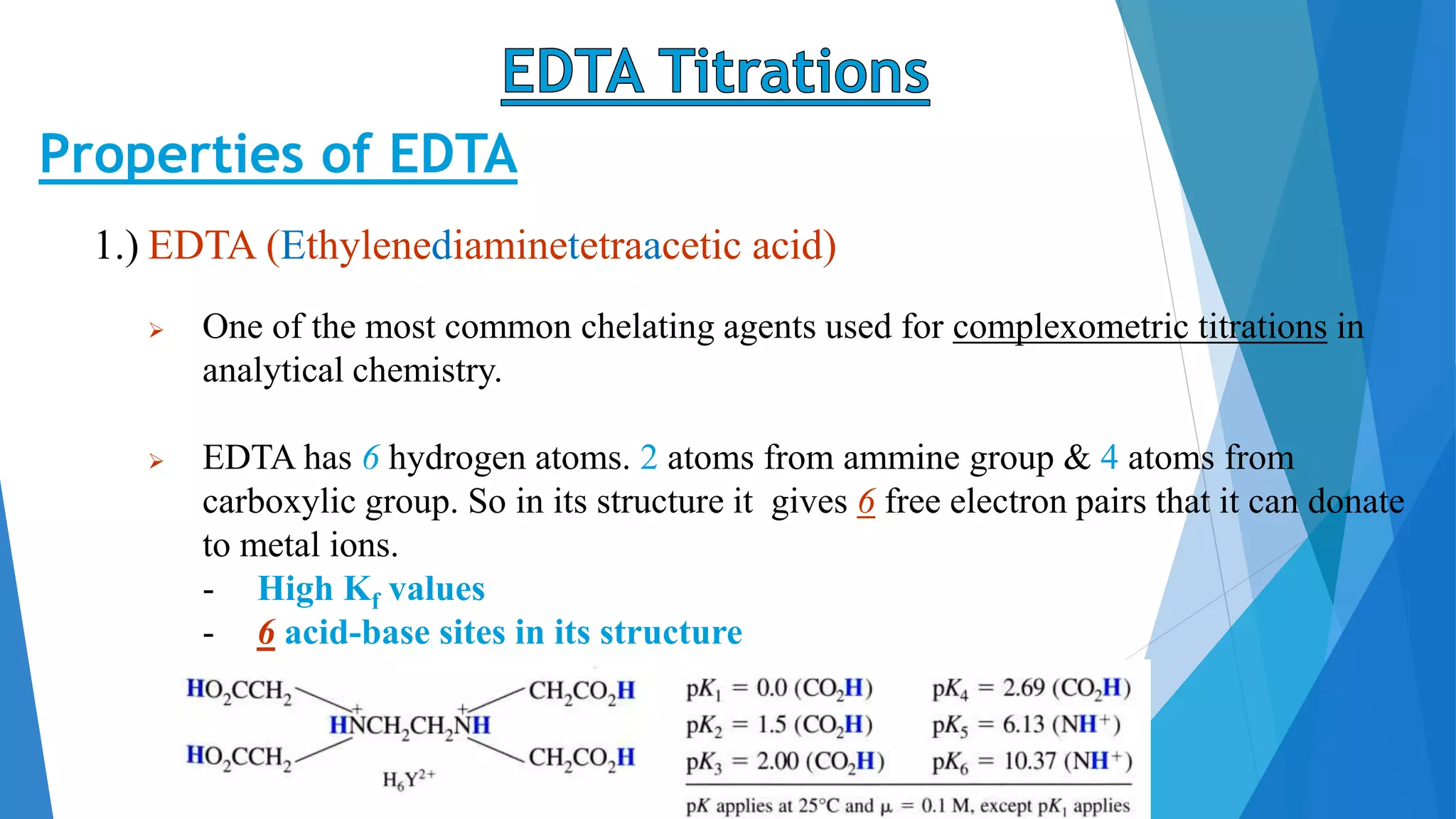
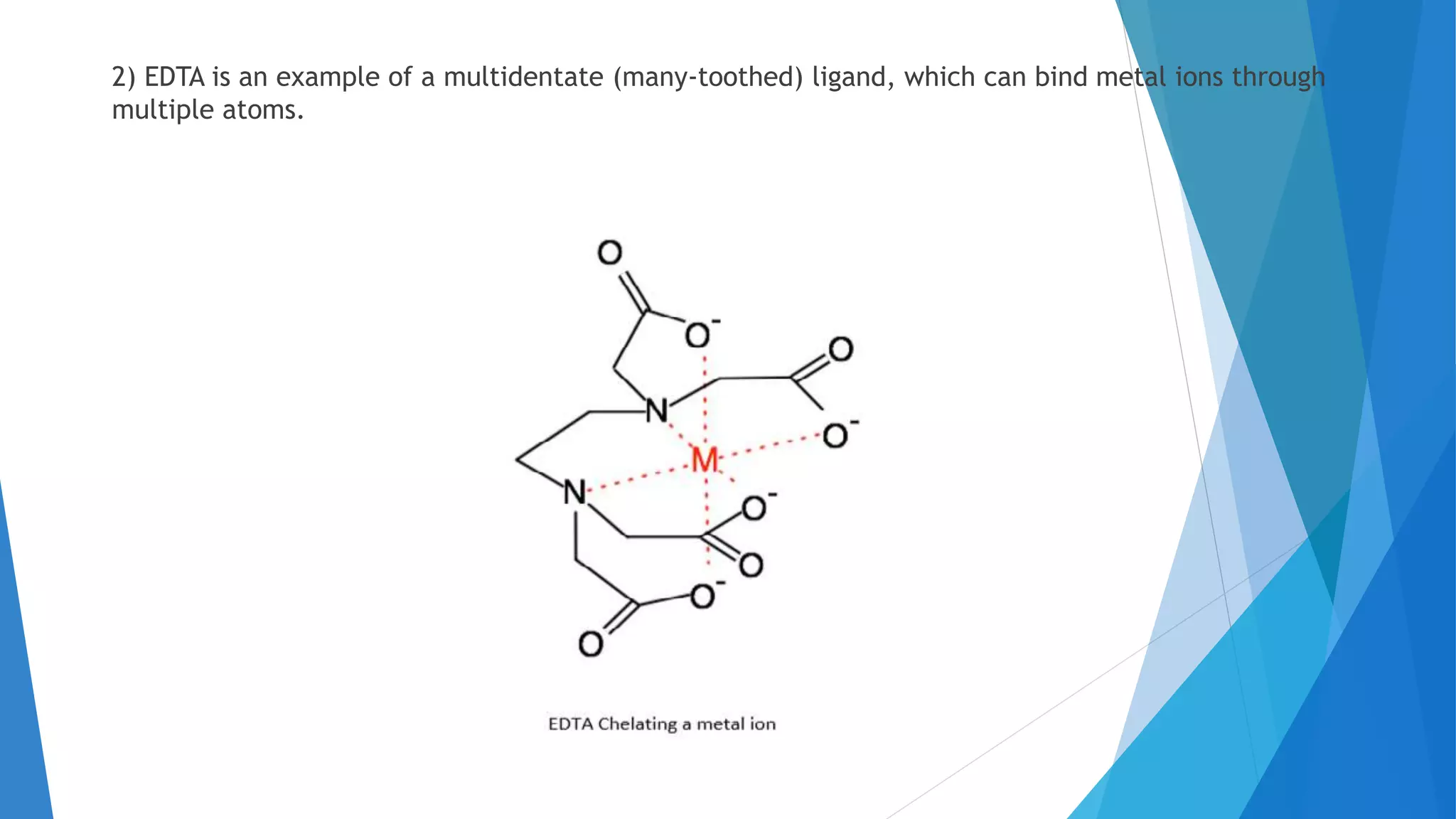
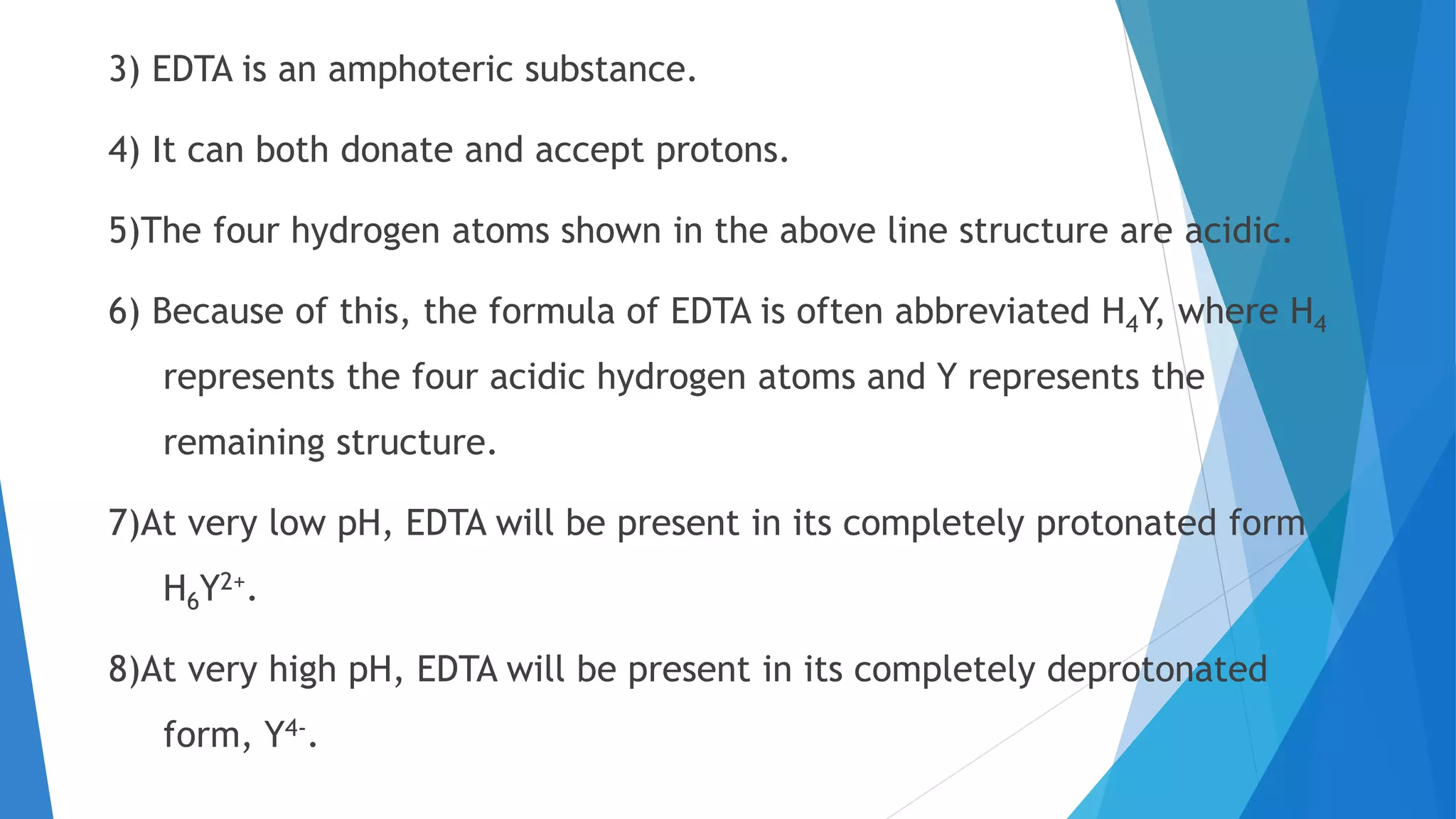
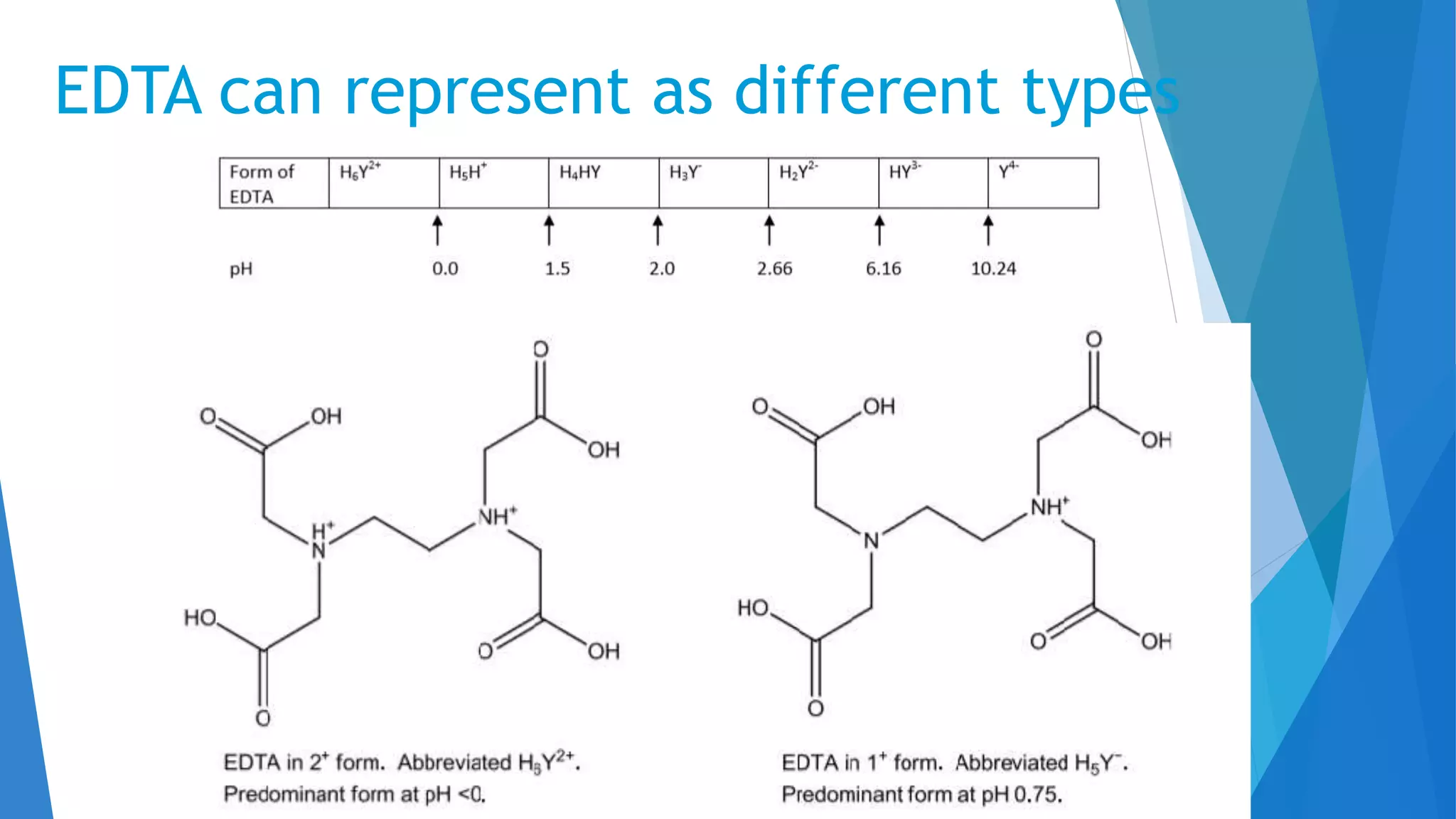
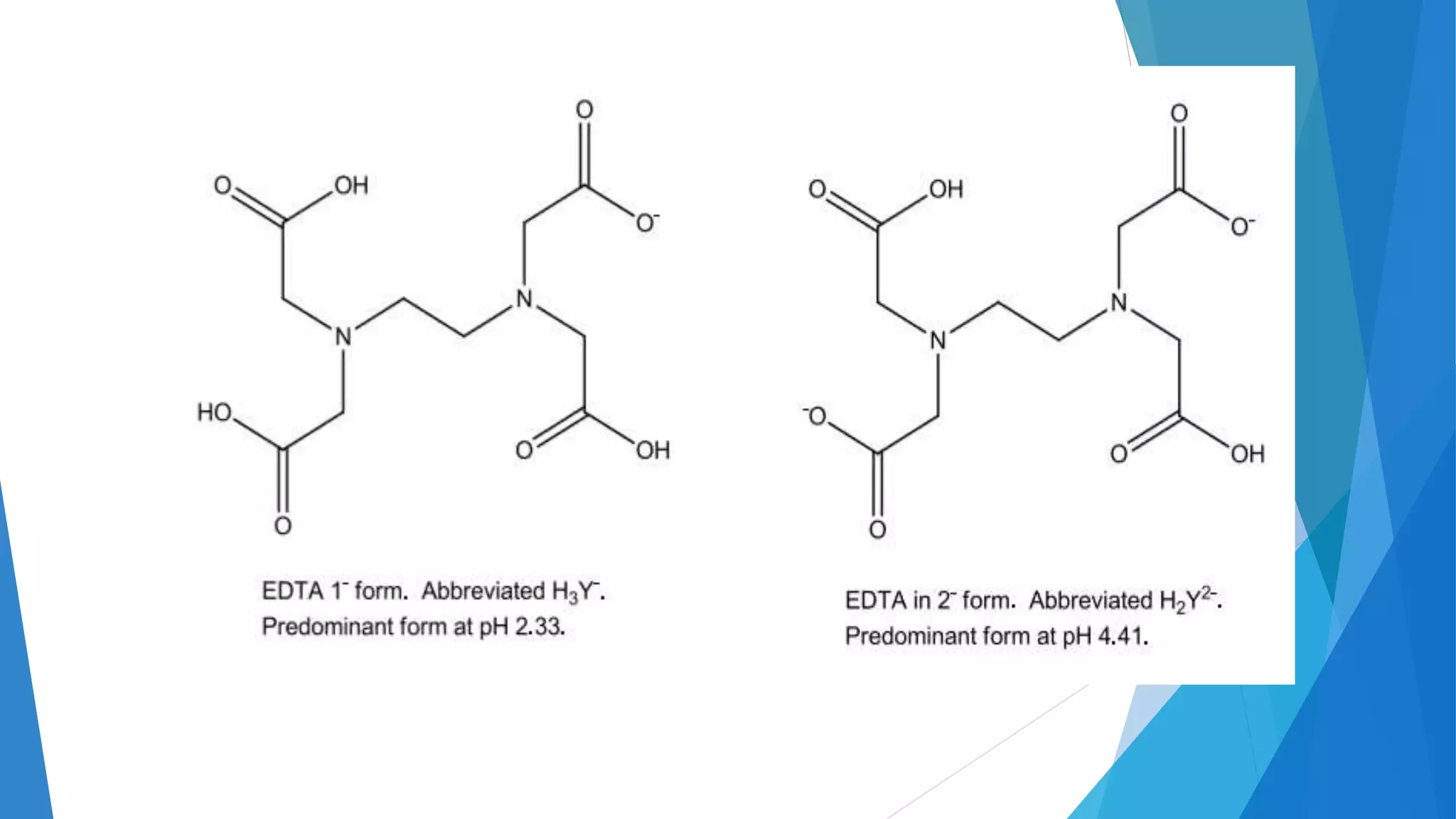
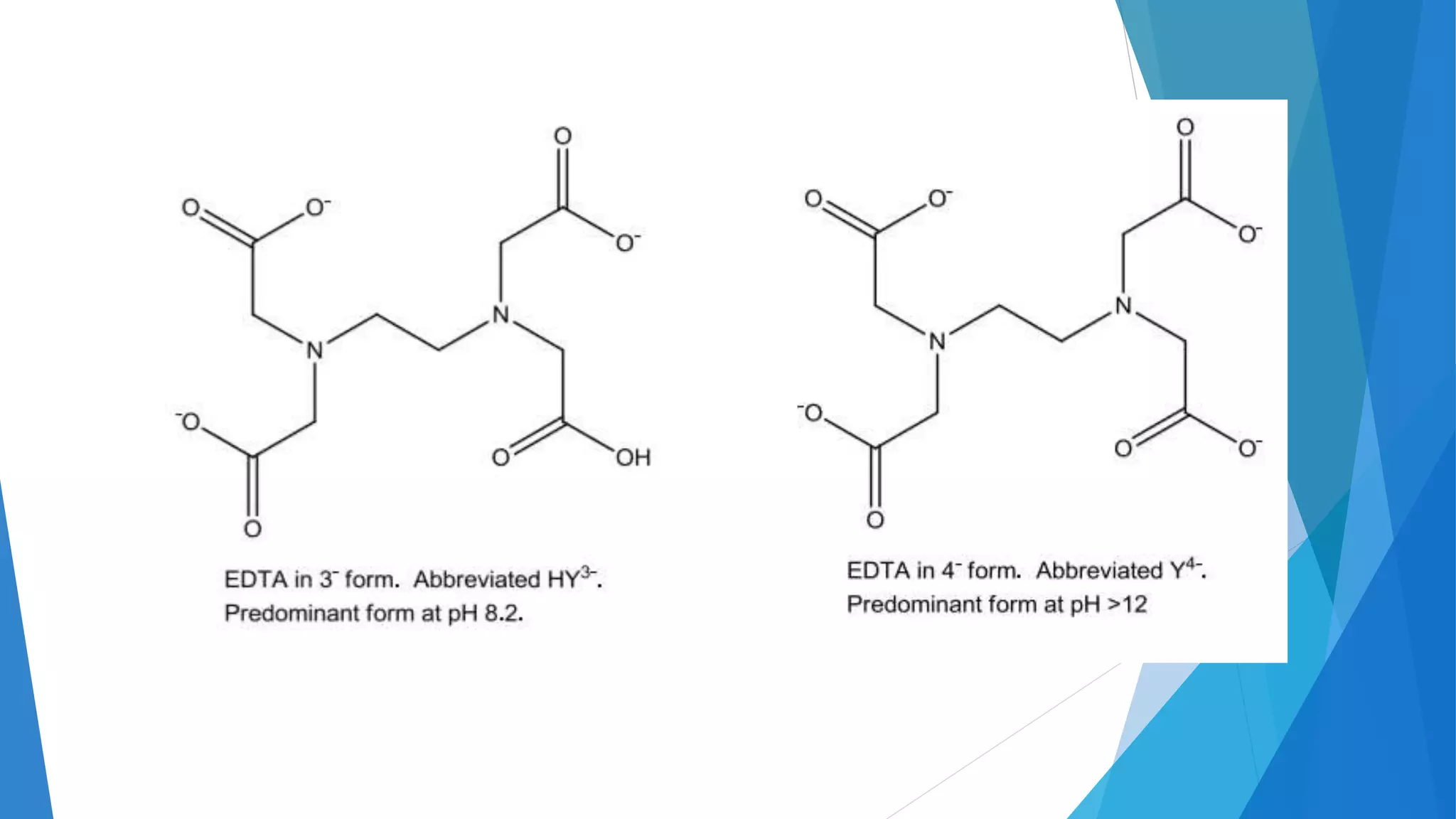
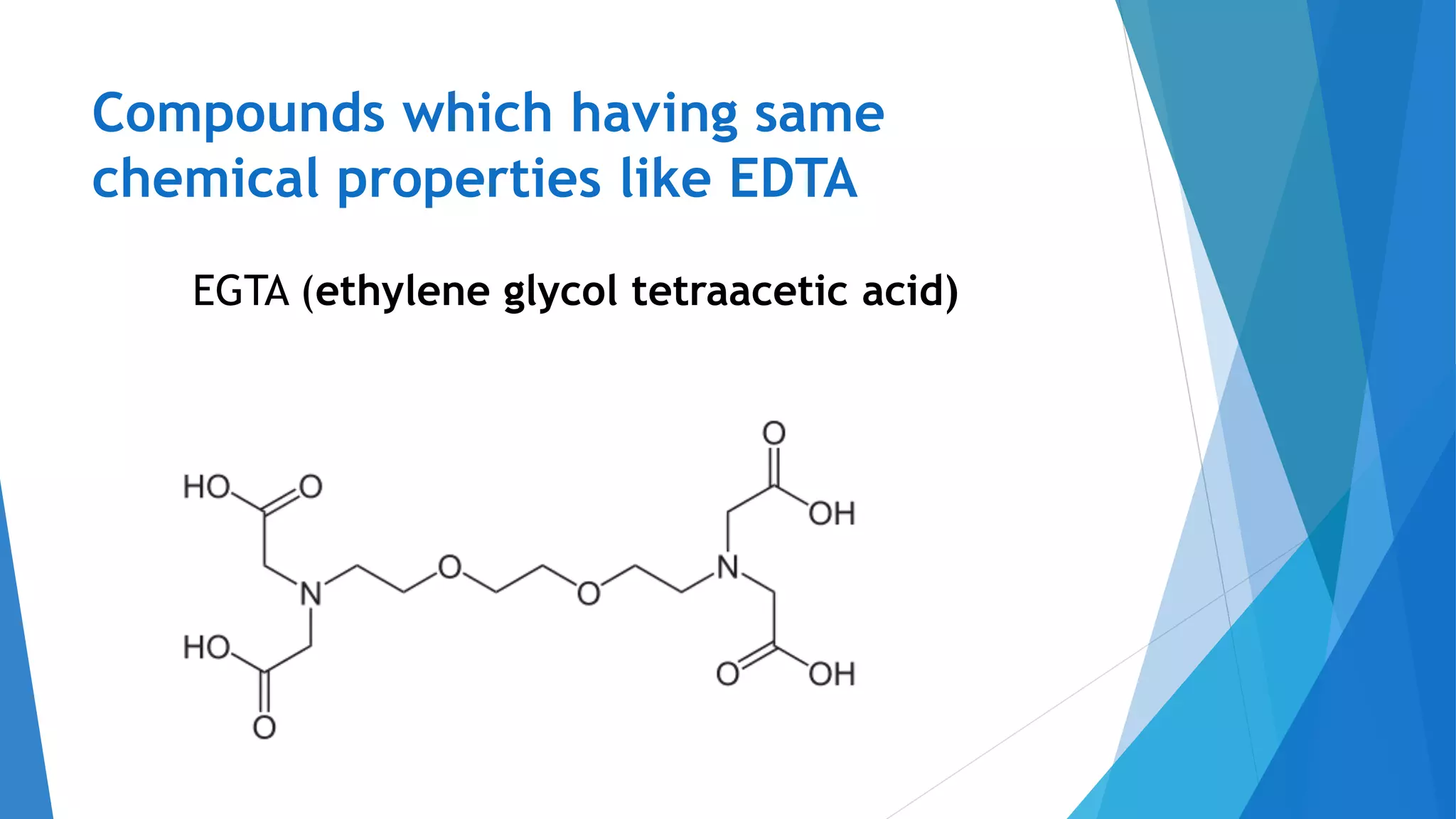
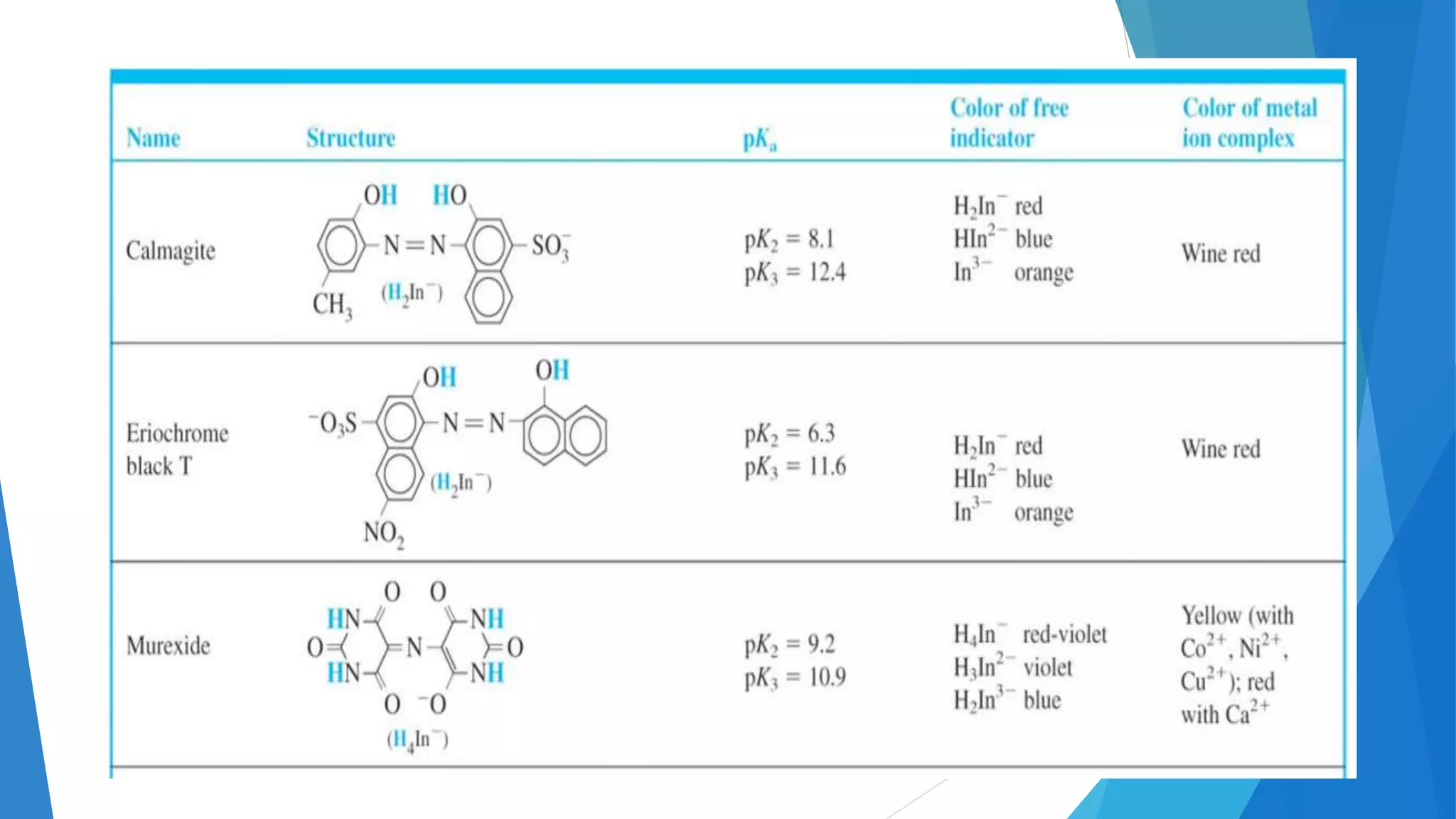
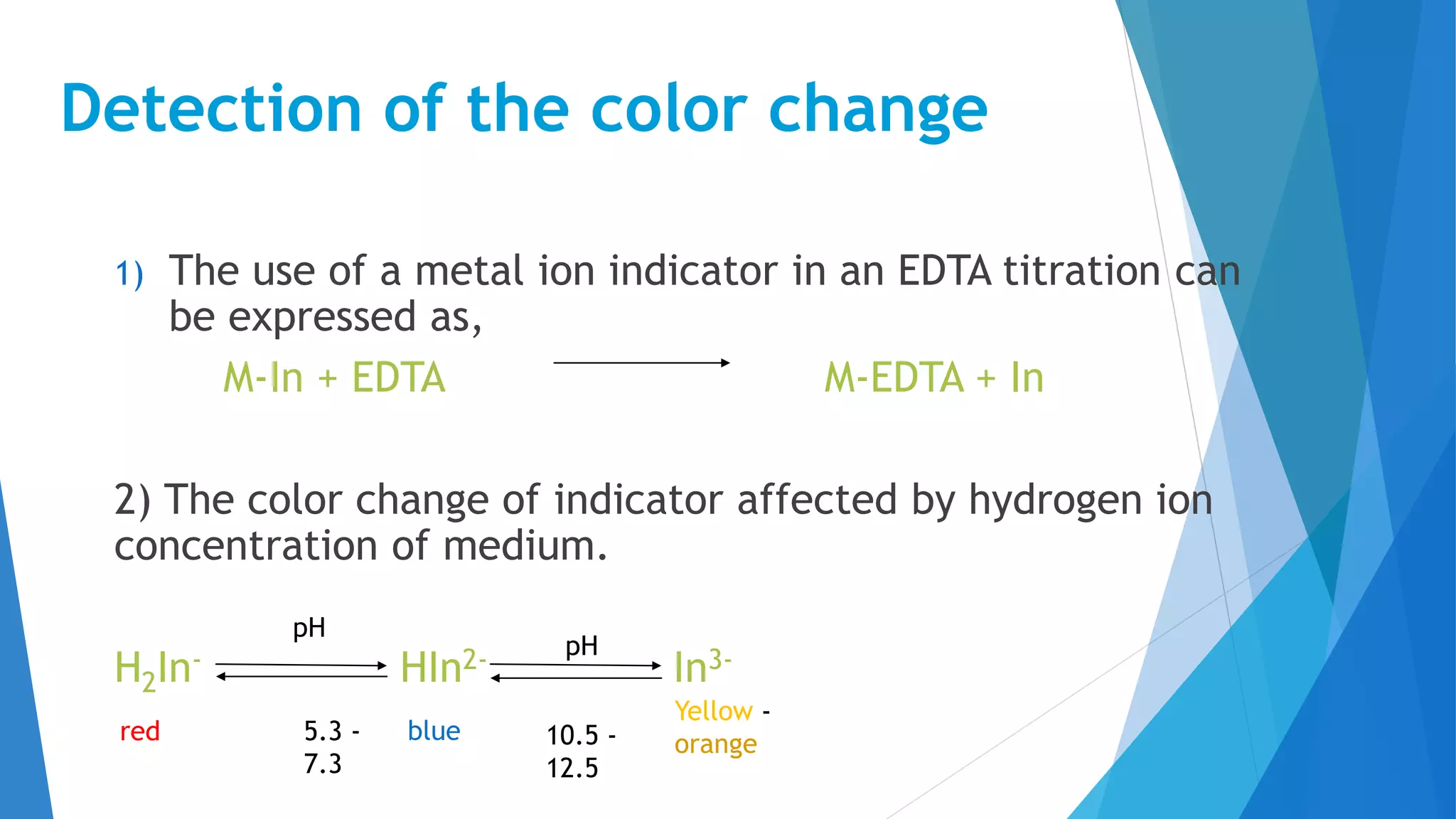
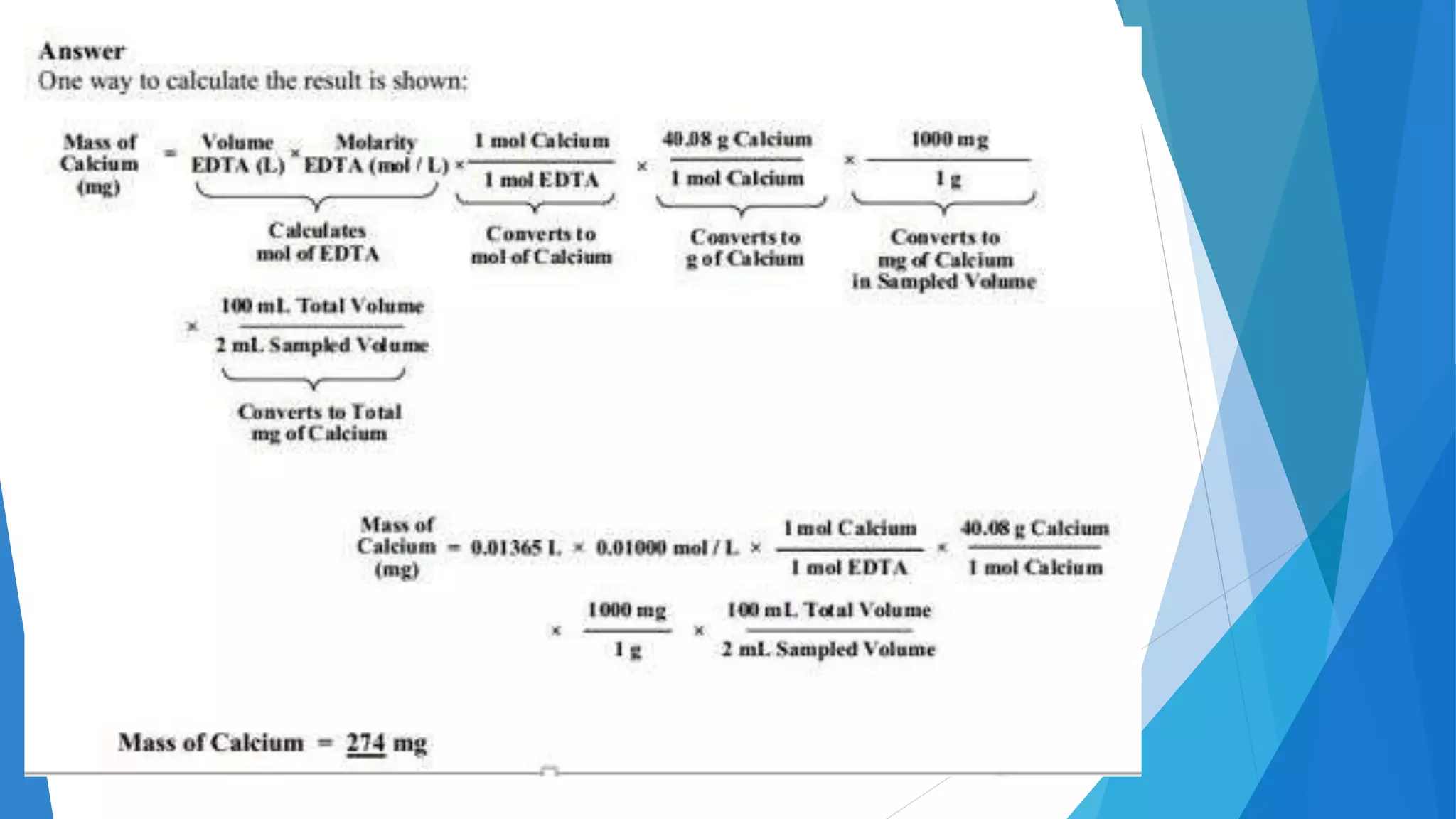
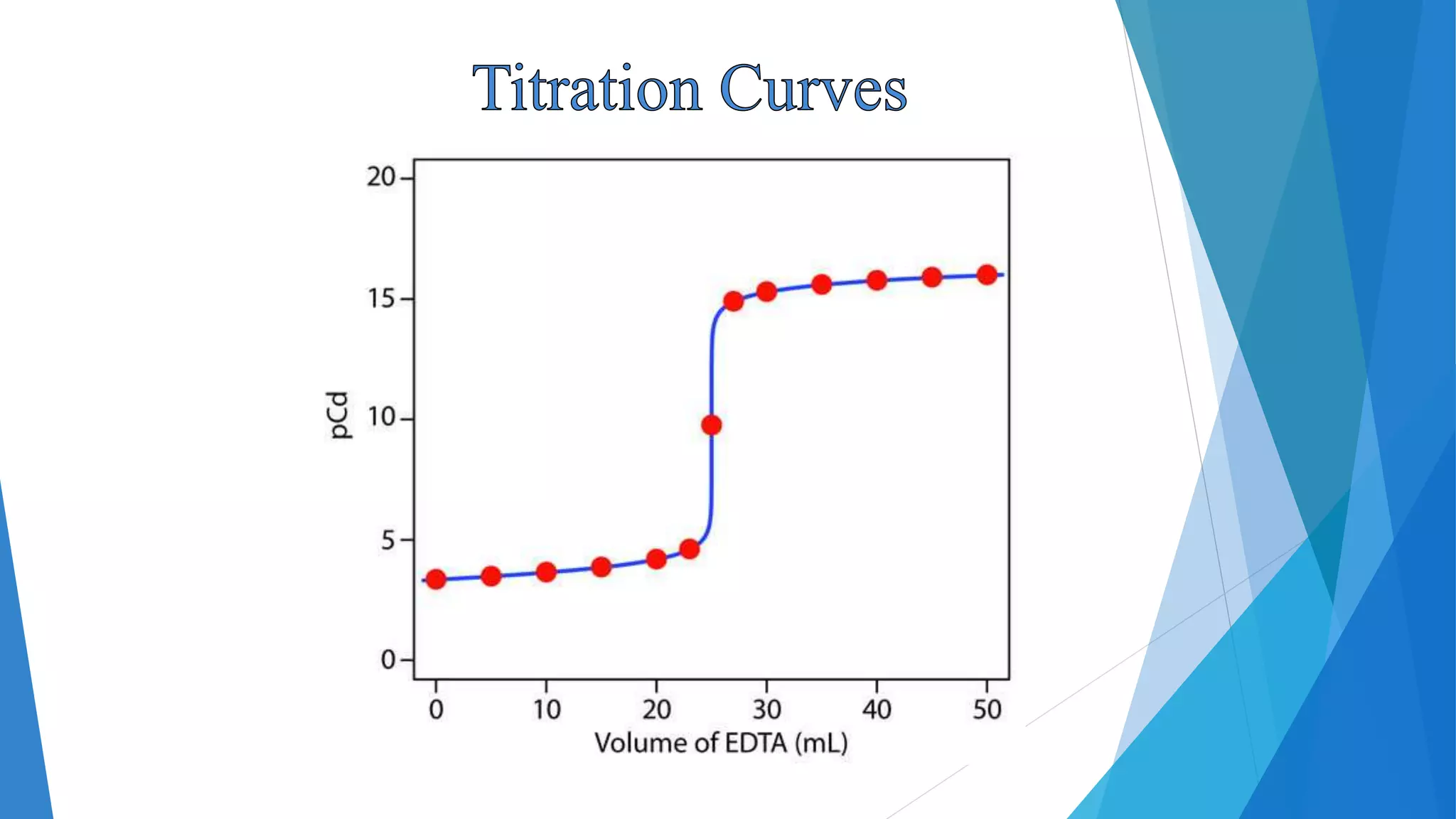
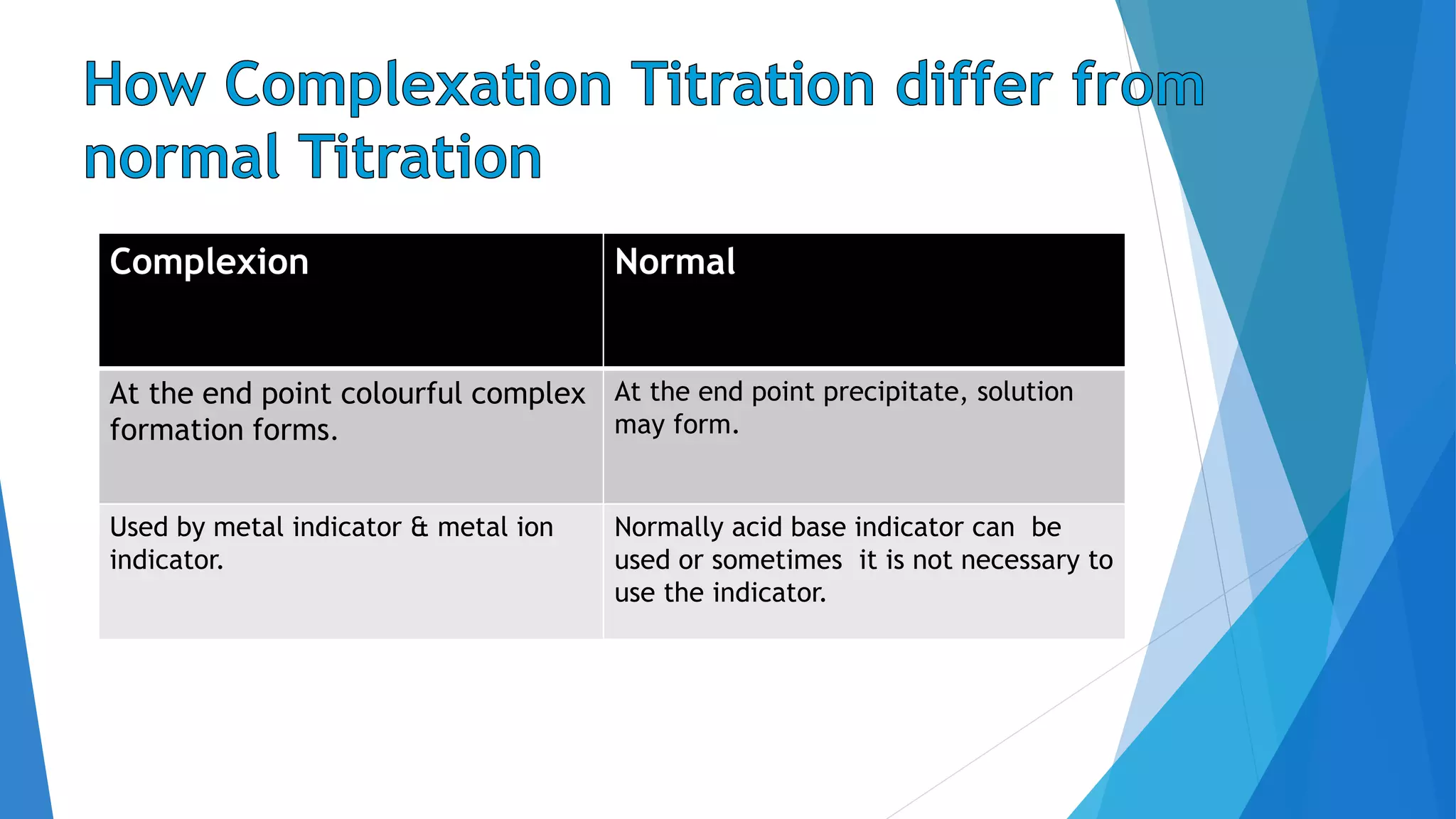
This document discusses complexation titration and the use of EDTA titration. Complexation titration involves the titration of a metal ion with a ligand like EDTA to form a colored complex. EDTA is a common chelating agent used due to its high stability constants. It can bind metal ions through multiple atoms. EDTA titrations can be direct, indirect, back, or displacement titrations depending on the method used. Metal ion indicators are also used to detect the color change at the endpoint of the titration.






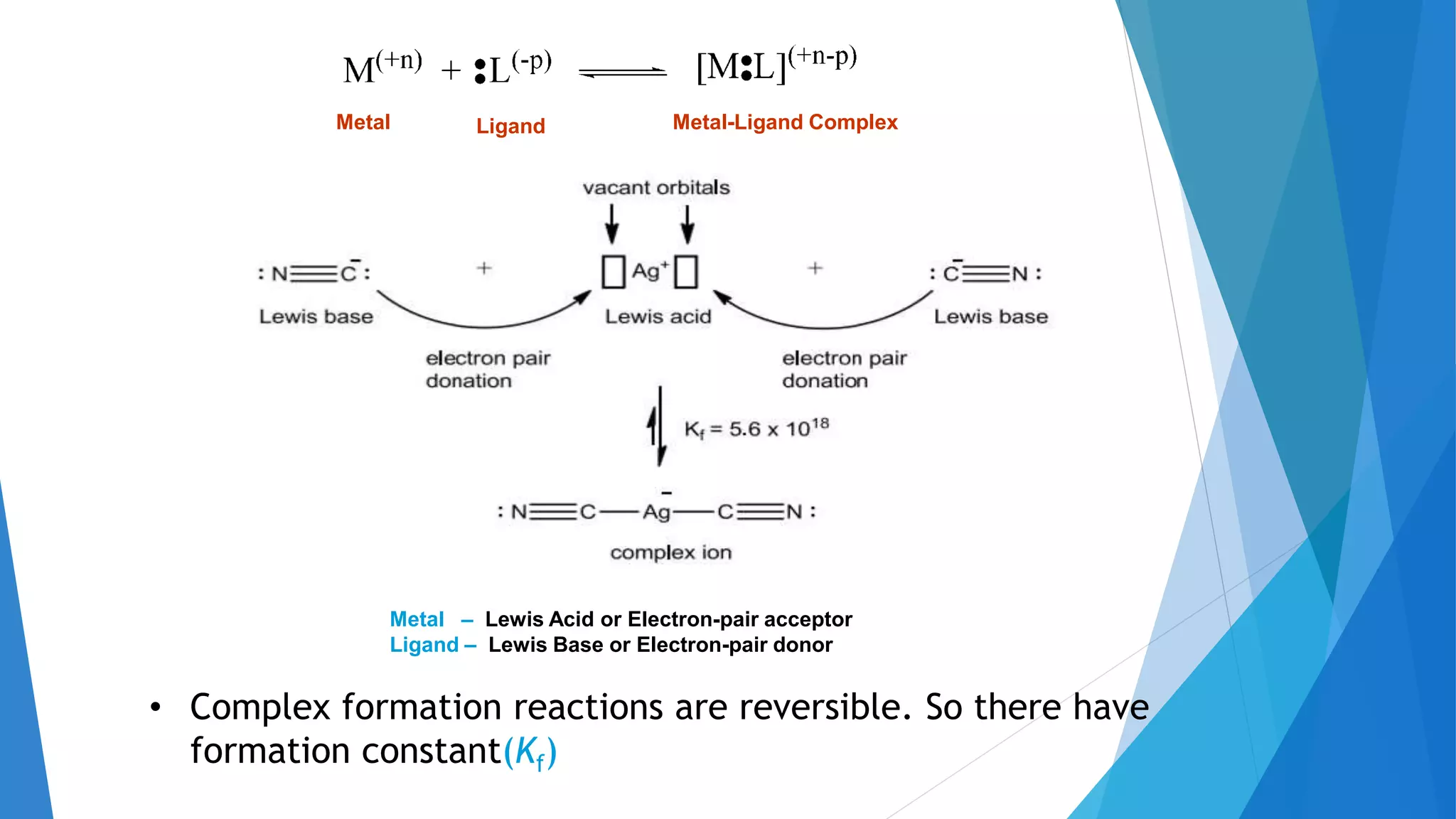
![ Complex: metal + ligand
Ligand: has at least one pair of unshared electrons available for
bond formation.
Complex formation has a specific colour.
(electron donor) Ex: H2O, NH3, Cl-, Br-, I-……
~ ~ An ion or a molecule that forms a covalent bond with a cation or
a neutral metal atom by donating a pair of electrons, which is
then shared by the two atoms.
Ex: [Cu(NH3)4]2+, [CuCl4]2-, [Cr(NH3)6]3+](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/complexationtitration11-150220190513-conversion-gate02/75/Complexation-titration-1-1-10-2048.jpg)

![The equilibrium constant for the reaction between a
metal ion (M+n) and a chelating agent (L-P) is known as
a formation constant or stability constant.
][Y][M
]Y[M
K
YMYM
b
ab
f
ab
b
a
a](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/complexationtitration11-150220190513-conversion-gate02/75/Complexation-titration-1-1-13-2048.jpg)