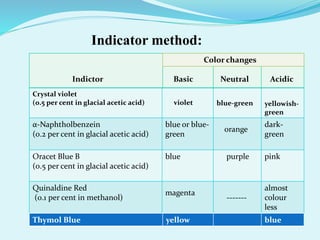
This presentation summarizes non-aqueous acid-base titration. It introduces the presenter, MD. Zahirul Isalam from the Department of Pharmacy at World University of Bangladesh. The presentation defines non-aqueous titration as titrating weakly acidic or basic substances using non-aqueous solvents to get a sharp endpoint. It discusses the different types of non-aqueous solvents including aprotic, protophilic, protogenic, and amphiprotic solvents. The presentation also covers determining the endpoint through potentiometric or indicator methods and describes examples of titrating weak bases and acids through non-aqueous methods.