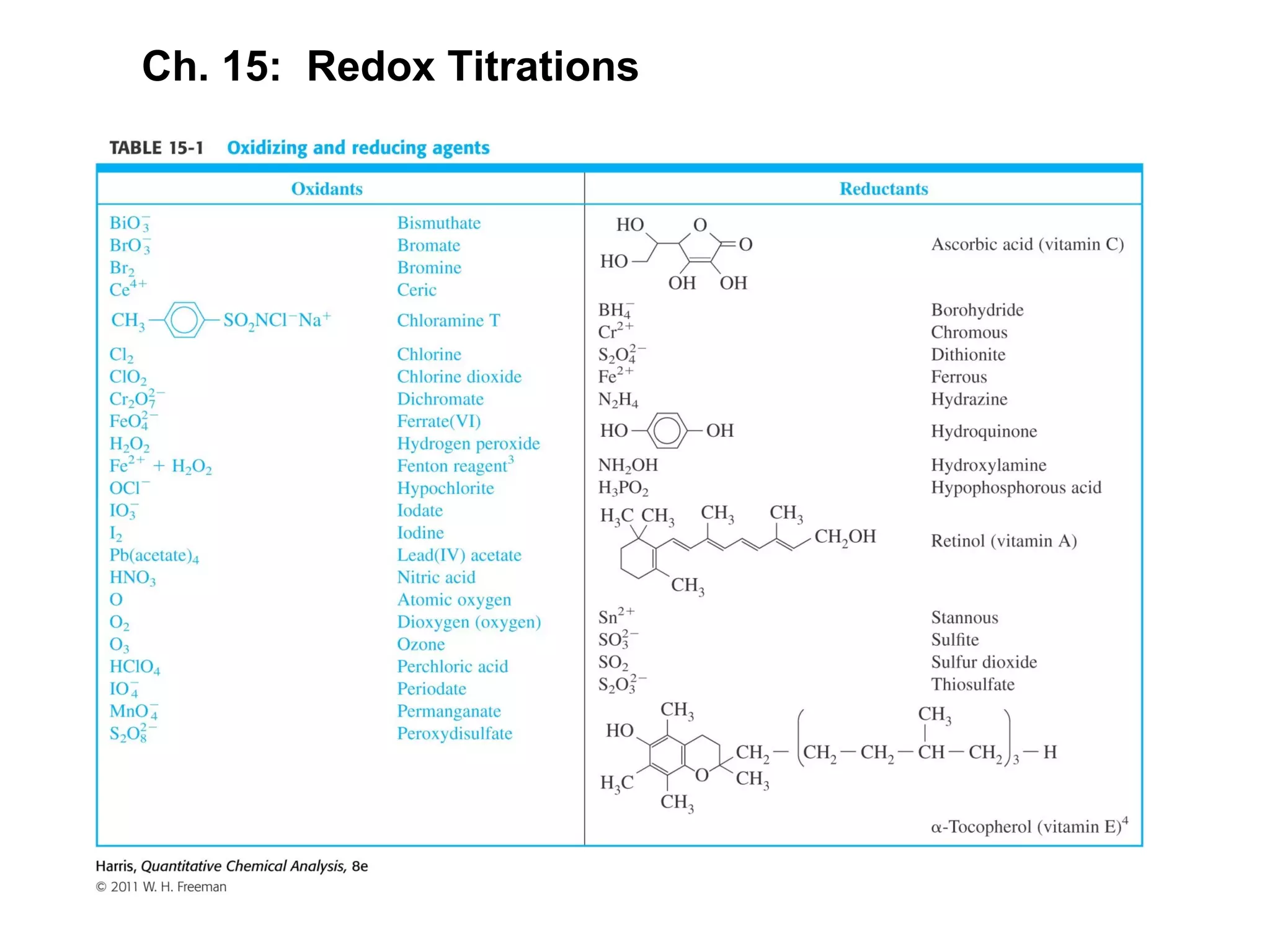
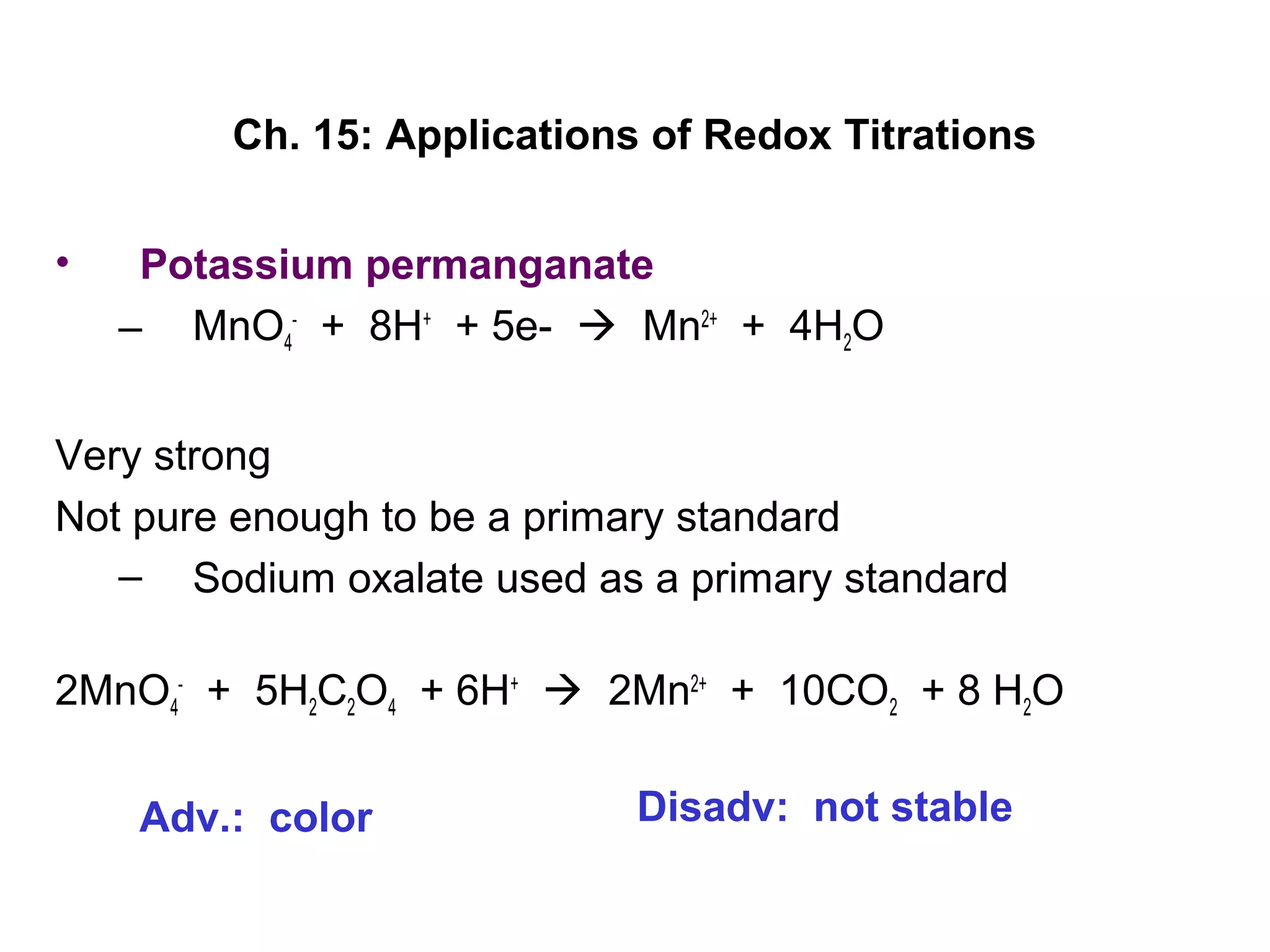
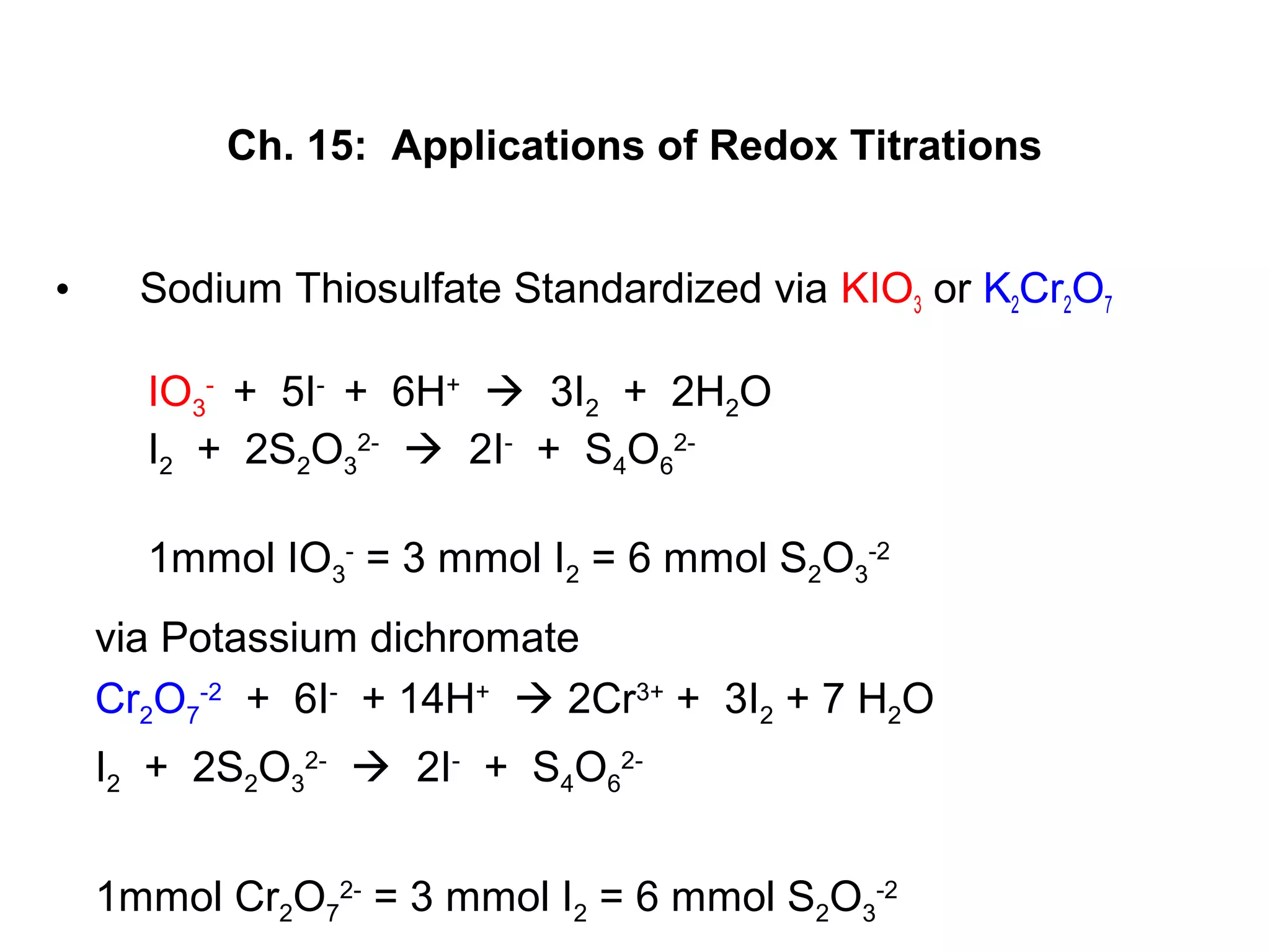
This document discusses redox titration methods. It describes the Winkler method for determining dissolved oxygen in waste water and determining whether bacteria present are aerobic or anaerobic. The Karl Fischer method for determining water content is also outlined, using iodine, sulfur dioxide, and pyridine dissolved in methanol to quantitatively reduce iodine in the presence of water. Common oxidizing agents used in redox titrations include potassium permanganate, potassium bromate, cerium(IV), and potassium dichromate. Sodium thiosulfate is also described as a moderately strong standard reducing agent often used in indirect iodometric titrations to determine oxidizing agents.