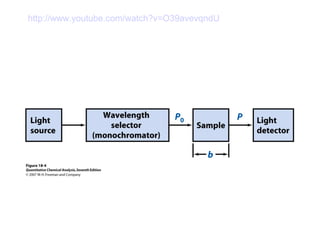
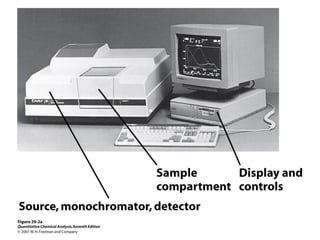
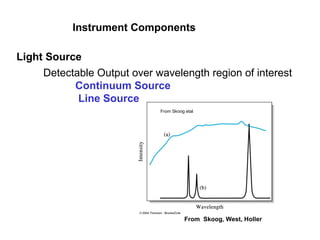
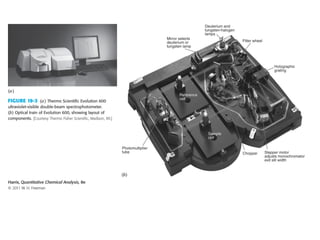
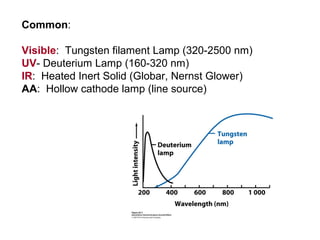
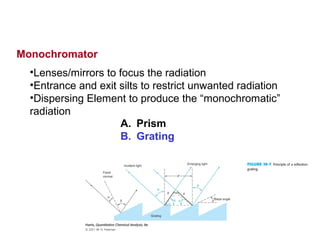
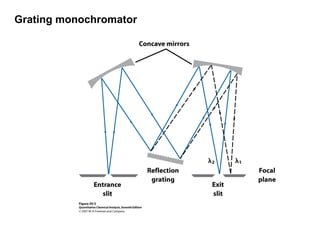
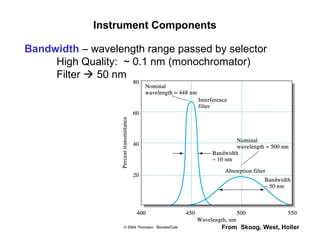
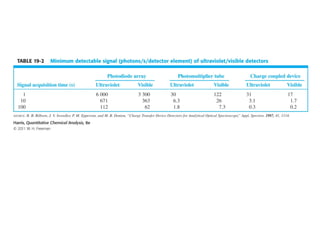
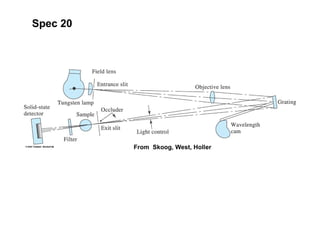
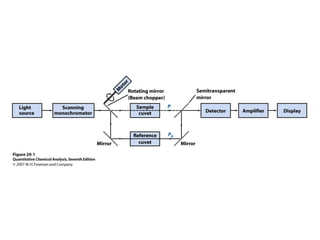
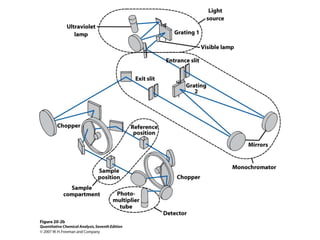
This document summarizes the major components of instrumentation used in absorption and emission spectroscopy experiments. It discusses common light sources, wavelength selectors like monochromators and filters, sample containers, detectors such as phototubes and photodiode arrays, and examples of single beam and double beam spectrophotometers. Key components are the light source, wavelength selector to produce monochromatic radiation, sample holder, and detector to measure the detectable output over the wavelength region of interest.





![An 8.64 ppm solution of [FeSCN]Cl (149 g/mol) has a T of 0.295
at 580 nm when measured in a 1.00-cm cell. Calculate
the molar absorptivity coefficient for the complex
at this wavelength.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter19instrumentcomponents-140707142833-phpapp02/85/Chapter-19-instrument-components-23-320.jpg)
