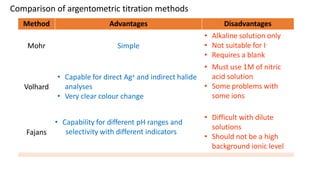
Precipitation titration involves titrating a solution with ions that will react to form an insoluble precipitate. Three common argentometric (involving silver ions) precipitation titration methods are described. Mohr's method uses potassium chromate as an indicator for chloride, bromide, and cyanide analysis in alkaline solutions. Volhard's method employs thiocyanate back titration for analyses in acidic solutions. Fajan's method utilizes adsorption indicators that change color upon binding to the precipitate surface at the endpoint. Each method has advantages and disadvantages depending on the analyte and solution conditions.