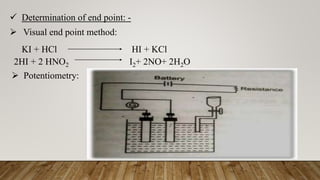
Diazotization titrations involve the reaction of primary aromatic amines with sodium nitrite in acidic solution to form unstable diazonium salts. This reaction can be used for both qualitative and quantitative analysis of compounds containing amino groups. The endpoint is detected using an external indicator like starch-iodide paper, which detects excess nitrous acid after all the aromatic amine has reacted. Some common compounds that can be assayed via diazotization titration include dapsone, sulphamethoxazole, and benzocaine.